Gene
KWMTBOMO15376
Pre Gene Modal
BGIBMGA005107
Annotation
Rad51_homolog_[Bombyx_mori]
Full name
DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog
+ More
DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1
DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1
Alternative Name
RAD51 homolog A
Location in the cell
Cytoplasmic Reliability : 2.331
Sequence
CDS
ATGAATACCACTGCTTCAGCAACTACGACTTCTTTGGATGAAGATGCTGACGAATGCGGGCCACAGCTGATCAGTAAATTAGAGGGCAATGGCATCACATCAGGAGATATAAAAAAGCTTGAGGAAGCGGGATATCATACTGTTGAATCTGTTGCCTATGCTCCAAAAAAATGGCTAATCACAATTAAAGGGATATCTGAAGCGAAGGCAGATAAAATATTAGCTGAAGCATCTAAATTGGTGCCAATGGGATTTACAACAGCTACTGAGTTTCATCAAAAGAGGGCTGAAATAATACAACTTACTACTGGTTCAAAGGAATTAGATAGATTACTGGGAGGTGGTATAGAAACTGGTTCTATAACTGAAATATTTGGTGAATTCCGTACTGGCAAAACCCAATTATGTCACACATTAGCAGTCACCTGCCAGCTACCCATTGAACAATCTGGTGGAGAGGGTAAATGCATGTACATCGATACAGAAGGAACATTCAGACCGGAAAGACTGCTGGCCGTTGCACAGCGATACGGTATGGAAGGTGCGGCAGTCTTGGACAATGTTGCATATGCAAGAGCTTATAACACAGACCATCAGACCCAATTGCTAGTGCAAGCTTGCGCCATGATGGCAGAGTCAAGATATTCCTTAATTATAGTTGATAGTGCAACCGCTCTATACAGGACAGACTATTCTGGACGAGGGGAACTGAATTCTAGACAACTACATCTGGGTCGTTTCATGAGAATGTTGCTCAGATTGGCTGATGAGTTTGGAGTAGCAGTAATCATAACAAACCAAGTGGTCGCACAAGTGGATGCTGTAGGAGTTTTCAATGCTGATACCAAGAAACCAATCGGAGGTCATATCATAGCGCACGCGTCCACAACTAGACTCTATTTACGGAAGGGTAGAGGTGATAATCGCGTGTGTAAAATATACGATAGTCCGTGCTTGCCCGAAACAGAAGCTATGTTTGCGATTAGCGCTGAAGGCATCACGGATGCTAAGGAATAA
Protein
MNTTASATTTSLDEDADECGPQLISKLEGNGITSGDIKKLEEAGYHTVESVAYAPKKWLITIKGISEAKADKILAEASKLVPMGFTTATEFHQKRAEIIQLTTGSKELDRLLGGGIETGSITEIFGEFRTGKTQLCHTLAVTCQLPIEQSGGEGKCMYIDTEGTFRPERLLAVAQRYGMEGAAVLDNVAYARAYNTDHQTQLLVQACAMMAESRYSLIIVDSATALYRTDYSGRGELNSRQLHLGRFMRMLLRLADEFGVAVIITNQVVAQVDAVGVFNADTKKPIGGHIIAHASTTRLYLRKGRGDNRVCKIYDSPCLPETEAMFAISAEGITDAKE
Summary
Description
Binds to single and double-stranded DNA and exhibits DNA-dependent ATPase activity. Underwinds duplex DNA.
Plays an important role in homologous strand exchange, a key step in DNA repair through homologous recombination. Binds to single and double-stranded DNA and exhibits DNA-dependent ATPase activity. Catalyzes the recognition of homology and strand exchange between homologous DNA partners to form a joint molecule between a processed DNA break and the repair template. Binds to single-stranded DNA in an ATP-dependent manner to form nucleoprotein filaments which are essential for the homology search and strand exchange.
Plays an important role in homologous strand exchange, a key step in DNA repair through homologous recombination (HR) (PubMed:28575658). Binds to single and double-stranded DNA and exhibits DNA-dependent ATPase activity. Catalyzes the recognition of homology and strand exchange between homologous DNA partners to form a joint molecule between a processed DNA break and the repair template. Binds to single-stranded DNA in an ATP-dependent manner to form nucleoprotein filaments which are essential for the homology search and strand exchange (PubMed:26681308). Part of a PALB2-scaffolded HR complex containing BRCA2 and RAD51C and which is thought to play a role in DNA repair by HR. Plays a role in regulating mitochondrial DNA copy number under conditions of oxidative stress in the presence of RAD51C and XRCC3. Also involved in interstrand cross-link repair (PubMed:26253028).
Plays an important role in homologous strand exchange, a key step in DNA repair through homologous recombination (HR). Binds to single and double-stranded DNA and exhibits DNA-dependent ATPase activity. Catalyzes the recognition of homology and strand exchange between homologous DNA partners to form a joint molecule between a processed DNA break and the repair template. Binds to single-stranded DNA in an ATP-dependent manner to form nucleoprotein filaments which are essential for the homology search and strand exchange. Part of a PALB2-scaffolded HR complex containing BRCA2 and RAD51C and which is thought to play a role in DNA repair by HR. Plays a role in regulating mitochondrial DNA copy number under conditions of oxidative stress in the presence of RAD51C and XRCC3. Also involved in interstrand cross-link repair.
Plays an important role in homologous strand exchange, a key step in DNA repair through homologous recombination (HR) (PubMed:15834424). Binds to single and double-stranded DNA and exhibits DNA-dependent ATPase activity. Catalyzes the recognition of homology and strand exchange between homologous DNA partners to form a joint molecule between a processed DNA break and the repair template. Binds to single-stranded DNA in an ATP-dependent manner to form nucleoprotein filaments which are essential for the homology search and strand exchange. Part of a PALB2-scaffolded HR complex containing BRCA2 and RAD51C and which is thought to play a role in DNA repair by HR. Plays a role in regulating mitochondrial DNA copy number under conditions of oxidative stress in the presence of RAD51C and XRCC3. Also involved in interstrand cross-link repair (By similarity).
Plays an important role in homologous strand exchange, a key step in DNA repair through homologous recombination. Binds to single and double-stranded DNA and exhibits DNA-dependent ATPase activity. Catalyzes the recognition of homology and strand exchange between homologous DNA partners to form a joint molecule between a processed DNA break and the repair template. Binds to single-stranded DNA in an ATP-dependent manner to form nucleoprotein filaments which are essential for the homology search and strand exchange.
Plays an important role in homologous strand exchange, a key step in DNA repair through homologous recombination (HR) (PubMed:28575658). Binds to single and double-stranded DNA and exhibits DNA-dependent ATPase activity. Catalyzes the recognition of homology and strand exchange between homologous DNA partners to form a joint molecule between a processed DNA break and the repair template. Binds to single-stranded DNA in an ATP-dependent manner to form nucleoprotein filaments which are essential for the homology search and strand exchange (PubMed:26681308). Part of a PALB2-scaffolded HR complex containing BRCA2 and RAD51C and which is thought to play a role in DNA repair by HR. Plays a role in regulating mitochondrial DNA copy number under conditions of oxidative stress in the presence of RAD51C and XRCC3. Also involved in interstrand cross-link repair (PubMed:26253028).
Plays an important role in homologous strand exchange, a key step in DNA repair through homologous recombination (HR). Binds to single and double-stranded DNA and exhibits DNA-dependent ATPase activity. Catalyzes the recognition of homology and strand exchange between homologous DNA partners to form a joint molecule between a processed DNA break and the repair template. Binds to single-stranded DNA in an ATP-dependent manner to form nucleoprotein filaments which are essential for the homology search and strand exchange. Part of a PALB2-scaffolded HR complex containing BRCA2 and RAD51C and which is thought to play a role in DNA repair by HR. Plays a role in regulating mitochondrial DNA copy number under conditions of oxidative stress in the presence of RAD51C and XRCC3. Also involved in interstrand cross-link repair.
Plays an important role in homologous strand exchange, a key step in DNA repair through homologous recombination (HR) (PubMed:15834424). Binds to single and double-stranded DNA and exhibits DNA-dependent ATPase activity. Catalyzes the recognition of homology and strand exchange between homologous DNA partners to form a joint molecule between a processed DNA break and the repair template. Binds to single-stranded DNA in an ATP-dependent manner to form nucleoprotein filaments which are essential for the homology search and strand exchange. Part of a PALB2-scaffolded HR complex containing BRCA2 and RAD51C and which is thought to play a role in DNA repair by HR. Plays a role in regulating mitochondrial DNA copy number under conditions of oxidative stress in the presence of RAD51C and XRCC3. Also involved in interstrand cross-link repair (By similarity).
Subunit
Forms linear homooligomers, giving rise to a RAD51 nucleoprotein filament, which is essential for strand-pairing reactions during DNA recombination. Interacts with BRCA1 and either directly or indirectly with p53. Interacts with XRCC3, RAD54L and RAD54B. Interacts with the BCDX2 subcomplex RAD51C:RAD51B. Interacts directly with PALB2 which may serve as a scaffold for a HR complex containing PALB2, BRCA2, RAD51C, RAD51 and XRCC3. Interacts with RAD51AP1 and RAD51AP2. Interacts with CHEK1, and this may require prior phosphorylation of CHEK1. Interacts with the MND1-PSMC3IP heterodimer. Found in a complex, at least composed of BLM, RAD51 and SPIDR; the complex formation is mediated by SPIDR. Interacts with SPIDR; the interaction is direct and recruits RAD51 to DNA damage sites. Interacts with FIGNL1 (via N-terminal one-half region); the interaction is direct. Interacts with RAD51AP1 (via C-terminal region); the interaction is direct. Interacts with NABP2, RPA1, PALB2 and RAD51. Interacts with SWI5/C9orf119, and at lower level with SFR1/MEIR5. Interacts with hyperphosphorylated RPA2; this interaction is necessary for efficient recruitment to chromatin in response to DNA damage. Interacts with SWSAP1; involved in homologous recombination repair. Interacts with PARPBP, BRCA2 and RECQL5; these interactions interfere with the formation of the RAD51-DNA homologous recombination structure. Interacts with POLQ; POLQ acts as an inhibitor of homology-recombination repair (HR) pathway by limiting RAD51 accumulation at resected ends (PubMed:25642963). Interacts with FBH1 (PubMed:23393192). Interacts with POLN (PubMed:19995904). Interacts with RFWD3 (PubMed:28575658). Interacts with the MCM8-MCM9 complex; the interaction recruits RAD51 to DNA damage sites (PubMed:23401855).
Forms linear homooligomers, giving rise to a RAD51 nucleoprotein filament, which is essential for strand-pairing reactions during DNA recombination. Interacts with BRCA1 and either directly or indirectly with p53. Interacts with XRCC3, RAD54L and RAD54B. Interacts with the BCDX2 subcomplex RAD51C:RAD51B. Interacts directly with PALB2 which may serve as a scaffold for a HR complex containing PALB2, BRCA2, RAD51C, RAD51 and XRCC3. Interacts with RAD51AP1 and RAD51AP2. Interacts with CHEK1, and this may require prior phosphorylation of CHEK1. Interacts with the MND1-PSMC3IP heterodimer. Found in a complex, at least composed of BLM, RAD51 and SPIDR; the complex formation is mediated by SPIDR. Interacts with SPIDR; the interaction is direct and recruits RAD51 to DNA damage sites. Interacts with FIGNL1 (via N-terminal one-half region); the interaction is direct. Interacts with RAD51AP1 (via C-terminal region); the interaction is direct. Interacts with NABP2, RPA1, PALB2 and RAD51. Interacts with SWI5/C9orf119, and at lower level with SFR1/MEIR5. Interacts with hyperphosphorylated RPA2; this interaction is necessary for efficient recruitment to chromatin in response to DNA damage. Interacts with SWSAP1; involved in homologous recombination repair. Interacts with PARPBP, BRCA2 and RECQL5; these interactions interfere with the formation of the RAD51-DNA homologous recombination structure. Interacts with POLQ; POLQ acts as an inhibitor of homology-recombination repair (HR) pathway by limiting RAD51 accumulation at resected ends. Interacts with FBH1. Interacts with POLN. Interacts with RFWD3. Interacts with the MCM8-MCM9 complex; the interaction recruits RAD51 to DNA damage sites.
Forms linear homooligomers, giving rise to a RAD51 nucleoprotein filament, which is essential for strand-pairing reactions during DNA recombination. Interacts with BRCA1 and either directly or indirectly with p53. Interacts with XRCC3, RAD54L and RAD54B. Interacts with the BCDX2 subcomplex RAD51C:RAD51B. Interacts directly with PALB2 which may serve as a scaffold for a HR complex containing PALB2, BRCA2, RAD51C, RAD51 and XRCC3. Interacts with RAD51AP1 and RAD51AP2. Interacts with CHEK1, and this may require prior phosphorylation of CHEK1 (By similarity). Interacts with the MND1-PSMC3IP heterodimer (PubMed:15834424). Found in a complex, at least composed of BLM, RAD51 and SPIDR; the complex formation is mediated by SPIDR. Interacts with SPIDR; the interaction is direct and recruits RAD51 to DNA damage sites. Interacts with FIGNL1 (via N-terminal one-half region); the interaction is direct. Interacts with RAD51AP1 (via C-terminal region); the interaction is direct (By similarity). Interacts with NABP2, RPA1, PALB2 and RAD51. Interacts with SWI5/C9orf119, and at lower level with SFR1/MEIR5 (PubMed:20976249). Interacts with hyperphosphorylated RPA2; this interaction is necessary for efficient recruitment to chromatin in response to DNA damage. Interacts with SWSAP1; involved in homologous recombination repair. Interacts with PARPBP, BRCA2 and RECQL5; these interactions interfere with the formation of the RAD51-DNA homologous recombination structure. Interacts with POLQ; POLQ acts as an inhibitor of homology-recombination repair (HR) pathway by limiting RAD51 accumulation at resected ends. Interacts with POLN (By similarity). Interacts with FBH1 (PubMed:24108124). Interacts with RFWD3 (By similarity). Interacts with the MCM8-MCM9 complex; the interaction recruits RAD51 to DNA damage sites (By similarity).
Forms linear homooligomers, giving rise to a RAD51 nucleoprotein filament, which is essential for strand-pairing reactions during DNA recombination. Interacts with BRCA1 and either directly or indirectly with p53. Interacts with XRCC3, RAD54L and RAD54B. Interacts with the BCDX2 subcomplex RAD51C:RAD51B. Interacts directly with PALB2 which may serve as a scaffold for a HR complex containing PALB2, BRCA2, RAD51C, RAD51 and XRCC3. Interacts with RAD51AP1 and RAD51AP2. Interacts with CHEK1, and this may require prior phosphorylation of CHEK1. Interacts with the MND1-PSMC3IP heterodimer. Found in a complex, at least composed of BLM, RAD51 and SPIDR; the complex formation is mediated by SPIDR. Interacts with SPIDR; the interaction is direct and recruits RAD51 to DNA damage sites. Interacts with FIGNL1 (via N-terminal one-half region); the interaction is direct. Interacts with RAD51AP1 (via C-terminal region); the interaction is direct. Interacts with NABP2, RPA1, PALB2 and RAD51. Interacts with SWI5/C9orf119, and at lower level with SFR1/MEIR5. Interacts with hyperphosphorylated RPA2; this interaction is necessary for efficient recruitment to chromatin in response to DNA damage. Interacts with SWSAP1; involved in homologous recombination repair. Interacts with PARPBP, BRCA2 and RECQL5; these interactions interfere with the formation of the RAD51-DNA homologous recombination structure. Interacts with POLQ; POLQ acts as an inhibitor of homology-recombination repair (HR) pathway by limiting RAD51 accumulation at resected ends. Interacts with FBH1. Interacts with POLN. Interacts with RFWD3. Interacts with the MCM8-MCM9 complex; the interaction recruits RAD51 to DNA damage sites.
Forms linear homooligomers, giving rise to a RAD51 nucleoprotein filament, which is essential for strand-pairing reactions during DNA recombination. Interacts with BRCA1 and either directly or indirectly with p53. Interacts with XRCC3, RAD54L and RAD54B. Interacts with the BCDX2 subcomplex RAD51C:RAD51B. Interacts directly with PALB2 which may serve as a scaffold for a HR complex containing PALB2, BRCA2, RAD51C, RAD51 and XRCC3. Interacts with RAD51AP1 and RAD51AP2. Interacts with CHEK1, and this may require prior phosphorylation of CHEK1 (By similarity). Interacts with the MND1-PSMC3IP heterodimer (PubMed:15834424). Found in a complex, at least composed of BLM, RAD51 and SPIDR; the complex formation is mediated by SPIDR. Interacts with SPIDR; the interaction is direct and recruits RAD51 to DNA damage sites. Interacts with FIGNL1 (via N-terminal one-half region); the interaction is direct. Interacts with RAD51AP1 (via C-terminal region); the interaction is direct (By similarity). Interacts with NABP2, RPA1, PALB2 and RAD51. Interacts with SWI5/C9orf119, and at lower level with SFR1/MEIR5 (PubMed:20976249). Interacts with hyperphosphorylated RPA2; this interaction is necessary for efficient recruitment to chromatin in response to DNA damage. Interacts with SWSAP1; involved in homologous recombination repair. Interacts with PARPBP, BRCA2 and RECQL5; these interactions interfere with the formation of the RAD51-DNA homologous recombination structure. Interacts with POLQ; POLQ acts as an inhibitor of homology-recombination repair (HR) pathway by limiting RAD51 accumulation at resected ends. Interacts with POLN (By similarity). Interacts with FBH1 (PubMed:24108124). Interacts with RFWD3 (By similarity). Interacts with the MCM8-MCM9 complex; the interaction recruits RAD51 to DNA damage sites (By similarity).
Miscellaneous
The nucleus of a mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells contains on average 4.7 x 10(5) molecules.
Similarity
Belongs to the RecA family. RAD51 subfamily.
Belongs to the RecA family.
Belongs to the RecA family.
Keywords
ATP-binding
Complete proteome
DNA-binding
Nucleotide-binding
Nucleus
Reference proteome
3D-structure
Acetylation
Alternative splicing
Chromosome
Cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton
Disease mutation
DNA damage
DNA recombination
DNA repair
Fanconi anemia
Isopeptide bond
Mitochondrion
Phosphoprotein
Ubl conjugation
Feature
chain DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1
splice variant In isoform 4.
sequence variant In FANCR; causes dominant negative loss of function in interstrand cross-link repair; shows high basal DNA-independent ATPase activity; results in decreased DNA binding.
splice variant In isoform 4.
sequence variant In FANCR; causes dominant negative loss of function in interstrand cross-link repair; shows high basal DNA-independent ATPase activity; results in decreased DNA binding.
Uniprot
H9J6G5
A0A2A4JZ86
A0A2H1VPY3
O01679
A0A1E1W8R0
A0A212EZ62
+ More
S4NSU5 A0A194RL40 A0A1B6G8Z2 A0A1W4WW34 A0A067QZL1 A0A1Q3F1H5 A0A1B6CDI5 A0A2W1BP08 B0W9S4 A0A093SKA5 A0A2C9JDB7 A0A182H0X9 A0A3M0JA07 H0ZAJ0 A0A093EFX4 A0A091ECR7 A0A3L8S5X0 A0A091HNA5 A0A087VLW2 A0A091L9I3 A0A093BNJ2 Q177M5 A0A099ZAQ4 A0A2I4CQ96 A0A091GGC9 A0A091VVW8 A0A091LQ02 A0A091JEP8 A0A2I0LQ90 R7VV42 A0A093G2J4 A0A091KWU9 A0A094K1X9 A0A087RAJ9 A0A094L9T4 A0A2Z5U228 A0A091SUH8 A0A1E1XBV5 A0A093QWL3 A0A091WYT8 A0A093G6B7 A0A0A0AZ45 A0A091TRB3 A0A091SGR3 A0A091P6L5 A0A093CNA7 K7G1R9 A0A093H997 A0A023GII5 G3MNM4 T1IIF6 A0A091MVL2 A0A0Q3M634 H0VQ96 P37383 A0A091U6K9 A0A060WW06 H9GKC7 B5X4V6 A0A2K5VNC1 A0A2I3H1V5 A0A0D9R5C5 A0A2R9CAJ7 A0A096NTH7 A0A2K6NAH8 H2NMV0 A0A1D5QVN1 A0A2I3SZ08 J3JVS9 Q06609 A0A091PSS5 A0A091RUG6 A0A2K5Q0D3 A0A2I2YW66 A0A2K5F8S9 F7IG78 A0A1V4JPT8 G5E7T1 A0A1U7RRI9 B5DF04 G3HYS4 P70099 A4IH92 A0A1S3ENF2 Q08297 A0A0N8EUC2 G3T2F7 A0A1U7UL65 B0M1M6 A0A293MQ09 A0A182FL32 A0A3Q0CHC1 G1TCL3 A0A2K5XYU7
S4NSU5 A0A194RL40 A0A1B6G8Z2 A0A1W4WW34 A0A067QZL1 A0A1Q3F1H5 A0A1B6CDI5 A0A2W1BP08 B0W9S4 A0A093SKA5 A0A2C9JDB7 A0A182H0X9 A0A3M0JA07 H0ZAJ0 A0A093EFX4 A0A091ECR7 A0A3L8S5X0 A0A091HNA5 A0A087VLW2 A0A091L9I3 A0A093BNJ2 Q177M5 A0A099ZAQ4 A0A2I4CQ96 A0A091GGC9 A0A091VVW8 A0A091LQ02 A0A091JEP8 A0A2I0LQ90 R7VV42 A0A093G2J4 A0A091KWU9 A0A094K1X9 A0A087RAJ9 A0A094L9T4 A0A2Z5U228 A0A091SUH8 A0A1E1XBV5 A0A093QWL3 A0A091WYT8 A0A093G6B7 A0A0A0AZ45 A0A091TRB3 A0A091SGR3 A0A091P6L5 A0A093CNA7 K7G1R9 A0A093H997 A0A023GII5 G3MNM4 T1IIF6 A0A091MVL2 A0A0Q3M634 H0VQ96 P37383 A0A091U6K9 A0A060WW06 H9GKC7 B5X4V6 A0A2K5VNC1 A0A2I3H1V5 A0A0D9R5C5 A0A2R9CAJ7 A0A096NTH7 A0A2K6NAH8 H2NMV0 A0A1D5QVN1 A0A2I3SZ08 J3JVS9 Q06609 A0A091PSS5 A0A091RUG6 A0A2K5Q0D3 A0A2I2YW66 A0A2K5F8S9 F7IG78 A0A1V4JPT8 G5E7T1 A0A1U7RRI9 B5DF04 G3HYS4 P70099 A4IH92 A0A1S3ENF2 Q08297 A0A0N8EUC2 G3T2F7 A0A1U7UL65 B0M1M6 A0A293MQ09 A0A182FL32 A0A3Q0CHC1 G1TCL3 A0A2K5XYU7
Pubmed
19121390
22118469
23622113
26354079
24845553
28756777
+ More
15562597 26483478 20360741 30282656 17510324 23371554 26760975 28503490 17381049 22216098 21993624 8479908 24755649 21881562 20433749 22722832 25362486 17431167 22002653 25319552 16136131 22516182 23537049 8358431 8479919 10493508 11535547 18417535 14702039 16572171 15489334 7988572 9321665 9396801 9192668 9461559 10851248 12205100 11842113 12427746 14580352 16215984 15665856 16990250 18449195 19783859 20348101 20413593 20705237 19995904 20231364 20154705 20871615 21276791 21252223 21965664 22305526 22153967 22814378 23401855 24013206 23393192 24141787 23754376 23509288 26253028 25642963 28575658 10390347 12442171 10807537 26681308 25539919 22398555 25243066 20838655 15057822 15632090 21804562 29704459 9611228 8341671 16141072 12531026 15834424 21183079 20976249 24108124 26319212
15562597 26483478 20360741 30282656 17510324 23371554 26760975 28503490 17381049 22216098 21993624 8479908 24755649 21881562 20433749 22722832 25362486 17431167 22002653 25319552 16136131 22516182 23537049 8358431 8479919 10493508 11535547 18417535 14702039 16572171 15489334 7988572 9321665 9396801 9192668 9461559 10851248 12205100 11842113 12427746 14580352 16215984 15665856 16990250 18449195 19783859 20348101 20413593 20705237 19995904 20231364 20154705 20871615 21276791 21252223 21965664 22305526 22153967 22814378 23401855 24013206 23393192 24141787 23754376 23509288 26253028 25642963 28575658 10390347 12442171 10807537 26681308 25539919 22398555 25243066 20838655 15057822 15632090 21804562 29704459 9611228 8341671 16141072 12531026 15834424 21183079 20976249 24108124 26319212
EMBL
BABH01019687
NWSH01000360
PCG76998.1
ODYU01003577
SOQ42512.1
U94993
+ More
AAB53330.1 GDQN01007727 JAT83327.1 AGBW02011359 OWR46788.1 GAIX01013907 JAA78653.1 KQ460045 KPJ18040.1 GECZ01023957 GECZ01010847 JAS45812.1 JAS58922.1 KK853153 KDR10565.1 GFDL01013639 JAV21406.1 GEDC01025968 GEDC01023052 GEDC01008361 GEDC01008200 JAS11330.1 JAS14246.1 JAS28937.1 JAS29098.1 KZ149949 PZC76698.1 DS231865 EDS40393.1 KL671651 KFW83089.1 JXUM01022600 KQ560636 KXJ81493.1 QRBI01000154 RMB98001.1 ABQF01001741 ABQF01001742 ABQF01001743 ABQF01001744 KL243738 KFV13426.1 KK718118 KFO54462.1 QUSF01000061 RLV97201.1 KL217671 KFO97753.1 KL498073 KFO13604.1 KL304997 KFP51963.1 KN126771 KFU92492.1 CH477373 EAT42393.1 KL890540 KGL77915.1 KL447413 KFO73187.1 KL411427 KFR07492.1 KK503549 KFP60542.1 KK502026 KFP19469.1 AKCR02000143 PKK19586.1 KB375693 EMC82304.1 KK402922 KFV60869.1 KK757121 KFP43715.1 KL338022 KFZ51145.1 KL226261 KFM10503.1 KL275757 KFZ66192.1 FX985854 BBA93741.1 KK485873 KFQ61948.1 GFAC01002455 JAT96733.1 KL427743 KFW90735.1 KK734340 KFR06501.1 KL215636 KFV65755.1 KL873572 KGL99192.1 KK463831 KFQ80658.1 KK819184 KFQ39425.1 KK653461 KFQ03265.1 KL467057 KFV17340.1 AGCU01123701 AGCU01123702 AGCU01123703 KL206137 KFV79183.1 GBBM01001651 JAC33767.1 JO843475 AEO35092.1 AFFK01014262 KK837354 KFP80619.1 LMAW01002691 KQK78037.1 AAKN02015884 AAKN02015885 L09655 S59426 KK416813 KFQ85490.1 FR904765 CDQ71381.1 AAWZ02022539 BT046075 ACI34337.1 AQIA01062288 AQIA01062289 AQIA01062290 AQIA01062291 AQIA01062292 AQIA01062293 ADFV01034026 ADFV01034027 ADFV01034028 ADFV01034029 ADFV01034030 ADFV01034031 ADFV01034032 ADFV01034033 AQIB01116312 AQIB01116313 AQIB01116314 AQIB01116315 AQIB01116316 AQIB01116317 AQIB01116318 AQIB01116319 AQIB01116320 AJFE02093122 AJFE02093123 AJFE02093124 AJFE02093125 AJFE02093126 AJFE02093127 AJFE02093128 AHZZ02030811 ABGA01322537 ABGA01322538 ABGA01322539 ABGA01322540 ABGA01322541 ABGA01322542 ABGA01322543 ABGA01322544 ABGA01322545 NDHI03003606 PNJ16221.1 JSUE03038057 JSUE03038058 JSUE03038059 JU473728 JV635768 CM001259 AFH30532.1 AFJ71108.1 EHH27216.1 AACZ04038084 AACZ04038085 GABC01001450 GABF01003101 GABD01009207 GABE01011245 NBAG03000046 JAA09888.1 JAA19044.1 JAA23893.1 JAA33494.1 PNI94354.1 APGK01035041 BT127347 KB740923 KB632326 AEE62309.1 ENN78154.1 ERL92440.1 D13804 D14134 AF165094 AF165088 AF165089 AF165090 AF165091 AF165092 AF165093 AF233744 AF233740 AF233741 AF233742 AF236021 AF233743 EU362635 AY196785 AK131299 AK291969 AK313503 CR536559 AC012476 AC022405 CH471125 BC001459 KK677825 KFQ10381.1 KK931883 KFQ45446.1 CABD030095572 CABD030095573 CABD030095574 GAMS01004701 JAB18435.1 LSYS01006880 OPJ74208.1 AC111293 BC168875 CH473949 AAI68875.1 EDL79891.1 JH000944 RAZU01000234 EGW09314.1 RLQ64482.1 Y08202 BC135425 AAI35426.1 D13473 D13803 AK011242 AK076468 AK151157 AK151177 BC027384 GEBF01001987 JAO01646.1 AEMK02000004 EU302125 AB355632 ABZ89107.1 BAG09486.1 GFWV01023020 MAA47747.1 AAGW02024517 AAGW02024518 AAGW02024519
AAB53330.1 GDQN01007727 JAT83327.1 AGBW02011359 OWR46788.1 GAIX01013907 JAA78653.1 KQ460045 KPJ18040.1 GECZ01023957 GECZ01010847 JAS45812.1 JAS58922.1 KK853153 KDR10565.1 GFDL01013639 JAV21406.1 GEDC01025968 GEDC01023052 GEDC01008361 GEDC01008200 JAS11330.1 JAS14246.1 JAS28937.1 JAS29098.1 KZ149949 PZC76698.1 DS231865 EDS40393.1 KL671651 KFW83089.1 JXUM01022600 KQ560636 KXJ81493.1 QRBI01000154 RMB98001.1 ABQF01001741 ABQF01001742 ABQF01001743 ABQF01001744 KL243738 KFV13426.1 KK718118 KFO54462.1 QUSF01000061 RLV97201.1 KL217671 KFO97753.1 KL498073 KFO13604.1 KL304997 KFP51963.1 KN126771 KFU92492.1 CH477373 EAT42393.1 KL890540 KGL77915.1 KL447413 KFO73187.1 KL411427 KFR07492.1 KK503549 KFP60542.1 KK502026 KFP19469.1 AKCR02000143 PKK19586.1 KB375693 EMC82304.1 KK402922 KFV60869.1 KK757121 KFP43715.1 KL338022 KFZ51145.1 KL226261 KFM10503.1 KL275757 KFZ66192.1 FX985854 BBA93741.1 KK485873 KFQ61948.1 GFAC01002455 JAT96733.1 KL427743 KFW90735.1 KK734340 KFR06501.1 KL215636 KFV65755.1 KL873572 KGL99192.1 KK463831 KFQ80658.1 KK819184 KFQ39425.1 KK653461 KFQ03265.1 KL467057 KFV17340.1 AGCU01123701 AGCU01123702 AGCU01123703 KL206137 KFV79183.1 GBBM01001651 JAC33767.1 JO843475 AEO35092.1 AFFK01014262 KK837354 KFP80619.1 LMAW01002691 KQK78037.1 AAKN02015884 AAKN02015885 L09655 S59426 KK416813 KFQ85490.1 FR904765 CDQ71381.1 AAWZ02022539 BT046075 ACI34337.1 AQIA01062288 AQIA01062289 AQIA01062290 AQIA01062291 AQIA01062292 AQIA01062293 ADFV01034026 ADFV01034027 ADFV01034028 ADFV01034029 ADFV01034030 ADFV01034031 ADFV01034032 ADFV01034033 AQIB01116312 AQIB01116313 AQIB01116314 AQIB01116315 AQIB01116316 AQIB01116317 AQIB01116318 AQIB01116319 AQIB01116320 AJFE02093122 AJFE02093123 AJFE02093124 AJFE02093125 AJFE02093126 AJFE02093127 AJFE02093128 AHZZ02030811 ABGA01322537 ABGA01322538 ABGA01322539 ABGA01322540 ABGA01322541 ABGA01322542 ABGA01322543 ABGA01322544 ABGA01322545 NDHI03003606 PNJ16221.1 JSUE03038057 JSUE03038058 JSUE03038059 JU473728 JV635768 CM001259 AFH30532.1 AFJ71108.1 EHH27216.1 AACZ04038084 AACZ04038085 GABC01001450 GABF01003101 GABD01009207 GABE01011245 NBAG03000046 JAA09888.1 JAA19044.1 JAA23893.1 JAA33494.1 PNI94354.1 APGK01035041 BT127347 KB740923 KB632326 AEE62309.1 ENN78154.1 ERL92440.1 D13804 D14134 AF165094 AF165088 AF165089 AF165090 AF165091 AF165092 AF165093 AF233744 AF233740 AF233741 AF233742 AF236021 AF233743 EU362635 AY196785 AK131299 AK291969 AK313503 CR536559 AC012476 AC022405 CH471125 BC001459 KK677825 KFQ10381.1 KK931883 KFQ45446.1 CABD030095572 CABD030095573 CABD030095574 GAMS01004701 JAB18435.1 LSYS01006880 OPJ74208.1 AC111293 BC168875 CH473949 AAI68875.1 EDL79891.1 JH000944 RAZU01000234 EGW09314.1 RLQ64482.1 Y08202 BC135425 AAI35426.1 D13473 D13803 AK011242 AK076468 AK151157 AK151177 BC027384 GEBF01001987 JAO01646.1 AEMK02000004 EU302125 AB355632 ABZ89107.1 BAG09486.1 GFWV01023020 MAA47747.1 AAGW02024517 AAGW02024518 AAGW02024519
Proteomes
UP000005204
UP000218220
UP000007151
UP000053240
UP000192223
UP000027135
+ More
UP000002320 UP000053258 UP000076420 UP000069940 UP000249989 UP000269221 UP000007754 UP000052976 UP000276834 UP000054308 UP000008820 UP000053641 UP000192220 UP000053760 UP000053283 UP000053119 UP000053872 UP000053286 UP000053605 UP000053875 UP000053858 UP000007267 UP000053584 UP000051836 UP000005447 UP000000539 UP000193380 UP000001646 UP000087266 UP000233100 UP000001073 UP000029965 UP000240080 UP000028761 UP000233200 UP000001595 UP000006718 UP000002277 UP000019118 UP000030742 UP000005640 UP000233040 UP000001519 UP000233020 UP000008225 UP000190648 UP000001645 UP000189705 UP000002494 UP000001075 UP000273346 UP000081671 UP000000589 UP000007646 UP000189704 UP000008227 UP000069272 UP000189706 UP000001811 UP000233140
UP000002320 UP000053258 UP000076420 UP000069940 UP000249989 UP000269221 UP000007754 UP000052976 UP000276834 UP000054308 UP000008820 UP000053641 UP000192220 UP000053760 UP000053283 UP000053119 UP000053872 UP000053286 UP000053605 UP000053875 UP000053858 UP000007267 UP000053584 UP000051836 UP000005447 UP000000539 UP000193380 UP000001646 UP000087266 UP000233100 UP000001073 UP000029965 UP000240080 UP000028761 UP000233200 UP000001595 UP000006718 UP000002277 UP000019118 UP000030742 UP000005640 UP000233040 UP000001519 UP000233020 UP000008225 UP000190648 UP000001645 UP000189705 UP000002494 UP000001075 UP000273346 UP000081671 UP000000589 UP000007646 UP000189704 UP000008227 UP000069272 UP000189706 UP000001811 UP000233140
Pfam
PF08423 Rad51
Interpro
IPR013632
DNA_recomb/repair_Rad51_C
+ More
IPR020588 RecA_ATP-bd
IPR027417 P-loop_NTPase
IPR010995 DNA_repair_Rad51/TF_NusA_a-hlx
IPR016467 DNA_recomb/repair_RecA-like
IPR020587 RecA_monomer-monomer_interface
IPR011941 DNA_recomb/repair_Rad51
IPR003593 AAA+_ATPase
IPR033925 Rad51_DMC1_RadA
IPR011940 Dmc1
IPR020588 RecA_ATP-bd
IPR027417 P-loop_NTPase
IPR010995 DNA_repair_Rad51/TF_NusA_a-hlx
IPR016467 DNA_recomb/repair_RecA-like
IPR020587 RecA_monomer-monomer_interface
IPR011941 DNA_recomb/repair_Rad51
IPR003593 AAA+_ATPase
IPR033925 Rad51_DMC1_RadA
IPR011940 Dmc1
ProteinModelPortal
H9J6G5
A0A2A4JZ86
A0A2H1VPY3
O01679
A0A1E1W8R0
A0A212EZ62
+ More
S4NSU5 A0A194RL40 A0A1B6G8Z2 A0A1W4WW34 A0A067QZL1 A0A1Q3F1H5 A0A1B6CDI5 A0A2W1BP08 B0W9S4 A0A093SKA5 A0A2C9JDB7 A0A182H0X9 A0A3M0JA07 H0ZAJ0 A0A093EFX4 A0A091ECR7 A0A3L8S5X0 A0A091HNA5 A0A087VLW2 A0A091L9I3 A0A093BNJ2 Q177M5 A0A099ZAQ4 A0A2I4CQ96 A0A091GGC9 A0A091VVW8 A0A091LQ02 A0A091JEP8 A0A2I0LQ90 R7VV42 A0A093G2J4 A0A091KWU9 A0A094K1X9 A0A087RAJ9 A0A094L9T4 A0A2Z5U228 A0A091SUH8 A0A1E1XBV5 A0A093QWL3 A0A091WYT8 A0A093G6B7 A0A0A0AZ45 A0A091TRB3 A0A091SGR3 A0A091P6L5 A0A093CNA7 K7G1R9 A0A093H997 A0A023GII5 G3MNM4 T1IIF6 A0A091MVL2 A0A0Q3M634 H0VQ96 P37383 A0A091U6K9 A0A060WW06 H9GKC7 B5X4V6 A0A2K5VNC1 A0A2I3H1V5 A0A0D9R5C5 A0A2R9CAJ7 A0A096NTH7 A0A2K6NAH8 H2NMV0 A0A1D5QVN1 A0A2I3SZ08 J3JVS9 Q06609 A0A091PSS5 A0A091RUG6 A0A2K5Q0D3 A0A2I2YW66 A0A2K5F8S9 F7IG78 A0A1V4JPT8 G5E7T1 A0A1U7RRI9 B5DF04 G3HYS4 P70099 A4IH92 A0A1S3ENF2 Q08297 A0A0N8EUC2 G3T2F7 A0A1U7UL65 B0M1M6 A0A293MQ09 A0A182FL32 A0A3Q0CHC1 G1TCL3 A0A2K5XYU7
S4NSU5 A0A194RL40 A0A1B6G8Z2 A0A1W4WW34 A0A067QZL1 A0A1Q3F1H5 A0A1B6CDI5 A0A2W1BP08 B0W9S4 A0A093SKA5 A0A2C9JDB7 A0A182H0X9 A0A3M0JA07 H0ZAJ0 A0A093EFX4 A0A091ECR7 A0A3L8S5X0 A0A091HNA5 A0A087VLW2 A0A091L9I3 A0A093BNJ2 Q177M5 A0A099ZAQ4 A0A2I4CQ96 A0A091GGC9 A0A091VVW8 A0A091LQ02 A0A091JEP8 A0A2I0LQ90 R7VV42 A0A093G2J4 A0A091KWU9 A0A094K1X9 A0A087RAJ9 A0A094L9T4 A0A2Z5U228 A0A091SUH8 A0A1E1XBV5 A0A093QWL3 A0A091WYT8 A0A093G6B7 A0A0A0AZ45 A0A091TRB3 A0A091SGR3 A0A091P6L5 A0A093CNA7 K7G1R9 A0A093H997 A0A023GII5 G3MNM4 T1IIF6 A0A091MVL2 A0A0Q3M634 H0VQ96 P37383 A0A091U6K9 A0A060WW06 H9GKC7 B5X4V6 A0A2K5VNC1 A0A2I3H1V5 A0A0D9R5C5 A0A2R9CAJ7 A0A096NTH7 A0A2K6NAH8 H2NMV0 A0A1D5QVN1 A0A2I3SZ08 J3JVS9 Q06609 A0A091PSS5 A0A091RUG6 A0A2K5Q0D3 A0A2I2YW66 A0A2K5F8S9 F7IG78 A0A1V4JPT8 G5E7T1 A0A1U7RRI9 B5DF04 G3HYS4 P70099 A4IH92 A0A1S3ENF2 Q08297 A0A0N8EUC2 G3T2F7 A0A1U7UL65 B0M1M6 A0A293MQ09 A0A182FL32 A0A3Q0CHC1 G1TCL3 A0A2K5XYU7
PDB
5NWL
E-value=8.18123e-142,
Score=1290
Ontologies
PATHWAY
GO
GO:0000724
GO:0000150
GO:0003690
GO:0005524
GO:0008094
GO:1990426
GO:0003697
GO:0005634
GO:0007131
GO:0006281
GO:0003677
GO:0071312
GO:0000784
GO:0070192
GO:0072711
GO:0001932
GO:0003682
GO:0010833
GO:1990414
GO:0000800
GO:0000722
GO:0006310
GO:0006312
GO:0005737
GO:0000730
GO:0006974
GO:0051321
GO:0006268
GO:0005654
GO:0042148
GO:0000228
GO:0043142
GO:0000794
GO:0000793
GO:0000790
GO:0000785
GO:0036297
GO:0005730
GO:0071479
GO:0032991
GO:0070317
GO:0051106
GO:0051260
GO:0016605
GO:0005829
GO:0070182
GO:0005739
GO:0031297
GO:0005815
GO:0005759
GO:0072757
GO:0010569
GO:0035861
GO:0008022
GO:0042802
GO:0048471
GO:0019899
GO:0014070
GO:0072719
GO:0010165
GO:0042493
GO:0007127
GO:1904631
GO:0071480
GO:0009636
GO:0032200
GO:0000795
GO:0000166
GO:0006259
Topology
Subcellular location
Nucleus
Cytoplasm Colocalizes with RAD51AP1 and RPA2 to multiple nuclear foci upon induction of DNA damage (PubMed:20154705). DNA damage induces an increase in nuclear levels (PubMed:20154705). Together with FIGNL1, redistributed in discrete nuclear DNA damage-induced foci after ionizing radiation (IR) or camptothecin (CPT) treatment (PubMed:23754376). Accumulated at sites of DNA damage in a SPIDR-dependent manner (PubMed:23509288). Recruited at sites of DNA damage in a MCM9-MCM8-dependent manner (PubMed:23401855). With evidence from 19 publications.
Perinuclear region Colocalizes with RAD51AP1 and RPA2 to multiple nuclear foci upon induction of DNA damage (PubMed:20154705). DNA damage induces an increase in nuclear levels (PubMed:20154705). Together with FIGNL1, redistributed in discrete nuclear DNA damage-induced foci after ionizing radiation (IR) or camptothecin (CPT) treatment (PubMed:23754376). Accumulated at sites of DNA damage in a SPIDR-dependent manner (PubMed:23509288). Recruited at sites of DNA damage in a MCM9-MCM8-dependent manner (PubMed:23401855). With evidence from 19 publications.
Mitochondrion matrix Colocalizes with RAD51AP1 and RPA2 to multiple nuclear foci upon induction of DNA damage (PubMed:20154705). DNA damage induces an increase in nuclear levels (PubMed:20154705). Together with FIGNL1, redistributed in discrete nuclear DNA damage-induced foci after ionizing radiation (IR) or camptothecin (CPT) treatment (PubMed:23754376). Accumulated at sites of DNA damage in a SPIDR-dependent manner (PubMed:23509288). Recruited at sites of DNA damage in a MCM9-MCM8-dependent manner (PubMed:23401855). With evidence from 19 publications.
Chromosome Colocalizes with RAD51AP1 and RPA2 to multiple nuclear foci upon induction of DNA damage (PubMed:20154705). DNA damage induces an increase in nuclear levels (PubMed:20154705). Together with FIGNL1, redistributed in discrete nuclear DNA damage-induced foci after ionizing radiation (IR) or camptothecin (CPT) treatment (PubMed:23754376). Accumulated at sites of DNA damage in a SPIDR-dependent manner (PubMed:23509288). Recruited at sites of DNA damage in a MCM9-MCM8-dependent manner (PubMed:23401855). With evidence from 19 publications.
Cytoskeleton Colocalizes with RAD51AP1 and RPA2 to multiple nuclear foci upon induction of DNA damage (PubMed:20154705). DNA damage induces an increase in nuclear levels (PubMed:20154705). Together with FIGNL1, redistributed in discrete nuclear DNA damage-induced foci after ionizing radiation (IR) or camptothecin (CPT) treatment (PubMed:23754376). Accumulated at sites of DNA damage in a SPIDR-dependent manner (PubMed:23509288). Recruited at sites of DNA damage in a MCM9-MCM8-dependent manner (PubMed:23401855). With evidence from 19 publications.
Microtubule organizing center Colocalizes with RAD51AP1 and RPA2 to multiple nuclear foci upon induction of DNA damage (PubMed:20154705). DNA damage induces an increase in nuclear levels (PubMed:20154705). Together with FIGNL1, redistributed in discrete nuclear DNA damage-induced foci after ionizing radiation (IR) or camptothecin (CPT) treatment (PubMed:23754376). Accumulated at sites of DNA damage in a SPIDR-dependent manner (PubMed:23509288). Recruited at sites of DNA damage in a MCM9-MCM8-dependent manner (PubMed:23401855). With evidence from 19 publications.
Centrosome Colocalizes with RAD51AP1 and RPA2 to multiple nuclear foci upon induction of DNA damage (PubMed:20154705). DNA damage induces an increase in nuclear levels (PubMed:20154705). Together with FIGNL1, redistributed in discrete nuclear DNA damage-induced foci after ionizing radiation (IR) or camptothecin (CPT) treatment (PubMed:23754376). Accumulated at sites of DNA damage in a SPIDR-dependent manner (PubMed:23509288). Recruited at sites of DNA damage in a MCM9-MCM8-dependent manner (PubMed:23401855). With evidence from 19 publications.
Cytoplasm Colocalizes with RAD51AP1 and RPA2 to multiple nuclear foci upon induction of DNA damage (PubMed:20154705). DNA damage induces an increase in nuclear levels (PubMed:20154705). Together with FIGNL1, redistributed in discrete nuclear DNA damage-induced foci after ionizing radiation (IR) or camptothecin (CPT) treatment (PubMed:23754376). Accumulated at sites of DNA damage in a SPIDR-dependent manner (PubMed:23509288). Recruited at sites of DNA damage in a MCM9-MCM8-dependent manner (PubMed:23401855). With evidence from 19 publications.
Perinuclear region Colocalizes with RAD51AP1 and RPA2 to multiple nuclear foci upon induction of DNA damage (PubMed:20154705). DNA damage induces an increase in nuclear levels (PubMed:20154705). Together with FIGNL1, redistributed in discrete nuclear DNA damage-induced foci after ionizing radiation (IR) or camptothecin (CPT) treatment (PubMed:23754376). Accumulated at sites of DNA damage in a SPIDR-dependent manner (PubMed:23509288). Recruited at sites of DNA damage in a MCM9-MCM8-dependent manner (PubMed:23401855). With evidence from 19 publications.
Mitochondrion matrix Colocalizes with RAD51AP1 and RPA2 to multiple nuclear foci upon induction of DNA damage (PubMed:20154705). DNA damage induces an increase in nuclear levels (PubMed:20154705). Together with FIGNL1, redistributed in discrete nuclear DNA damage-induced foci after ionizing radiation (IR) or camptothecin (CPT) treatment (PubMed:23754376). Accumulated at sites of DNA damage in a SPIDR-dependent manner (PubMed:23509288). Recruited at sites of DNA damage in a MCM9-MCM8-dependent manner (PubMed:23401855). With evidence from 19 publications.
Chromosome Colocalizes with RAD51AP1 and RPA2 to multiple nuclear foci upon induction of DNA damage (PubMed:20154705). DNA damage induces an increase in nuclear levels (PubMed:20154705). Together with FIGNL1, redistributed in discrete nuclear DNA damage-induced foci after ionizing radiation (IR) or camptothecin (CPT) treatment (PubMed:23754376). Accumulated at sites of DNA damage in a SPIDR-dependent manner (PubMed:23509288). Recruited at sites of DNA damage in a MCM9-MCM8-dependent manner (PubMed:23401855). With evidence from 19 publications.
Cytoskeleton Colocalizes with RAD51AP1 and RPA2 to multiple nuclear foci upon induction of DNA damage (PubMed:20154705). DNA damage induces an increase in nuclear levels (PubMed:20154705). Together with FIGNL1, redistributed in discrete nuclear DNA damage-induced foci after ionizing radiation (IR) or camptothecin (CPT) treatment (PubMed:23754376). Accumulated at sites of DNA damage in a SPIDR-dependent manner (PubMed:23509288). Recruited at sites of DNA damage in a MCM9-MCM8-dependent manner (PubMed:23401855). With evidence from 19 publications.
Microtubule organizing center Colocalizes with RAD51AP1 and RPA2 to multiple nuclear foci upon induction of DNA damage (PubMed:20154705). DNA damage induces an increase in nuclear levels (PubMed:20154705). Together with FIGNL1, redistributed in discrete nuclear DNA damage-induced foci after ionizing radiation (IR) or camptothecin (CPT) treatment (PubMed:23754376). Accumulated at sites of DNA damage in a SPIDR-dependent manner (PubMed:23509288). Recruited at sites of DNA damage in a MCM9-MCM8-dependent manner (PubMed:23401855). With evidence from 19 publications.
Centrosome Colocalizes with RAD51AP1 and RPA2 to multiple nuclear foci upon induction of DNA damage (PubMed:20154705). DNA damage induces an increase in nuclear levels (PubMed:20154705). Together with FIGNL1, redistributed in discrete nuclear DNA damage-induced foci after ionizing radiation (IR) or camptothecin (CPT) treatment (PubMed:23754376). Accumulated at sites of DNA damage in a SPIDR-dependent manner (PubMed:23509288). Recruited at sites of DNA damage in a MCM9-MCM8-dependent manner (PubMed:23401855). With evidence from 19 publications.
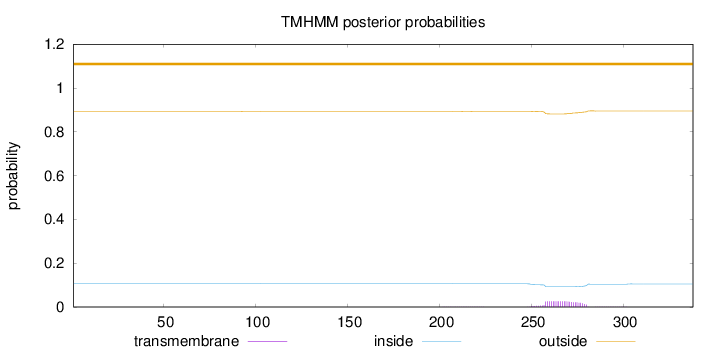
Length:
338
Number of predicted TMHs:
0
Exp number of AAs in TMHs:
0.59352
Exp number, first 60 AAs:
0
Total prob of N-in:
0.10637
outside
1 - 338
Population Genetic Test Statistics
Pi
232.439992
Theta
154.481114
Tajima's D
1.724245
CLR
0
CSRT
0.832858357082146
Interpretation
Uncertain
