Gene
KWMTBOMO16335
Pre Gene Modal
BGIBMGA013784
Annotation
uncharacterized_protein_LOC767623_[Bombyx_mori]
Full name
Protein IMPACT-B
+ More
Protein IMPACT
Protein IMPACT
Alternative Name
Imprinted and ancient gene protein homolog B
Imprinted and ancient gene protein homolog
Imprinted and ancient gene protein
Ximpact
Imprinted and ancient gene protein homolog
Imprinted and ancient gene protein
Ximpact
Location in the cell
Nuclear Reliability : 2.59
Sequence
CDS
ATGGAAGTCGACAACTTATCAAGACAGGTTGAAGAAATTGAAGCTTTAAAATCTATTTACACAGAAGAATTGACTATAGATAGTGAAATTACCAGGTCTTATACTATTAGAATTGAAGAAAATAAGAAAGAAGTGCTTCTTTACGTGACATTACCAGAAGATTACCCGTCGAGTTCTCCACCGAAATTCGAATTGTCTGCACCGTGGATGGACCGACAAACCAAAACGAATCTTCACAAAACCTTGCACGAAATATACTTGGATAACGTCGGTGAAACTGTGATATTTCAATGGGTCGAGATGATAAGGGAAGTGTTACAAACCGTATGCAAAGTAGAAAAAAAAATTGAAGTCACGGAACCTAAAGTCGACAGTTTGGATCTCACTACGATAGAAATAAACTGCCCTGAAATTACACATGGTGAAATCATAGCAGACAGGAAGAGCATATTCCAAGGACATGCAGCTGAAGTACACAGTATAGATGATGTAAAAGCTGTACTAAATAAATTAAAACAGAACAGAAAGATCTTAAATGCTACACATAATATGTATGCATATAGAATAGAAAGAAAAACTGCCAAAGGTACGAATGTACTTCAAGACTGTGATGATGACGGGGAAGCTCACGCCGGAGGTAGAATGTTGCATCTACTGCAAGTTTTGAATCAGAAGAACACACTTGTTGTTGTGTCGAGATGGTATGGAGGAGTACAATTAGGGCCGGACAGATTCCGTCACATAAACAATGCAAGCCGACAAGTGATTCAGCAAGCTGGACTATTAAAGAAATGA
Protein
MEVDNLSRQVEEIEALKSIYTEELTIDSEITRSYTIRIEENKKEVLLYVTLPEDYPSSSPPKFELSAPWMDRQTKTNLHKTLHEIYLDNVGETVIFQWVEMIREVLQTVCKVEKKIEVTEPKVDSLDLTTIEINCPEITHGEIIADRKSIFQGHAAEVHSIDDVKAVLNKLKQNRKILNATHNMYAYRIERKTAKGTNVLQDCDDDGEAHAGGRMLHLLQVLNQKNTLVVVSRWYGGVQLGPDRFRHINNASRQVIQQAGLLKK
Summary
Description
Translational regulator that ensures constant high levels of translation upon a variety of stress conditions, such as amino acid starvation, UV-C irradiation, proteasome inhibitor treatment and glucose deprivation. Plays a role as a negative regulator of the EIF2AK4/GCN2 kinase activity; impairs GCN1-mediated EIF2AK4/GCN2 activation, and hence EIF2AK4/GCN2-mediated eIF-2-alpha phosphorylation and subsequent down-regulation of protein synthesis. Plays a role in differentiation of neuronal cells by stimulating neurite outgrowth.
Translational regulator that ensures constant high levels of translation upon a variety of stress conditions, such as amino acid starvation, UV-C irradiation, proteasome inhibitor treatment and glucose deprivation. Plays a role as a negative regulator of the EIF2AK4/GCN2 kinase activity; impairs GCN1-mediated EIF2AK4/GCN2 activation, and hence EIF2AK4/GCN2-mediated eIF-2-alpha phosphorylation and subsequent down-regulation of protein synthesis (PubMed:15937339, PubMed:23447528, PubMed:24333428). May be required to regulate translation in specific neuronal cells under amino acid starvation conditions by preventing GCN2 activation and therefore ATF4 synthesis (PubMed:15937339, PubMed:23447528). Through its inhibitory action on EIF2AK4/GCN2, plays a role in differentiation of neuronal cells by stimulating neurite outgrowth (PubMed:23447528).
Translational regulator that ensures constant high levels of translation upon a variety of stress conditions, such as amino acid starvation, UV-C irradiation, proteasome inhibitor treatment and glucose deprivation. Plays a role as a negative regulator of the EIF2AK4/GCN2 kinase activity; impairs GCN1-mediated EIF2AK4/GCN2 activation, and hence EIF2AK4/GCN2-mediated eIF-2-alpha phosphorylation and subsequent down-regulation of protein synthesis. May be required to regulate translation in specific neuronal cells under amino acid starvation conditions by preventing GCN2 activation and therefore ATF4 synthesis. Through its inhibitory action on EIF2AK4/GCN2, plays a role in differentiation of neuronal cells by stimulating neurite outgrowth.
Translational regulator that ensures constant high levels of translation upon a variety of stress conditions, such as amino acid starvation, UV-C irradiation, proteasome inhibitor treatment and glucose deprivation. Plays a role as a negative regulator of the EIF2AK4/GCN2 kinase activity; impairs GCN1-mediated EIF2AK4/GCN2 activation, and hence EIF2AK4/GCN2-mediated eIF-2-alpha phosphorylation and subsequent down-regulation of protein synthesis (PubMed:15937339, PubMed:23447528, PubMed:24333428). May be required to regulate translation in specific neuronal cells under amino acid starvation conditions by preventing GCN2 activation and therefore ATF4 synthesis (PubMed:15937339, PubMed:23447528). Through its inhibitory action on EIF2AK4/GCN2, plays a role in differentiation of neuronal cells by stimulating neurite outgrowth (PubMed:23447528).
Translational regulator that ensures constant high levels of translation upon a variety of stress conditions, such as amino acid starvation, UV-C irradiation, proteasome inhibitor treatment and glucose deprivation. Plays a role as a negative regulator of the EIF2AK4/GCN2 kinase activity; impairs GCN1-mediated EIF2AK4/GCN2 activation, and hence EIF2AK4/GCN2-mediated eIF-2-alpha phosphorylation and subsequent down-regulation of protein synthesis. May be required to regulate translation in specific neuronal cells under amino acid starvation conditions by preventing GCN2 activation and therefore ATF4 synthesis. Through its inhibitory action on EIF2AK4/GCN2, plays a role in differentiation of neuronal cells by stimulating neurite outgrowth.
Subunit
Interacts with GCN1; prevents the interaction of GCN1 with EIF2AK4/GCN2 and inhibits EIF2AK4/GCN2 kinase activity. Interaction with RPL39; this interaction occurs in a GCN1-independent manner. Associates with ribosomes; this interaction occurs in a GCN1-independent manner. Associates with actin; this interaction occurs in a GCN1-independent manner.
Interacts with GCN1; prevents the interaction of GCN1 with EIF2AK4/GCN2 and inhibits EIF2AK4/GCN2 kinase activity (PubMed:15937339, PubMed:22404850). Interaction with RPL39; this interaction occurs in a GCN1-independent manner (PubMed:22404850). Associates with ribosomes; this interaction occurs in a GCN1-independent manner (PubMed:22404850). Associates with actin; this interaction occurs in a GCN1-independent manner (PubMed:22404850).
Interacts with GCN1; prevents the interaction of GCN1 with EIF2AK4/GCN2 and inhibits EIF2AK4/GCN2 kinase activity (PubMed:15937339, PubMed:22404850). Interaction with RPL39; this interaction occurs in a GCN1-independent manner (PubMed:22404850). Associates with ribosomes; this interaction occurs in a GCN1-independent manner (PubMed:22404850). Associates with actin; this interaction occurs in a GCN1-independent manner (PubMed:22404850).
Miscellaneous
The Impact locus is imprinted. Paternal inherited gene is expressed, while the maternal inherited gene is silenced. In contrast with most imprinted genes, neighboring genes are apparently not imprinted.
In contrast to the mouse or rabbit ortholog, the IMPACT locus is not imprinted in Xenopus.
In contrast to the mouse or rabbit ortholog, the IMPACT locus is not imprinted in human.
In contrast to the mouse or rabbit ortholog, the IMPACT locus is not imprinted in Xenopus.
In contrast to the mouse or rabbit ortholog, the IMPACT locus is not imprinted in human.
Similarity
Belongs to the IMPACT family.
Keywords
Complete proteome
Cytoplasm
Differentiation
Neurogenesis
Reference proteome
Repressor
Stress response
Translation regulation
Actin-binding
Phosphoprotein
Alternative splicing
Polymorphism
Feature
chain Protein IMPACT-B
splice variant In isoform 2.
sequence variant In dbSNP:rs544203385.
splice variant In isoform 2.
sequence variant In dbSNP:rs544203385.
Uniprot
Q09GQ0
A0A2A4J6F7
A0A194PWI8
A0A0N1PH62
S4PIS9
A0A2W1BDF3
+ More
A0A3S2M6M4 A0A1E1W1K1 A0A212EV50 A0A212FL81 A0A3S2TQA1 A0A2H1VSM6 A0A3S2NHD8 A0A2J7QAC0 A0A1B6MFS3 K7INC1 A0A232EYU5 A0A1B6H196 A0A1B6HJJ2 A0A067RFM4 A0A0P4VWR0 D6WDT9 A0A165A7X1 E9FS84 A0A0P5YWC1 A0A0P6A7F8 A0A1Y1L1R2 A0A2K6U666 F1R3T9 A9UMG5 Q642J4 G3MPG5 A0A210QJE4 X2ASX8 V9L780 A0A293LFS6 A0A0K2TUG2 A0A3B4D019 H2ZPV9 A0A3P8Y0S6 W5LQA6 M3XHQ1 O55091 A0A0B6ZR41 Q5GFD9 V5I0D4 C1BWA3 A0A0L8FJD8 Q9W625 A0A3P8ZWC6 C1BN26 A0A2K5IF79 A0A2T7NJI9 A0A3Q0K081 A0A0E9X3G9 F6YSG2 F1SBA9 B7Q5D7 A0A2K6F3L4 A0A2U9C3Q9 U3DNP8 A0A286XFC7 C3XUC8 A0A2K5DXS6 A0A2K5SAQ2 A0A2K6U633 H3DJU3 A0A2K5DY20 A0A3P8Y2L8 A0A3P8UVY6 A0A3Q2Z351 F6WEH8 A0A3P8UUB8 A0A2K6K7L7 M3XF26 A0A224Z2A1 A0A3Q1IQL6 A0A0D9RYX5 A0A3B3ITH3 G1R485 A0A2K6EAC3 A0A2K5VX90 A0A2K6QJ74 F6RUS8 A0A024RC24 A0A2Y9PH39 G9K5R0 H0X0N8 Q9P2X3 A0A2K5YRE8 A0A2K5MYL9 W5PBP5 L7MD96 A0A131X6P0 A0A096NDH1 A0A3B5LUN8 H2NW26 A0A2U4AYK2 A0A3Q7VSE9 H2UUE3
A0A3S2M6M4 A0A1E1W1K1 A0A212EV50 A0A212FL81 A0A3S2TQA1 A0A2H1VSM6 A0A3S2NHD8 A0A2J7QAC0 A0A1B6MFS3 K7INC1 A0A232EYU5 A0A1B6H196 A0A1B6HJJ2 A0A067RFM4 A0A0P4VWR0 D6WDT9 A0A165A7X1 E9FS84 A0A0P5YWC1 A0A0P6A7F8 A0A1Y1L1R2 A0A2K6U666 F1R3T9 A9UMG5 Q642J4 G3MPG5 A0A210QJE4 X2ASX8 V9L780 A0A293LFS6 A0A0K2TUG2 A0A3B4D019 H2ZPV9 A0A3P8Y0S6 W5LQA6 M3XHQ1 O55091 A0A0B6ZR41 Q5GFD9 V5I0D4 C1BWA3 A0A0L8FJD8 Q9W625 A0A3P8ZWC6 C1BN26 A0A2K5IF79 A0A2T7NJI9 A0A3Q0K081 A0A0E9X3G9 F6YSG2 F1SBA9 B7Q5D7 A0A2K6F3L4 A0A2U9C3Q9 U3DNP8 A0A286XFC7 C3XUC8 A0A2K5DXS6 A0A2K5SAQ2 A0A2K6U633 H3DJU3 A0A2K5DY20 A0A3P8Y2L8 A0A3P8UVY6 A0A3Q2Z351 F6WEH8 A0A3P8UUB8 A0A2K6K7L7 M3XF26 A0A224Z2A1 A0A3Q1IQL6 A0A0D9RYX5 A0A3B3ITH3 G1R485 A0A2K6EAC3 A0A2K5VX90 A0A2K6QJ74 F6RUS8 A0A024RC24 A0A2Y9PH39 G9K5R0 H0X0N8 Q9P2X3 A0A2K5YRE8 A0A2K5MYL9 W5PBP5 L7MD96 A0A131X6P0 A0A096NDH1 A0A3B5LUN8 H2NW26 A0A2U4AYK2 A0A3Q7VSE9 H2UUE3
Pubmed
19121390
26354079
23622113
28756777
22118469
20075255
+ More
28648823 24845553 18362917 19820115 21292972 28004739 22216098 28812685 23254933 24402279 25069045 25329095 9215903 9256468 11116084 15489334 16141072 15871461 15937339 18260151 19131326 21183079 22404850 23447528 24333428 15752730 22673903 25765539 20433749 10066441 25613341 12481130 15114417 30723633 25243066 21993624 18563158 15496914 24487278 20431018 17975172 28797301 16177791 21269460 24275569 25362486 17431167 25319552 11181995 23236062 11244491 14702039 27607563 20809919 25576852 28049606 21551351
28648823 24845553 18362917 19820115 21292972 28004739 22216098 28812685 23254933 24402279 25069045 25329095 9215903 9256468 11116084 15489334 16141072 15871461 15937339 18260151 19131326 21183079 22404850 23447528 24333428 15752730 22673903 25765539 20433749 10066441 25613341 12481130 15114417 30723633 25243066 21993624 18563158 15496914 24487278 20431018 17975172 28797301 16177791 21269460 24275569 25362486 17431167 25319552 11181995 23236062 11244491 14702039 27607563 20809919 25576852 28049606 21551351
EMBL
BABH01025368
DQ904009
ABI73987.1
NWSH01002936
PCG67258.1
KQ459588
+ More
KPI97736.1 KQ461053 KPJ09932.1 GAIX01000084 JAA92476.1 KZ150137 PZC72978.1 RSAL01000025 RVE52167.1 GDQN01010283 JAT80771.1 AGBW02012254 OWR45337.1 AGBW02007882 OWR54449.1 RVE52166.1 ODYU01004197 SOQ43808.1 RSAL01004541 RVE40129.1 NEVH01016331 PNF25509.1 GEBQ01005213 JAT34764.1 NNAY01001603 OXU23457.1 GECZ01001351 JAS68418.1 GECU01032842 JAS74864.1 KK852498 KDR22562.1 GDRN01091016 JAI60350.1 KQ971323 EFA00826.2 LRGB01000642 KZS17280.1 GL732523 EFX89990.1 GDIP01052366 JAM51349.1 GDIP01033702 JAM70013.1 GEZM01068881 JAV66718.1 BC165237 AAI65237.1 BC157649 BC081507 BC152160 JO843766 AEO35383.1 NEDP02003383 OWF48806.1 AMQN01000480 JW875148 AFP07665.1 GFWV01000815 MAA25545.1 HACA01012317 CDW29678.1 AFYH01028777 AFYH01028778 AFYH01028779 AFYH01028780 AFYH01028781 AFYH01028782 AFYH01028783 AFYH01028784 AFYH01028785 AFYH01028786 D87973 AF232228 BC020524 AK138136 HACG01024244 CEK71109.1 AY574213 GANP01002016 JAB82452.1 BT078882 ACO13306.1 KQ430417 KOF64181.1 AB020319 BC099309 BT076005 ACO10429.1 PZQS01000012 PVD21327.1 GBXM01011551 JAH97026.1 AEMK02000045 DQIR01210929 DQIR01257274 HDB66406.1 HDC12752.1 ABJB010692574 ABJB010960445 DS860803 EEC14059.1 CP026254 AWP11244.1 GAMT01005245 GAMS01000982 GAMR01000090 GAMR01000066 GAMQ01005502 GAMP01003743 GAMP01003742 JAB06616.1 JAB22154.1 JAB33842.1 JAB36349.1 JAB49012.1 AAKN02020636 AAKN02020637 GG666464 EEN68502.1 AAMC01131372 AAMC01131373 AAMC01131374 AAMC01131375 AANG04003548 GFPF01009076 MAA20222.1 AQIB01129095 AC007922 ADFV01007067 ADFV01007068 AQIA01032710 JSUE03019320 JU335330 JU335331 JU476283 JV047564 AFE79083.1 AFH33087.1 AFI37635.1 CH471088 EAX01187.1 JP011637 AES00235.1 AAQR03029173 AAQR03029174 AAQR03029175 AAQR03029176 AAQR03029177 AF232229 AB026264 AF208694 AK292533 AC020937 BC034016 BC036074 AMGL01066563 GACK01003237 JAA61797.1 GEFH01005177 JAP63404.1 AHZZ02012425 ABGA01240443 ABGA01240444 NDHI03003366 PNJ81019.1
KPI97736.1 KQ461053 KPJ09932.1 GAIX01000084 JAA92476.1 KZ150137 PZC72978.1 RSAL01000025 RVE52167.1 GDQN01010283 JAT80771.1 AGBW02012254 OWR45337.1 AGBW02007882 OWR54449.1 RVE52166.1 ODYU01004197 SOQ43808.1 RSAL01004541 RVE40129.1 NEVH01016331 PNF25509.1 GEBQ01005213 JAT34764.1 NNAY01001603 OXU23457.1 GECZ01001351 JAS68418.1 GECU01032842 JAS74864.1 KK852498 KDR22562.1 GDRN01091016 JAI60350.1 KQ971323 EFA00826.2 LRGB01000642 KZS17280.1 GL732523 EFX89990.1 GDIP01052366 JAM51349.1 GDIP01033702 JAM70013.1 GEZM01068881 JAV66718.1 BC165237 AAI65237.1 BC157649 BC081507 BC152160 JO843766 AEO35383.1 NEDP02003383 OWF48806.1 AMQN01000480 JW875148 AFP07665.1 GFWV01000815 MAA25545.1 HACA01012317 CDW29678.1 AFYH01028777 AFYH01028778 AFYH01028779 AFYH01028780 AFYH01028781 AFYH01028782 AFYH01028783 AFYH01028784 AFYH01028785 AFYH01028786 D87973 AF232228 BC020524 AK138136 HACG01024244 CEK71109.1 AY574213 GANP01002016 JAB82452.1 BT078882 ACO13306.1 KQ430417 KOF64181.1 AB020319 BC099309 BT076005 ACO10429.1 PZQS01000012 PVD21327.1 GBXM01011551 JAH97026.1 AEMK02000045 DQIR01210929 DQIR01257274 HDB66406.1 HDC12752.1 ABJB010692574 ABJB010960445 DS860803 EEC14059.1 CP026254 AWP11244.1 GAMT01005245 GAMS01000982 GAMR01000090 GAMR01000066 GAMQ01005502 GAMP01003743 GAMP01003742 JAB06616.1 JAB22154.1 JAB33842.1 JAB36349.1 JAB49012.1 AAKN02020636 AAKN02020637 GG666464 EEN68502.1 AAMC01131372 AAMC01131373 AAMC01131374 AAMC01131375 AANG04003548 GFPF01009076 MAA20222.1 AQIB01129095 AC007922 ADFV01007067 ADFV01007068 AQIA01032710 JSUE03019320 JU335330 JU335331 JU476283 JV047564 AFE79083.1 AFH33087.1 AFI37635.1 CH471088 EAX01187.1 JP011637 AES00235.1 AAQR03029173 AAQR03029174 AAQR03029175 AAQR03029176 AAQR03029177 AF232229 AB026264 AF208694 AK292533 AC020937 BC034016 BC036074 AMGL01066563 GACK01003237 JAA61797.1 GEFH01005177 JAP63404.1 AHZZ02012425 ABGA01240443 ABGA01240444 NDHI03003366 PNJ81019.1
Proteomes
UP000005204
UP000218220
UP000053268
UP000053240
UP000283053
UP000007151
+ More
UP000235965 UP000002358 UP000215335 UP000027135 UP000007266 UP000076858 UP000000305 UP000233220 UP000008143 UP000000437 UP000242188 UP000261440 UP000007875 UP000265140 UP000018467 UP000008672 UP000000589 UP000002494 UP000053454 UP000233080 UP000245119 UP000008144 UP000008227 UP000001555 UP000233160 UP000246464 UP000008225 UP000005447 UP000001554 UP000233020 UP000233040 UP000007303 UP000265120 UP000264820 UP000233180 UP000011712 UP000265040 UP000029965 UP000005640 UP000001073 UP000233120 UP000233100 UP000233200 UP000006718 UP000248483 UP000005225 UP000233140 UP000233060 UP000002356 UP000028761 UP000261380 UP000001595 UP000245320 UP000286642 UP000005226
UP000235965 UP000002358 UP000215335 UP000027135 UP000007266 UP000076858 UP000000305 UP000233220 UP000008143 UP000000437 UP000242188 UP000261440 UP000007875 UP000265140 UP000018467 UP000008672 UP000000589 UP000002494 UP000053454 UP000233080 UP000245119 UP000008144 UP000008227 UP000001555 UP000233160 UP000246464 UP000008225 UP000005447 UP000001554 UP000233020 UP000233040 UP000007303 UP000265120 UP000264820 UP000233180 UP000011712 UP000265040 UP000029965 UP000005640 UP000001073 UP000233120 UP000233100 UP000233200 UP000006718 UP000248483 UP000005225 UP000233140 UP000233060 UP000002356 UP000028761 UP000261380 UP000001595 UP000245320 UP000286642 UP000005226
Interpro
Gene 3D
ProteinModelPortal
Q09GQ0
A0A2A4J6F7
A0A194PWI8
A0A0N1PH62
S4PIS9
A0A2W1BDF3
+ More
A0A3S2M6M4 A0A1E1W1K1 A0A212EV50 A0A212FL81 A0A3S2TQA1 A0A2H1VSM6 A0A3S2NHD8 A0A2J7QAC0 A0A1B6MFS3 K7INC1 A0A232EYU5 A0A1B6H196 A0A1B6HJJ2 A0A067RFM4 A0A0P4VWR0 D6WDT9 A0A165A7X1 E9FS84 A0A0P5YWC1 A0A0P6A7F8 A0A1Y1L1R2 A0A2K6U666 F1R3T9 A9UMG5 Q642J4 G3MPG5 A0A210QJE4 X2ASX8 V9L780 A0A293LFS6 A0A0K2TUG2 A0A3B4D019 H2ZPV9 A0A3P8Y0S6 W5LQA6 M3XHQ1 O55091 A0A0B6ZR41 Q5GFD9 V5I0D4 C1BWA3 A0A0L8FJD8 Q9W625 A0A3P8ZWC6 C1BN26 A0A2K5IF79 A0A2T7NJI9 A0A3Q0K081 A0A0E9X3G9 F6YSG2 F1SBA9 B7Q5D7 A0A2K6F3L4 A0A2U9C3Q9 U3DNP8 A0A286XFC7 C3XUC8 A0A2K5DXS6 A0A2K5SAQ2 A0A2K6U633 H3DJU3 A0A2K5DY20 A0A3P8Y2L8 A0A3P8UVY6 A0A3Q2Z351 F6WEH8 A0A3P8UUB8 A0A2K6K7L7 M3XF26 A0A224Z2A1 A0A3Q1IQL6 A0A0D9RYX5 A0A3B3ITH3 G1R485 A0A2K6EAC3 A0A2K5VX90 A0A2K6QJ74 F6RUS8 A0A024RC24 A0A2Y9PH39 G9K5R0 H0X0N8 Q9P2X3 A0A2K5YRE8 A0A2K5MYL9 W5PBP5 L7MD96 A0A131X6P0 A0A096NDH1 A0A3B5LUN8 H2NW26 A0A2U4AYK2 A0A3Q7VSE9 H2UUE3
A0A3S2M6M4 A0A1E1W1K1 A0A212EV50 A0A212FL81 A0A3S2TQA1 A0A2H1VSM6 A0A3S2NHD8 A0A2J7QAC0 A0A1B6MFS3 K7INC1 A0A232EYU5 A0A1B6H196 A0A1B6HJJ2 A0A067RFM4 A0A0P4VWR0 D6WDT9 A0A165A7X1 E9FS84 A0A0P5YWC1 A0A0P6A7F8 A0A1Y1L1R2 A0A2K6U666 F1R3T9 A9UMG5 Q642J4 G3MPG5 A0A210QJE4 X2ASX8 V9L780 A0A293LFS6 A0A0K2TUG2 A0A3B4D019 H2ZPV9 A0A3P8Y0S6 W5LQA6 M3XHQ1 O55091 A0A0B6ZR41 Q5GFD9 V5I0D4 C1BWA3 A0A0L8FJD8 Q9W625 A0A3P8ZWC6 C1BN26 A0A2K5IF79 A0A2T7NJI9 A0A3Q0K081 A0A0E9X3G9 F6YSG2 F1SBA9 B7Q5D7 A0A2K6F3L4 A0A2U9C3Q9 U3DNP8 A0A286XFC7 C3XUC8 A0A2K5DXS6 A0A2K5SAQ2 A0A2K6U633 H3DJU3 A0A2K5DY20 A0A3P8Y2L8 A0A3P8UVY6 A0A3Q2Z351 F6WEH8 A0A3P8UUB8 A0A2K6K7L7 M3XF26 A0A224Z2A1 A0A3Q1IQL6 A0A0D9RYX5 A0A3B3ITH3 G1R485 A0A2K6EAC3 A0A2K5VX90 A0A2K6QJ74 F6RUS8 A0A024RC24 A0A2Y9PH39 G9K5R0 H0X0N8 Q9P2X3 A0A2K5YRE8 A0A2K5MYL9 W5PBP5 L7MD96 A0A131X6P0 A0A096NDH1 A0A3B5LUN8 H2NW26 A0A2U4AYK2 A0A3Q7VSE9 H2UUE3
PDB
6BQI
E-value=3.99256e-27,
Score=300
Ontologies
GO
GO:0097201
GO:0060548
GO:0005737
GO:0072755
GO:0071264
GO:0060733
GO:1990138
GO:1990253
GO:0042149
GO:0071468
GO:0071494
GO:0031333
GO:0001933
GO:0000122
GO:0070301
GO:0045666
GO:0031953
GO:0034198
GO:0005844
GO:0003779
GO:0043022
GO:0006446
GO:0016874
GO:0016021
GO:0000139
GO:0005515
GO:0005576
GO:0007275
GO:0016055
GO:0009166
GO:0005839
GO:0051603
GO:0046835
GO:0006281
GO:0006259
Topology
Subcellular location
Cytoplasm
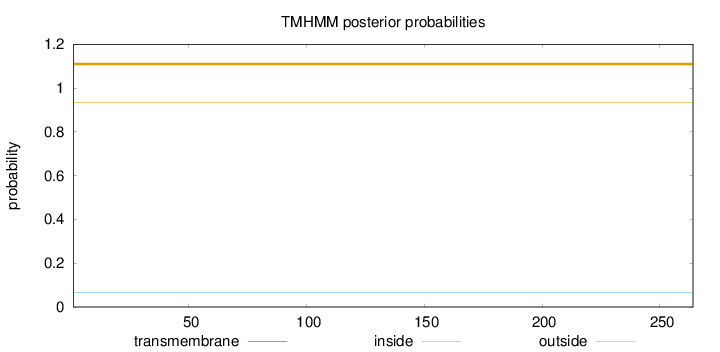
Length:
264
Number of predicted TMHs:
0
Exp number of AAs in TMHs:
0.00156
Exp number, first 60 AAs:
0
Total prob of N-in:
0.06597
outside
1 - 264
Population Genetic Test Statistics
Pi
270.161143
Theta
168.673411
Tajima's D
1.561494
CLR
0
CSRT
0.798610069496525
Interpretation
Uncertain
