Gene
KWMTBOMO11679
Pre Gene Modal
BGIBMGA004136
Annotation
PREDICTED:_tumor_susceptibility_gene_101_protein_[Amyelois_transitella]
Full name
Tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein
Alternative Name
ESCRT-I complex subunit TSG101
Location in the cell
Nuclear Reliability : 3.145
Sequence
CDS
ATGACCAACCACGAAGCTGTATTGAAACAATTGTTATCGAAATATAAACATCGGGACTTCACTTCTCGAGAAGTAATTAACTTGCTACAAGTGTACAGAAGCTTAACTTATCGTTTGGAAGCATTTATCTTTAATAATGGTTCCAGAAAAGAGCTTTTGAATATTGAAGGTACAATTCCCGTAAATTACAAAGGAGCCTTTTATAACATACCCGTGTCAATATGGCTCATGGACACTCATCCTCAAAATGCGCCTTTGTGTTTTGTGAAACCGACATCTGACATGTCTATCAAGGTATCGAAGTACGTTGACACTAACGGAAAAGTTTATTTACCTTATCTTCACGAGTGGTCTTCGAATTCTTCCACTTTGAAGAATCTGGTGCAGTGCATGATTACAGCATTTGGTGAATTACCTCCGGTGTATTCTAAGCCACGTAATGTTGCTATGCCTATGTTCGCTGCGAAACCGTTTATGCCAGAATCGTCAGGATATCCCTTACCAATGCCTACTCCAGGGTATCCTACTACAACACCATATCCTACAACTTCAAGTTTACCATATCCTAATTATGGTTCACCATATCCTGGAACAGCGAGTACAAATGGTCTGCCATATCCTCCAGCACCAATAACTACACCTTACCCCCCTGCATCACAATATGGTCCTAGTACAGAAGGTGCTGGGGGTACCATTACTGAAGAGCATATTAAAGCATCGCTACTGTCTGCTGTTGAAGACAAATTAAGAAGACGTCTTAAAGAACAATCTCAGCAATCACAGGCTGAACTTGAAACCTTACGTAGGACTCAGCAAGAACTTGGTGAAGGAAAGTCTCGGATTGAAGACATAATTACGAGACTTCAAAGGGAGCGTTCAGAACTAGATAAGAATGTAATGATTTTACAAGAGAAGGAAAAAGAGTTGCAAGCAGCCGTGGAACGTTTGGCTGACCAGGAGGGTGTGGATGTTGATGAAGCAGTAGTGACAACTGCACCACTGTATTCCCAACTTCTAAATGCTTTTGCTGAAGAAGCTACCCTAGAAGATGCTATTTATTACATGGGTGAAGCTCTGCGGAAGGAAGTTATAGATTTGGACACATTTTTGAAGCAAGTCCGCACATTGGCACGTCGACAGTTTACACTAAGGGCATTGATGCATAAATGCAGGCAAAAGGCTCAGTTAGCTTGCTAA
Protein
MTNHEAVLKQLLSKYKHRDFTSREVINLLQVYRSLTYRLEAFIFNNGSRKELLNIEGTIPVNYKGAFYNIPVSIWLMDTHPQNAPLCFVKPTSDMSIKVSKYVDTNGKVYLPYLHEWSSNSSTLKNLVQCMITAFGELPPVYSKPRNVAMPMFAAKPFMPESSGYPLPMPTPGYPTTTPYPTTSSLPYPNYGSPYPGTASTNGLPYPPAPITTPYPPASQYGPSTEGAGGTITEEHIKASLLSAVEDKLRRRLKEQSQQSQAELETLRRTQQELGEGKSRIEDIITRLQRERSELDKNVMILQEKEKELQAAVERLADQEGVDVDEAVVTTAPLYSQLLNAFAEEATLEDAIYYMGEALRKEVIDLDTFLKQVRTLARRQFTLRALMHKCRQKAQLAC
Summary
Description
Component of the ESCRT-I complex, a regulator of vesicular trafficking process. Binds to ubiquitinated cargo proteins and is required for the sorting of endocytic ubiquitinated cargos into multivesicular bodies (MVBs). Mediates the association between the ESCRT-0 and ESCRT-I complex. Required for completion of cytokinesis; the function requires CEP55. May be involved in cell growth and differentiation. Acts as a negative growth regulator. Involved in the budding of many viruses through an interaction with viral proteins that contain a late-budding motif P-[ST]-A-P. This interaction is essential for viral particle budding of numerous retroviruses. Required for the exosomal release of SDCBP, CD63 and syndecan (PubMed:22660413). It may also play a role in the extracellular release of microvesicles that differ from the exosomes (PubMed:22315426).
Subunit
Component of the ESCRT-I complex (endosomal sorting complex required for transport I) which consists of TSG101, VPS28, a VPS37 protein (VPS37A to -D) and MVB12A or MVB12B in a 1:1:1:1 stoichiometry (PubMed:18005716). Interacts with VPS37A, VPS37B and VPS37C (PubMed:15218037, PubMed:15509564). Interacts with DMAP1 (PubMed:10888872). Interacts with ubiquitin (PubMed:11595185). Interacts with stathmin, GMCL and AATF (By similarity). Component of an ESCRT-I complex (endosomal sorting complex required for transport I) which consists of TSG101, VPS28, VPS37A and UBAP1 in a 1:1:1:1 stoichiometry (PubMed:21757351). Interacts with HGS; the interaction mediates the association with the ESCRT-0 complex. Interacts with GGA1 and GGA3 (PubMed:15143060, PubMed:15039775). Interacts (via UEV domain) with PDCD6IP/AIP1 (PubMed:14505570, PubMed:14519844). Interacts with VPS28, SNF8 and VPS36 (PubMed:14505570). Self-associates (PubMed:14505570, PubMed:14519844). Interacts with MVB12A; the association appears to be mediated by the TSG101-VPS37 binary subcomplex. Interacts with VPS37D. Interacts with LRSAM1. Interacts with CEP55; the interaction is required for cytokinesis but not for viral budding (PubMed:17853893). Interacts with PDCD6 (PubMed:18256029). Interacts with LITAF (PubMed:23166352). Interacts with MGRN1 (PubMed:17229889). Interacts with ARRDC1; recruits TSG101 to the plasma membrane (PubMed:21191027, PubMed:22315426).
(Microbial infection) Interacts with HIV-1 p6.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with human spumavirus Gag.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with HTLV-1 Gag.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with Ebola virus VP40.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with EIAV p9; the interaction has been shown in vitro.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with Lassa virus protein Z.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with hepatitis E virus protein ORF3.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with HIV-1 p6.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with human spumavirus Gag.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with HTLV-1 Gag.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with Ebola virus VP40.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with EIAV p9; the interaction has been shown in vitro.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with Lassa virus protein Z.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with hepatitis E virus protein ORF3.
Similarity
Belongs to the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family. UEV subfamily.
Keywords
3D-structure
Acetylation
Alternative splicing
Cell cycle
Cell division
Coiled coil
Complete proteome
Cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton
Endosome
Growth regulation
Host-virus interaction
Membrane
Nucleus
Phosphoprotein
Polymorphism
Protein transport
Reference proteome
Transport
Ubl conjugation
Feature
chain Tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein
splice variant In isoform 2.
sequence variant In dbSNP:rs34385327.
splice variant In isoform 2.
sequence variant In dbSNP:rs34385327.
Uniprot
A0A2A4JPS1
A0A1E1WLK1
A0A1V0JHU5
A0A0L7LM77
A0A194R3P8
A0A194QCS8
+ More
H9J3P9 V9IJQ0 A0A2A3E0U5 A0A2J7RDC7 A0A088A8G9 A0A212FP45 A0A026WXG7 A0A151X6V4 V5IA93 A0A195EGD8 A0A1L8EDD6 A0A195FF75 E2AZS6 U5EZQ5 D3TNE1 A0A0L7QSC2 A0A034WB09 A0A195AWK8 A0A182MA76 W8CB77 A0A195CCW6 A0A1A9ZU67 A0A1A9V3W5 A0A1A9W4A6 B4KZ07 A0A182Q067 A0A0K8WKT9 A0A0M9A6L5 B4LE79 A0A182WKR6 A0A0M4F1U6 A0A1Q3FE78 A0A3B0KNR9 W8C786 A0A182NIP5 A0A182JNM1 B3NDH1 A0A1C7CZF1 A0A1Y9GL68 Q7Q6B6 A0A1Y1K7W7 A0A182JGT1 A0A182S6Z9 A0A182THL7 A0A1J1I6S8 B4H4C4 Q16LW0 A0A1S4FWC1 B0WII4 A0A182X6Z6 A0A182VKZ5 A0A1I8M8H1 A0A023ERB3 A0A182G9Q0 A0A1I8PKF7 A0A182GPL4 A0A310SS95 D6WIH5 A0A1B6CLS7 B3M4D5 A0A182RZR1 A0A0A1XCQ7 A0A182YD34 A0A232EJM5 A0A182FCA5 A0A1B6LBT4 A0A336KYH5 A0A336L0Q4 A0A0A9WFR4 A0A1B6GN30 A0A2K5C4J4 A0A2K5S838 F6YJ85 A0A067RQG0 A0A2K6UNI7 A0A2J8UQP2 A0A2K6DP04 G3R4B1 G1S7V5 A0A2K5ZAD9 A0A0D9QYD5 A0A2R9AQ37 A0A2I3N4L1 A0A2K6NCD4 G7PQL3 G7NDS4 A0A2I3SDN5 Q99816 A0A2K5I652 H9FZ74 A0A1B6JWT1 K7C918 F6ZA94 I0FUS3
H9J3P9 V9IJQ0 A0A2A3E0U5 A0A2J7RDC7 A0A088A8G9 A0A212FP45 A0A026WXG7 A0A151X6V4 V5IA93 A0A195EGD8 A0A1L8EDD6 A0A195FF75 E2AZS6 U5EZQ5 D3TNE1 A0A0L7QSC2 A0A034WB09 A0A195AWK8 A0A182MA76 W8CB77 A0A195CCW6 A0A1A9ZU67 A0A1A9V3W5 A0A1A9W4A6 B4KZ07 A0A182Q067 A0A0K8WKT9 A0A0M9A6L5 B4LE79 A0A182WKR6 A0A0M4F1U6 A0A1Q3FE78 A0A3B0KNR9 W8C786 A0A182NIP5 A0A182JNM1 B3NDH1 A0A1C7CZF1 A0A1Y9GL68 Q7Q6B6 A0A1Y1K7W7 A0A182JGT1 A0A182S6Z9 A0A182THL7 A0A1J1I6S8 B4H4C4 Q16LW0 A0A1S4FWC1 B0WII4 A0A182X6Z6 A0A182VKZ5 A0A1I8M8H1 A0A023ERB3 A0A182G9Q0 A0A1I8PKF7 A0A182GPL4 A0A310SS95 D6WIH5 A0A1B6CLS7 B3M4D5 A0A182RZR1 A0A0A1XCQ7 A0A182YD34 A0A232EJM5 A0A182FCA5 A0A1B6LBT4 A0A336KYH5 A0A336L0Q4 A0A0A9WFR4 A0A1B6GN30 A0A2K5C4J4 A0A2K5S838 F6YJ85 A0A067RQG0 A0A2K6UNI7 A0A2J8UQP2 A0A2K6DP04 G3R4B1 G1S7V5 A0A2K5ZAD9 A0A0D9QYD5 A0A2R9AQ37 A0A2I3N4L1 A0A2K6NCD4 G7PQL3 G7NDS4 A0A2I3SDN5 Q99816 A0A2K5I652 H9FZ74 A0A1B6JWT1 K7C918 F6ZA94 I0FUS3
Pubmed
26227816
26354079
19121390
22118469
24508170
30249741
+ More
20798317 20353571 25348373 24495485 17994087 20966253 12364791 14747013 17210077 28004739 17510324 25315136 24945155 26483478 18362917 19820115 25830018 25244985 28648823 25401762 26823975 25243066 24845553 22398555 22722832 25362486 22002653 17431167 16136131 9019400 9867424 15489334 9366528 9242438 9840940 10888872 11595185 11427703 11916981 14505570 12900394 12559917 14581525 12802020 14519844 15256501 15218037 15143060 15039775 15509564 15858022 16571837 18005716 17853893 17229889 17556548 18256029 19413330 19520058 19703557 21269460 21757351 21068219 21191027 23166352 22660413 22814378 22315426 23186163 25944712 12006492 12379843 15053872 16552148 21070952 21643473 25319552 19892987
20798317 20353571 25348373 24495485 17994087 20966253 12364791 14747013 17210077 28004739 17510324 25315136 24945155 26483478 18362917 19820115 25830018 25244985 28648823 25401762 26823975 25243066 24845553 22398555 22722832 25362486 22002653 17431167 16136131 9019400 9867424 15489334 9366528 9242438 9840940 10888872 11595185 11427703 11916981 14505570 12900394 12559917 14581525 12802020 14519844 15256501 15218037 15143060 15039775 15509564 15858022 16571837 18005716 17853893 17229889 17556548 18256029 19413330 19520058 19703557 21269460 21757351 21068219 21191027 23166352 22660413 22814378 22315426 23186163 25944712 12006492 12379843 15053872 16552148 21070952 21643473 25319552 19892987
EMBL
NWSH01000825
PCG74001.1
GDQN01003170
JAT87884.1
KY694528
ODYU01009243
+ More
ARD08869.1 SOQ53520.1 JTDY01000654 KOB76316.1 KQ460949 KPJ10466.1 KQ459185 KPJ03224.1 BABH01021730 JX569222 AFW03817.1 JR050819 AEY61358.1 KZ288470 PBC25338.1 NEVH01005291 PNF38832.1 AGBW02003976 OWR55479.1 KK107078 QOIP01000011 EZA60436.1 RLU17272.1 KQ982476 KYQ56064.1 GALX01001585 JAB66881.1 KQ978957 KYN27303.1 GFDG01002061 JAV16738.1 KQ981636 KYN38872.1 GL444277 EFN61055.1 GANO01000351 JAB59520.1 EZ422943 ADD19219.1 KQ414758 KOC61543.1 GAKP01007063 JAC51889.1 KQ976725 KYM76633.1 AXCM01008814 GAMC01000694 JAC05862.1 KQ978023 KYM98061.1 CH933809 EDW17804.1 AXCN02000418 GDHF01000568 JAI51746.1 KQ435724 KOX78305.1 CH940647 EDW69035.1 CP012525 ALC44982.1 GFDL01009174 JAV25871.1 OUUW01000012 SPP87506.1 GAMC01000692 JAC05864.1 CH954178 EDV52033.1 APCN01000100 AAAB01008960 EAA11918.4 GEZM01095070 JAV55526.1 CVRI01000043 CRK96015.1 CH479208 EDW31239.1 CH477889 EAT35314.1 DS231949 EDS28507.1 GAPW01001883 JAC11715.1 JXUM01154663 KQ572013 KXJ68089.1 JXUM01078851 KQ563092 KXJ74490.1 KQ761005 OAD58412.1 KQ971334 EEZ99668.1 GEDC01022874 JAS14424.1 CH902618 EDV40429.1 GBXI01006049 JAD08243.1 NNAY01003963 OXU18570.1 GEBQ01018837 JAT21140.1 UFQS01001240 UFQT01001240 SSX09883.1 SSX29606.1 UFQS01000770 UFQT01000770 SSX06750.1 SSX27095.1 GBHO01039909 GBHO01039908 GBRD01011388 GDHC01020427 JAG03695.1 JAG03696.1 JAG54436.1 JAP98201.1 GECZ01005958 JAS63811.1 GAMT01001463 GAMT01001462 GAMS01002450 GAMR01007290 GAMQ01003838 GAMP01007994 JAB10398.1 JAB20686.1 JAB26642.1 JAB38013.1 JAB44761.1 KK852528 KDR21984.1 NDHI03003449 PNJ47587.1 CABD030077714 CABD030077715 CABD030077716 CABD030077717 ADFV01112683 ADFV01112684 ADFV01112685 ADFV01112686 ADFV01112687 ADFV01112688 AQIB01085129 AQIB01085130 AQIB01085131 AQIB01085132 AJFE02062316 AJFE02062317 AJFE02062318 AJFE02062319 AJFE02062320 AJFE02062321 AHZZ02006885 AHZZ02006886 AHZZ02006887 AHZZ02006888 AQIA01020876 CM001289 EHH56403.1 JSUE03012634 JSUE03012635 CM001266 EHH23052.1 AACZ04016563 GABC01010505 GABF01004794 GABD01003086 NBAG03000219 JAA00833.1 JAA17351.1 JAA30014.1 PNI79014.1 U82130 BC002487 JU336180 JU477035 AFE79933.1 AFH33839.1 GECU01004056 JAT03651.1 GABE01005673 JAA39066.1 JV048128 AFI38199.1
ARD08869.1 SOQ53520.1 JTDY01000654 KOB76316.1 KQ460949 KPJ10466.1 KQ459185 KPJ03224.1 BABH01021730 JX569222 AFW03817.1 JR050819 AEY61358.1 KZ288470 PBC25338.1 NEVH01005291 PNF38832.1 AGBW02003976 OWR55479.1 KK107078 QOIP01000011 EZA60436.1 RLU17272.1 KQ982476 KYQ56064.1 GALX01001585 JAB66881.1 KQ978957 KYN27303.1 GFDG01002061 JAV16738.1 KQ981636 KYN38872.1 GL444277 EFN61055.1 GANO01000351 JAB59520.1 EZ422943 ADD19219.1 KQ414758 KOC61543.1 GAKP01007063 JAC51889.1 KQ976725 KYM76633.1 AXCM01008814 GAMC01000694 JAC05862.1 KQ978023 KYM98061.1 CH933809 EDW17804.1 AXCN02000418 GDHF01000568 JAI51746.1 KQ435724 KOX78305.1 CH940647 EDW69035.1 CP012525 ALC44982.1 GFDL01009174 JAV25871.1 OUUW01000012 SPP87506.1 GAMC01000692 JAC05864.1 CH954178 EDV52033.1 APCN01000100 AAAB01008960 EAA11918.4 GEZM01095070 JAV55526.1 CVRI01000043 CRK96015.1 CH479208 EDW31239.1 CH477889 EAT35314.1 DS231949 EDS28507.1 GAPW01001883 JAC11715.1 JXUM01154663 KQ572013 KXJ68089.1 JXUM01078851 KQ563092 KXJ74490.1 KQ761005 OAD58412.1 KQ971334 EEZ99668.1 GEDC01022874 JAS14424.1 CH902618 EDV40429.1 GBXI01006049 JAD08243.1 NNAY01003963 OXU18570.1 GEBQ01018837 JAT21140.1 UFQS01001240 UFQT01001240 SSX09883.1 SSX29606.1 UFQS01000770 UFQT01000770 SSX06750.1 SSX27095.1 GBHO01039909 GBHO01039908 GBRD01011388 GDHC01020427 JAG03695.1 JAG03696.1 JAG54436.1 JAP98201.1 GECZ01005958 JAS63811.1 GAMT01001463 GAMT01001462 GAMS01002450 GAMR01007290 GAMQ01003838 GAMP01007994 JAB10398.1 JAB20686.1 JAB26642.1 JAB38013.1 JAB44761.1 KK852528 KDR21984.1 NDHI03003449 PNJ47587.1 CABD030077714 CABD030077715 CABD030077716 CABD030077717 ADFV01112683 ADFV01112684 ADFV01112685 ADFV01112686 ADFV01112687 ADFV01112688 AQIB01085129 AQIB01085130 AQIB01085131 AQIB01085132 AJFE02062316 AJFE02062317 AJFE02062318 AJFE02062319 AJFE02062320 AJFE02062321 AHZZ02006885 AHZZ02006886 AHZZ02006887 AHZZ02006888 AQIA01020876 CM001289 EHH56403.1 JSUE03012634 JSUE03012635 CM001266 EHH23052.1 AACZ04016563 GABC01010505 GABF01004794 GABD01003086 NBAG03000219 JAA00833.1 JAA17351.1 JAA30014.1 PNI79014.1 U82130 BC002487 JU336180 JU477035 AFE79933.1 AFH33839.1 GECU01004056 JAT03651.1 GABE01005673 JAA39066.1 JV048128 AFI38199.1
Proteomes
UP000218220
UP000037510
UP000053240
UP000053268
UP000005204
UP000242457
+ More
UP000235965 UP000005203 UP000007151 UP000053097 UP000279307 UP000075809 UP000078492 UP000078541 UP000000311 UP000053825 UP000078540 UP000075883 UP000078542 UP000092445 UP000078200 UP000091820 UP000009192 UP000075886 UP000053105 UP000008792 UP000075920 UP000092553 UP000268350 UP000075884 UP000075881 UP000008711 UP000075882 UP000075840 UP000007062 UP000075880 UP000075901 UP000075902 UP000183832 UP000008744 UP000008820 UP000002320 UP000076407 UP000075903 UP000095301 UP000069940 UP000249989 UP000095300 UP000007266 UP000007801 UP000075900 UP000076408 UP000215335 UP000069272 UP000233020 UP000233040 UP000008225 UP000027135 UP000233220 UP000233120 UP000001519 UP000001073 UP000233140 UP000029965 UP000240080 UP000028761 UP000233200 UP000009130 UP000233100 UP000006718 UP000002277 UP000005640 UP000233080 UP000002281
UP000235965 UP000005203 UP000007151 UP000053097 UP000279307 UP000075809 UP000078492 UP000078541 UP000000311 UP000053825 UP000078540 UP000075883 UP000078542 UP000092445 UP000078200 UP000091820 UP000009192 UP000075886 UP000053105 UP000008792 UP000075920 UP000092553 UP000268350 UP000075884 UP000075881 UP000008711 UP000075882 UP000075840 UP000007062 UP000075880 UP000075901 UP000075902 UP000183832 UP000008744 UP000008820 UP000002320 UP000076407 UP000075903 UP000095301 UP000069940 UP000249989 UP000095300 UP000007266 UP000007801 UP000075900 UP000076408 UP000215335 UP000069272 UP000233020 UP000233040 UP000008225 UP000027135 UP000233220 UP000233120 UP000001519 UP000001073 UP000233140 UP000029965 UP000240080 UP000028761 UP000233200 UP000009130 UP000233100 UP000006718 UP000002277 UP000005640 UP000233080 UP000002281
Interpro
Gene 3D
ProteinModelPortal
A0A2A4JPS1
A0A1E1WLK1
A0A1V0JHU5
A0A0L7LM77
A0A194R3P8
A0A194QCS8
+ More
H9J3P9 V9IJQ0 A0A2A3E0U5 A0A2J7RDC7 A0A088A8G9 A0A212FP45 A0A026WXG7 A0A151X6V4 V5IA93 A0A195EGD8 A0A1L8EDD6 A0A195FF75 E2AZS6 U5EZQ5 D3TNE1 A0A0L7QSC2 A0A034WB09 A0A195AWK8 A0A182MA76 W8CB77 A0A195CCW6 A0A1A9ZU67 A0A1A9V3W5 A0A1A9W4A6 B4KZ07 A0A182Q067 A0A0K8WKT9 A0A0M9A6L5 B4LE79 A0A182WKR6 A0A0M4F1U6 A0A1Q3FE78 A0A3B0KNR9 W8C786 A0A182NIP5 A0A182JNM1 B3NDH1 A0A1C7CZF1 A0A1Y9GL68 Q7Q6B6 A0A1Y1K7W7 A0A182JGT1 A0A182S6Z9 A0A182THL7 A0A1J1I6S8 B4H4C4 Q16LW0 A0A1S4FWC1 B0WII4 A0A182X6Z6 A0A182VKZ5 A0A1I8M8H1 A0A023ERB3 A0A182G9Q0 A0A1I8PKF7 A0A182GPL4 A0A310SS95 D6WIH5 A0A1B6CLS7 B3M4D5 A0A182RZR1 A0A0A1XCQ7 A0A182YD34 A0A232EJM5 A0A182FCA5 A0A1B6LBT4 A0A336KYH5 A0A336L0Q4 A0A0A9WFR4 A0A1B6GN30 A0A2K5C4J4 A0A2K5S838 F6YJ85 A0A067RQG0 A0A2K6UNI7 A0A2J8UQP2 A0A2K6DP04 G3R4B1 G1S7V5 A0A2K5ZAD9 A0A0D9QYD5 A0A2R9AQ37 A0A2I3N4L1 A0A2K6NCD4 G7PQL3 G7NDS4 A0A2I3SDN5 Q99816 A0A2K5I652 H9FZ74 A0A1B6JWT1 K7C918 F6ZA94 I0FUS3
H9J3P9 V9IJQ0 A0A2A3E0U5 A0A2J7RDC7 A0A088A8G9 A0A212FP45 A0A026WXG7 A0A151X6V4 V5IA93 A0A195EGD8 A0A1L8EDD6 A0A195FF75 E2AZS6 U5EZQ5 D3TNE1 A0A0L7QSC2 A0A034WB09 A0A195AWK8 A0A182MA76 W8CB77 A0A195CCW6 A0A1A9ZU67 A0A1A9V3W5 A0A1A9W4A6 B4KZ07 A0A182Q067 A0A0K8WKT9 A0A0M9A6L5 B4LE79 A0A182WKR6 A0A0M4F1U6 A0A1Q3FE78 A0A3B0KNR9 W8C786 A0A182NIP5 A0A182JNM1 B3NDH1 A0A1C7CZF1 A0A1Y9GL68 Q7Q6B6 A0A1Y1K7W7 A0A182JGT1 A0A182S6Z9 A0A182THL7 A0A1J1I6S8 B4H4C4 Q16LW0 A0A1S4FWC1 B0WII4 A0A182X6Z6 A0A182VKZ5 A0A1I8M8H1 A0A023ERB3 A0A182G9Q0 A0A1I8PKF7 A0A182GPL4 A0A310SS95 D6WIH5 A0A1B6CLS7 B3M4D5 A0A182RZR1 A0A0A1XCQ7 A0A182YD34 A0A232EJM5 A0A182FCA5 A0A1B6LBT4 A0A336KYH5 A0A336L0Q4 A0A0A9WFR4 A0A1B6GN30 A0A2K5C4J4 A0A2K5S838 F6YJ85 A0A067RQG0 A0A2K6UNI7 A0A2J8UQP2 A0A2K6DP04 G3R4B1 G1S7V5 A0A2K5ZAD9 A0A0D9QYD5 A0A2R9AQ37 A0A2I3N4L1 A0A2K6NCD4 G7PQL3 G7NDS4 A0A2I3SDN5 Q99816 A0A2K5I652 H9FZ74 A0A1B6JWT1 K7C918 F6ZA94 I0FUS3
PDB
4YC1
E-value=1.59341e-47,
Score=478
Ontologies
GO
GO:0015031
GO:0006464
GO:0006487
GO:0034998
GO:0016021
GO:0036258
GO:0035090
GO:0016322
GO:0000813
GO:0044130
GO:0045571
GO:0005886
GO:1903551
GO:0044877
GO:2000397
GO:0070062
GO:0003714
GO:0030216
GO:0007175
GO:0008285
GO:0043162
GO:0005770
GO:0006858
GO:0042803
GO:0045892
GO:1990182
GO:0005829
GO:0046755
GO:0001558
GO:1903774
GO:0043405
GO:0046790
GO:0043130
GO:1902188
GO:0007050
GO:0031625
GO:0005769
GO:0048306
GO:0005730
GO:1903543
GO:0005737
GO:0042059
GO:0016236
GO:0005815
GO:0090543
GO:0005768
GO:0003677
GO:0030374
GO:0005771
GO:0010008
GO:0097352
GO:0019058
GO:0031901
GO:0008333
GO:0039702
GO:0051301
GO:0016197
GO:0075733
GO:0031902
GO:0043657
GO:0006513
GO:0006412
GO:0007264
GO:0006468
GO:0006811
GO:0016020
GO:0043564
GO:0006418
GO:0003824
Topology
Subcellular location
Cytoplasm
Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
Early endosome membrane Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
Late endosome membrane Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
Cytoskeleton Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
Microtubule organizing center Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
Centrosome Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
Midbody Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
Midbody ring Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
Nucleus Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
Early endosome membrane Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
Late endosome membrane Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
Cytoskeleton Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
Microtubule organizing center Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
Centrosome Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
Midbody Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
Midbody ring Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
Nucleus Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. With evidence from 34 publications.
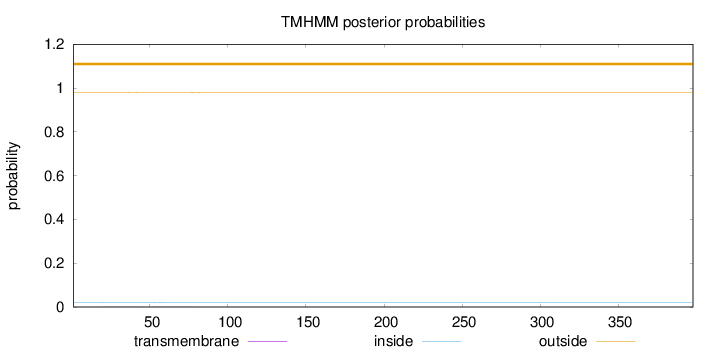
Length:
398
Number of predicted TMHs:
0
Exp number of AAs in TMHs:
0.03198
Exp number, first 60 AAs:
0.01388
Total prob of N-in:
0.02095
outside
1 - 398
Population Genetic Test Statistics
Pi
192.983239
Theta
221.566371
Tajima's D
-0.354765
CLR
1.395168
CSRT
0.27763611819409
Interpretation
Uncertain
