Gene
KWMTBOMO11653
Pre Gene Modal
BGIBMGA003995
Annotation
PREDICTED:_centromere_protein_X-like_[Amyelois_transitella]
Full name
Centromere protein X
Alternative Name
FANCM-interacting histone fold protein 2
Fanconi anemia-associated polypeptide of 10 kDa
Stimulated by retinoic acid gene 13 protein homolog
FANCM-associated histone fold protein 2
Retinoic acid-inducible gene D9 protein homolog
Immediate-early-response protein D9
Retinoic acid-inducible gene D9 protein
Fanconi anemia-associated polypeptide of 10 kDa
Stimulated by retinoic acid gene 13 protein homolog
FANCM-associated histone fold protein 2
Retinoic acid-inducible gene D9 protein homolog
Immediate-early-response protein D9
Retinoic acid-inducible gene D9 protein
Location in the cell
Cytoplasmic Reliability : 1.395 Extracellular Reliability : 1.627 Mitochondrial Reliability : 1.065
Sequence
CDS
ATGGCCCGCAATATTAAGGACAATAATAATATTGATCCGGCTACTTTATTGTCTAATGTGAAAAGTACAATTAAAAAGGATGTAATAAAGGAACTATTAGAAAACCACTTCCAAGAAAGTAAAACCAAGATTGCCCCACATGCTCTTATGTTGTTGGCAGATGTGGCCAAATGTCTGGTCACCGAGACATGCCTGCGTGCAGTCAAACAAGCACAGAGAGAGGGTTCTAACAAAGTTGATGTAGAACATATTGAGAAATGTTTACCCCAGCTGATGCTGGACTTCCCTTAA
Protein
MARNIKDNNNIDPATLLSNVKSTIKKDVIKELLENHFQESKTKIAPHALMLLADVAKCLVTETCLRAVKQAQREGSNKVDVEHIEKCLPQLMLDFP
Summary
Description
DNA-binding component of the Fanconi anemia (FA) core complex. Required for the normal activation of the FA pathway, leading to monoubiquitination of the FANCI-FANCD2 complex in response to DNA damage, cellular resistance to DNA cross-linking drugs, and prevention of chromosomal breakage. In complex with CENPS (MHF heterodimer), crucial cofactor for FANCM in both binding and ATP-dependent remodeling of DNA. Stabilizes FANCM. In complex with CENPS and FANCM (but not other FANC proteins), rapidly recruited to blocked forks and promotes gene conversion at blocked replication forks. In complex with CENPS, CENPT and CENPW (CENP-T-W-S-X heterotetramer), involved in the formation of a functional kinetochore outer plate, which is essential for kinetochore-microtubule attachment and faithful mitotic progression. As a component of MHF and CENP-T-W-S-X complexes, binds DNA and bends it to form a nucleosome-like structure. DNA-binding function is fulfilled in the presence of CENPS, with the following preference for DNA substates: Holliday junction > double-stranded > splay arm > single-stranded. Does not bind DNA on its own.
DNA-binding component of the Fanconi anemia (FA) core complex. Required for the normal activation of the FA pathway, leading to monoubiquitination of the FANCI-FANCD2 complex in response to DNA damage, cellular resistance to DNA cross-linking drugs, and prevention of chromosomal breakage (PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429). In complex with CENPS (MHF heterodimer), crucial cofactor for FANCM in both binding and ATP-dependent remodeling of DNA. Stabilizes FANCM. In complex with CENPS and FANCM (but not other FANC proteins), rapidly recruited to blocked forks and promotes gene conversion at blocked replication forks (PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429). In complex with CENPS, CENPT and CENPW (CENP-T-W-S-X heterotetramer), involved in the formation of a functional kinetochore outer plate, which is essential for kinetochore-microtubule attachment and faithful mitotic progression (PubMed:19620631). As a component of MHF and CENP-T-W-S-X complexes, binds DNA and bends it to form a nucleosome-like structure (PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429). DNA-binding function is fulfilled in the presence of CENPS, with the following preference for DNA substates: Holliday junction > double-stranded > splay arm > single-stranded. Does not bind DNA on its own (PubMed:20347429).
DNA-binding component of the Fanconi anemia (FA) core complex. Required for the normal activation of the FA pathway, leading to monoubiquitination of the FANCI-FANCD2 complex in response to DNA damage, cellular resistance to DNA cross-linking drugs, and prevention of chromosomal breakage (PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429). In complex with CENPS (MHF heterodimer), crucial cofactor for FANCM in both binding and ATP-dependent remodeling of DNA. Stabilizes FANCM. In complex with CENPS and FANCM (but not other FANC proteins), rapidly recruited to blocked forks and promotes gene conversion at blocked replication forks (PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429). In complex with CENPS, CENPT and CENPW (CENP-T-W-S-X heterotetramer), involved in the formation of a functional kinetochore outer plate, which is essential for kinetochore-microtubule attachment and faithful mitotic progression (PubMed:19620631). As a component of MHF and CENP-T-W-S-X complexes, binds DNA and bends it to form a nucleosome-like structure (PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429). DNA-binding function is fulfilled in the presence of CENPS, with the following preference for DNA substates: Holliday junction > double-stranded > splay arm > single-stranded. Does not bind DNA on its own (PubMed:20347429).
Subunit
Heterodimer with CENPX, sometimes called MHF; this interaction stabilizes both partners. MHF heterodimers can assemble to form tetrameric structures. MHF also coassemble with CENPT-CENPW heterodimers at centromeres to form the tetrameric CENP-T-W-S-X complex. Forms a discrete complex with FANCM and CENPX, called FANCM-MHF; this interaction, probably mediated by direct binding between CENPS and FANCM, leads to synergistic activation of double-stranded DNA binding and strongly stimulates FANCM-mediated DNA remodeling. Recruited by FANCM to the Fanconi anemia (FA) core complex, which consists of CENPS, CENPX, FANCA, FANCB, FANCC, FANCE, FANCF, FANCG, FANCL, FANCM, FAAP24 and FAAP100. The FA core complex associates with Bloom syndrome (BLM) complex, which consists of at least BLM, DNA topoisomerase 3-alpha (TOP3A), RMI1/BLAP75, RPA1/RPA70 and RPA2/RPA32. The super complex between FA and BLM is called BRAFT.
Heterodimer with CENPX, sometimes called MHF; this interaction stabilizes both partners (PubMed:19620631, PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429, PubMed:24522885). MHF heterodimers can assemble to form tetrameric structures (PubMed:22304917). MHF also coassemble with CENPT-CENPW heterodimers at centromeres to form the tetrameric CENP-T-W-S-X complex (PubMed:22304917, PubMed:24522885). Forms a discrete complex with FANCM and CENPX, called FANCM-MHF; this interaction, probably mediated by direct binding between CENPS and FANCM, leads to synergistic activation of double-stranded DNA binding and strongly stimulates FANCM-mediated DNA remodeling (PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429). Recruited by FANCM to the Fanconi anemia (FA) core complex, which consists of CENPS, CENPX, FANCA, FANCB, FANCC, FANCE, FANCF, FANCG, FANCL, FANCM, FAAP24 and FAAP100. The FA core complex associates with Bloom syndrome (BLM) complex, which consists of at least BLM, DNA topoisomerase 3-alpha (TOP3A), RMI1/BLAP75, RPA1/RPA70 and RPA2/RPA32. The super complex between FA and BLM is called BRAFT (PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429).
Heterodimer with CENPX, sometimes called MHF; this interaction stabilizes both partners (PubMed:19620631, PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429, PubMed:24522885). MHF heterodimers can assemble to form tetrameric structures (PubMed:22304917). MHF also coassemble with CENPT-CENPW heterodimers at centromeres to form the tetrameric CENP-T-W-S-X complex (PubMed:22304917, PubMed:24522885). Forms a discrete complex with FANCM and CENPX, called FANCM-MHF; this interaction, probably mediated by direct binding between CENPS and FANCM, leads to synergistic activation of double-stranded DNA binding and strongly stimulates FANCM-mediated DNA remodeling (PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429). Recruited by FANCM to the Fanconi anemia (FA) core complex, which consists of CENPS, CENPX, FANCA, FANCB, FANCC, FANCE, FANCF, FANCG, FANCL, FANCM, FAAP24 and FAAP100. The FA core complex associates with Bloom syndrome (BLM) complex, which consists of at least BLM, DNA topoisomerase 3-alpha (TOP3A), RMI1/BLAP75, RPA1/RPA70 and RPA2/RPA32. The super complex between FA and BLM is called BRAFT (PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429).
Similarity
Belongs to the CENP-X/MHF2 family.
Keywords
Acetylation
Cell cycle
Cell division
Centromere
Chromosome
Complete proteome
DNA damage
DNA repair
DNA-binding
Kinetochore
Mitosis
Nucleus
Reference proteome
3D-structure
Alternative splicing
Feature
chain Centromere protein X
splice variant In isoform 2 and isoform 3.
splice variant In isoform 2 and isoform 3.
Uniprot
A0A060N0C9
A0A2A4JHR6
H9J3A8
A0A212F870
S4P445
A0A2J7QK80
+ More
Q2NKU0 A0A0D9S4S4 W5Q881 A0A1D1VQZ4 A0A3Q7UHI1 I3JCS9 A0A340XLY1 A0A341CPN6 A0A2Y9PNX9 A0A2Y9FKP2 A0A3Q3KD95 R4G9G6 A0A1A8HNJ8 A0A067QR41 A0A287DE05 A0A3P8R7H4 A0A3P9C5J7 A8MT69 A0A1S3S1T3 A0A2K6DKQ6 A0A212DAV1 A0A2J8JFR3 A0A2J8XZ79 Q5RBU1 A0A2K6U1S0 A0A1U7T2J8 A0A3Q4B8H2 A0A2K5Q201 A0A3Q7PIL0 A0A3P9HNS5 A0A3B3I5Y3 A0A337SG66 U3FD76 A0A2Y9LCL7 A0A091DXE8 A0A1A8CQV2 A0A1A8U3D1 A0A1A8A7R0 A0A1A8DDK5 A0A3Q7SHD5 A0A1A8K5L7 A0A3B5K538 A0A2K5W525 A0A146NN91 A0A2U3W8F7 A0A1S3WD60 A0A3B3D9J4 A0A3P9A2B8 A0A2Y9QU33 G1MG80 A0A3Q3AC05 A0A1S3GI75 A0A2P8XP01 A0A3B4UD40 A0A286XDM1 A0A384CCA1 L9KZ08 A0A2I4BCN2 A0A2U3YHH6 G3PAR2 A0A2K6G5D4 A0A1D5Q7B4 A0A3Q3D548 A0A1A8NWX3 G3PAR4 A0A1A8Q954 A0A1A8HKN1 A0A1A8SHQ2 A0A1A8F4Q2 A0A3Q7S8C2 H3CWL8 A0A2Y9GBP2 A0A3B1ISB1 A0A3Q1B6X9 A0A2Y9PIA1 A0A341CPG4 E7F1X6 A0A1A7XLG7 N6U9D1 A0A194QY70 A0A3B3YPI9 A0A2Y9FKH4 A0A2U9CS22 V5I4P8 Q8C4X1 A0A194QCH9 A0A384AFC6 A0A2R8MZB2 A0A3Q3NAA2 A0A3B4D0T2 L8I194 A0A061I3E9 A0A1A7YSF1
Q2NKU0 A0A0D9S4S4 W5Q881 A0A1D1VQZ4 A0A3Q7UHI1 I3JCS9 A0A340XLY1 A0A341CPN6 A0A2Y9PNX9 A0A2Y9FKP2 A0A3Q3KD95 R4G9G6 A0A1A8HNJ8 A0A067QR41 A0A287DE05 A0A3P8R7H4 A0A3P9C5J7 A8MT69 A0A1S3S1T3 A0A2K6DKQ6 A0A212DAV1 A0A2J8JFR3 A0A2J8XZ79 Q5RBU1 A0A2K6U1S0 A0A1U7T2J8 A0A3Q4B8H2 A0A2K5Q201 A0A3Q7PIL0 A0A3P9HNS5 A0A3B3I5Y3 A0A337SG66 U3FD76 A0A2Y9LCL7 A0A091DXE8 A0A1A8CQV2 A0A1A8U3D1 A0A1A8A7R0 A0A1A8DDK5 A0A3Q7SHD5 A0A1A8K5L7 A0A3B5K538 A0A2K5W525 A0A146NN91 A0A2U3W8F7 A0A1S3WD60 A0A3B3D9J4 A0A3P9A2B8 A0A2Y9QU33 G1MG80 A0A3Q3AC05 A0A1S3GI75 A0A2P8XP01 A0A3B4UD40 A0A286XDM1 A0A384CCA1 L9KZ08 A0A2I4BCN2 A0A2U3YHH6 G3PAR2 A0A2K6G5D4 A0A1D5Q7B4 A0A3Q3D548 A0A1A8NWX3 G3PAR4 A0A1A8Q954 A0A1A8HKN1 A0A1A8SHQ2 A0A1A8F4Q2 A0A3Q7S8C2 H3CWL8 A0A2Y9GBP2 A0A3B1ISB1 A0A3Q1B6X9 A0A2Y9PIA1 A0A341CPG4 E7F1X6 A0A1A7XLG7 N6U9D1 A0A194QY70 A0A3B3YPI9 A0A2Y9FKH4 A0A2U9CS22 V5I4P8 Q8C4X1 A0A194QCH9 A0A384AFC6 A0A2R8MZB2 A0A3Q3NAA2 A0A3B4D0T2 L8I194 A0A061I3E9 A0A1A7YSF1
Pubmed
24286570
19121390
22118469
23622113
20809919
27649274
+ More
25186727 24845553 16625196 15489334 19620631 20347428 20347429 22304917 22814378 24522885 17554307 17975172 25243066 21551351 29451363 25069045 20010809 29403074 21993624 23385571 17431167 15496914 25329095 23594743 23537049 26354079 25765539 8839844 16141072 19468303 22751099 23929341
25186727 24845553 16625196 15489334 19620631 20347428 20347429 22304917 22814378 24522885 17554307 17975172 25243066 21551351 29451363 25069045 20010809 29403074 21993624 23385571 17431167 15496914 25329095 23594743 23537049 26354079 25765539 8839844 16141072 19468303 22751099 23929341
EMBL
AB766233
BAN29074.1
NWSH01001413
PCG71316.1
BABH01021684
BABH01021685
+ More
BABH01021686 AGBW02009781 OWR49930.1 GAIX01006169 JAA86391.1 NEVH01013275 PNF28991.1 BC111642 AQIB01145127 AMGL01019053 BDGG01000008 GAV02613.1 AERX01023620 HAED01000100 SBQ85945.1 KK853060 KDR11906.1 AGTP01070805 U95006 U95007 AC137723 BC009571 BC011610 MKHE01000005 OWK15379.1 NBAG03000462 PNI21615.1 NDHI03003285 PNJ87331.1 CR858542 AANG04004184 GAMT01004525 GAMR01010676 GAMQ01007701 GAMP01002097 JAB07336.1 JAB23256.1 JAB34150.1 JAB50658.1 KN121670 KFO35722.1 HADZ01018203 SBP82144.1 HAEJ01001156 SBS41613.1 HADY01012629 SBP51114.1 HAEA01002514 SBQ30994.1 HAEE01006934 SBR26954.1 AQIA01029018 GCES01153822 JAQ32500.1 ACTA01112152 PYGN01001624 PSN33705.1 AAKN02047352 KB320577 ELW68190.1 JSUE03017652 HAEG01005132 SBR73364.1 HAEH01010665 SBR90295.1 HAEC01014998 SBQ83215.1 HAEI01014979 SBS17448.1 HAEB01006557 SBQ53084.1 CU571328 HADW01017438 SBP18838.1 APGK01035370 KB740923 KB632333 ENN78300.1 ERL92727.1 KQ460949 KPJ10488.1 CP026261 AWP18973.1 GANP01001065 JAB83403.1 U95003 U95004 U95005 AK076181 AK080500 AK170126 AL663030 KQ459185 KPJ03248.1 JH882459 ELR49319.1 KE682086 ERE67860.1 HADX01010894 SBP33126.1
BABH01021686 AGBW02009781 OWR49930.1 GAIX01006169 JAA86391.1 NEVH01013275 PNF28991.1 BC111642 AQIB01145127 AMGL01019053 BDGG01000008 GAV02613.1 AERX01023620 HAED01000100 SBQ85945.1 KK853060 KDR11906.1 AGTP01070805 U95006 U95007 AC137723 BC009571 BC011610 MKHE01000005 OWK15379.1 NBAG03000462 PNI21615.1 NDHI03003285 PNJ87331.1 CR858542 AANG04004184 GAMT01004525 GAMR01010676 GAMQ01007701 GAMP01002097 JAB07336.1 JAB23256.1 JAB34150.1 JAB50658.1 KN121670 KFO35722.1 HADZ01018203 SBP82144.1 HAEJ01001156 SBS41613.1 HADY01012629 SBP51114.1 HAEA01002514 SBQ30994.1 HAEE01006934 SBR26954.1 AQIA01029018 GCES01153822 JAQ32500.1 ACTA01112152 PYGN01001624 PSN33705.1 AAKN02047352 KB320577 ELW68190.1 JSUE03017652 HAEG01005132 SBR73364.1 HAEH01010665 SBR90295.1 HAEC01014998 SBQ83215.1 HAEI01014979 SBS17448.1 HAEB01006557 SBQ53084.1 CU571328 HADW01017438 SBP18838.1 APGK01035370 KB740923 KB632333 ENN78300.1 ERL92727.1 KQ460949 KPJ10488.1 CP026261 AWP18973.1 GANP01001065 JAB83403.1 U95003 U95004 U95005 AK076181 AK080500 AK170126 AL663030 KQ459185 KPJ03248.1 JH882459 ELR49319.1 KE682086 ERE67860.1 HADX01010894 SBP33126.1
Proteomes
UP000218220
UP000005204
UP000007151
UP000235965
UP000009136
UP000029965
+ More
UP000002356 UP000186922 UP000286642 UP000005207 UP000265300 UP000252040 UP000248483 UP000248484 UP000261600 UP000001646 UP000027135 UP000005215 UP000265100 UP000265160 UP000005640 UP000087266 UP000233120 UP000001595 UP000233220 UP000189704 UP000261620 UP000233040 UP000286641 UP000265200 UP000001038 UP000011712 UP000008225 UP000248482 UP000028990 UP000286640 UP000005226 UP000233100 UP000245340 UP000079721 UP000261560 UP000265140 UP000248480 UP000008912 UP000264800 UP000081671 UP000245037 UP000261420 UP000005447 UP000261680 UP000011518 UP000192220 UP000245341 UP000007635 UP000233160 UP000006718 UP000264820 UP000007303 UP000248481 UP000018467 UP000257160 UP000000437 UP000019118 UP000030742 UP000053240 UP000261480 UP000246464 UP000000589 UP000053268 UP000261660 UP000261440 UP000030759
UP000002356 UP000186922 UP000286642 UP000005207 UP000265300 UP000252040 UP000248483 UP000248484 UP000261600 UP000001646 UP000027135 UP000005215 UP000265100 UP000265160 UP000005640 UP000087266 UP000233120 UP000001595 UP000233220 UP000189704 UP000261620 UP000233040 UP000286641 UP000265200 UP000001038 UP000011712 UP000008225 UP000248482 UP000028990 UP000286640 UP000005226 UP000233100 UP000245340 UP000079721 UP000261560 UP000265140 UP000248480 UP000008912 UP000264800 UP000081671 UP000245037 UP000261420 UP000005447 UP000261680 UP000011518 UP000192220 UP000245341 UP000007635 UP000233160 UP000006718 UP000264820 UP000007303 UP000248481 UP000018467 UP000257160 UP000000437 UP000019118 UP000030742 UP000053240 UP000261480 UP000246464 UP000000589 UP000053268 UP000261660 UP000261440 UP000030759
Pfam
PF09415 CENP-X
SUPFAM
SSF47113
SSF47113
ProteinModelPortal
A0A060N0C9
A0A2A4JHR6
H9J3A8
A0A212F870
S4P445
A0A2J7QK80
+ More
Q2NKU0 A0A0D9S4S4 W5Q881 A0A1D1VQZ4 A0A3Q7UHI1 I3JCS9 A0A340XLY1 A0A341CPN6 A0A2Y9PNX9 A0A2Y9FKP2 A0A3Q3KD95 R4G9G6 A0A1A8HNJ8 A0A067QR41 A0A287DE05 A0A3P8R7H4 A0A3P9C5J7 A8MT69 A0A1S3S1T3 A0A2K6DKQ6 A0A212DAV1 A0A2J8JFR3 A0A2J8XZ79 Q5RBU1 A0A2K6U1S0 A0A1U7T2J8 A0A3Q4B8H2 A0A2K5Q201 A0A3Q7PIL0 A0A3P9HNS5 A0A3B3I5Y3 A0A337SG66 U3FD76 A0A2Y9LCL7 A0A091DXE8 A0A1A8CQV2 A0A1A8U3D1 A0A1A8A7R0 A0A1A8DDK5 A0A3Q7SHD5 A0A1A8K5L7 A0A3B5K538 A0A2K5W525 A0A146NN91 A0A2U3W8F7 A0A1S3WD60 A0A3B3D9J4 A0A3P9A2B8 A0A2Y9QU33 G1MG80 A0A3Q3AC05 A0A1S3GI75 A0A2P8XP01 A0A3B4UD40 A0A286XDM1 A0A384CCA1 L9KZ08 A0A2I4BCN2 A0A2U3YHH6 G3PAR2 A0A2K6G5D4 A0A1D5Q7B4 A0A3Q3D548 A0A1A8NWX3 G3PAR4 A0A1A8Q954 A0A1A8HKN1 A0A1A8SHQ2 A0A1A8F4Q2 A0A3Q7S8C2 H3CWL8 A0A2Y9GBP2 A0A3B1ISB1 A0A3Q1B6X9 A0A2Y9PIA1 A0A341CPG4 E7F1X6 A0A1A7XLG7 N6U9D1 A0A194QY70 A0A3B3YPI9 A0A2Y9FKH4 A0A2U9CS22 V5I4P8 Q8C4X1 A0A194QCH9 A0A384AFC6 A0A2R8MZB2 A0A3Q3NAA2 A0A3B4D0T2 L8I194 A0A061I3E9 A0A1A7YSF1
Q2NKU0 A0A0D9S4S4 W5Q881 A0A1D1VQZ4 A0A3Q7UHI1 I3JCS9 A0A340XLY1 A0A341CPN6 A0A2Y9PNX9 A0A2Y9FKP2 A0A3Q3KD95 R4G9G6 A0A1A8HNJ8 A0A067QR41 A0A287DE05 A0A3P8R7H4 A0A3P9C5J7 A8MT69 A0A1S3S1T3 A0A2K6DKQ6 A0A212DAV1 A0A2J8JFR3 A0A2J8XZ79 Q5RBU1 A0A2K6U1S0 A0A1U7T2J8 A0A3Q4B8H2 A0A2K5Q201 A0A3Q7PIL0 A0A3P9HNS5 A0A3B3I5Y3 A0A337SG66 U3FD76 A0A2Y9LCL7 A0A091DXE8 A0A1A8CQV2 A0A1A8U3D1 A0A1A8A7R0 A0A1A8DDK5 A0A3Q7SHD5 A0A1A8K5L7 A0A3B5K538 A0A2K5W525 A0A146NN91 A0A2U3W8F7 A0A1S3WD60 A0A3B3D9J4 A0A3P9A2B8 A0A2Y9QU33 G1MG80 A0A3Q3AC05 A0A1S3GI75 A0A2P8XP01 A0A3B4UD40 A0A286XDM1 A0A384CCA1 L9KZ08 A0A2I4BCN2 A0A2U3YHH6 G3PAR2 A0A2K6G5D4 A0A1D5Q7B4 A0A3Q3D548 A0A1A8NWX3 G3PAR4 A0A1A8Q954 A0A1A8HKN1 A0A1A8SHQ2 A0A1A8F4Q2 A0A3Q7S8C2 H3CWL8 A0A2Y9GBP2 A0A3B1ISB1 A0A3Q1B6X9 A0A2Y9PIA1 A0A341CPG4 E7F1X6 A0A1A7XLG7 N6U9D1 A0A194QY70 A0A3B3YPI9 A0A2Y9FKH4 A0A2U9CS22 V5I4P8 Q8C4X1 A0A194QCH9 A0A384AFC6 A0A2R8MZB2 A0A3Q3NAA2 A0A3B4D0T2 L8I194 A0A061I3E9 A0A1A7YSF1
PDB
4E45
E-value=6.41735e-13,
Score=172
Ontologies
GO
PANTHER
Topology
Subcellular location
Nucleus
Assembly of CENPS and CENPX and its partner subunits CENPT and CENPW at centromeres occurs through a dynamic exchange mechanism. Although exchange is continuous in the cell cycle, de novo assembly starts principally during mid-late S phase and is complete by G2. CENPX being less stably bound at the kinetochore than CENPS. With evidence from 1 publications.
Chromosome Assembly of CENPS and CENPX and its partner subunits CENPT and CENPW at centromeres occurs through a dynamic exchange mechanism. Although exchange is continuous in the cell cycle, de novo assembly starts principally during mid-late S phase and is complete by G2. CENPX being less stably bound at the kinetochore than CENPS. With evidence from 1 publications.
Centromere Assembly of CENPS and CENPX and its partner subunits CENPT and CENPW at centromeres occurs through a dynamic exchange mechanism. Although exchange is continuous in the cell cycle, de novo assembly starts principally during mid-late S phase and is complete by G2. CENPX being less stably bound at the kinetochore than CENPS. With evidence from 1 publications.
Kinetochore Assembly of CENPS and CENPX and its partner subunits CENPT and CENPW at centromeres occurs through a dynamic exchange mechanism. Although exchange is continuous in the cell cycle, de novo assembly starts principally during mid-late S phase and is complete by G2. CENPX being less stably bound at the kinetochore than CENPS. With evidence from 1 publications.
Chromosome Assembly of CENPS and CENPX and its partner subunits CENPT and CENPW at centromeres occurs through a dynamic exchange mechanism. Although exchange is continuous in the cell cycle, de novo assembly starts principally during mid-late S phase and is complete by G2. CENPX being less stably bound at the kinetochore than CENPS. With evidence from 1 publications.
Centromere Assembly of CENPS and CENPX and its partner subunits CENPT and CENPW at centromeres occurs through a dynamic exchange mechanism. Although exchange is continuous in the cell cycle, de novo assembly starts principally during mid-late S phase and is complete by G2. CENPX being less stably bound at the kinetochore than CENPS. With evidence from 1 publications.
Kinetochore Assembly of CENPS and CENPX and its partner subunits CENPT and CENPW at centromeres occurs through a dynamic exchange mechanism. Although exchange is continuous in the cell cycle, de novo assembly starts principally during mid-late S phase and is complete by G2. CENPX being less stably bound at the kinetochore than CENPS. With evidence from 1 publications.
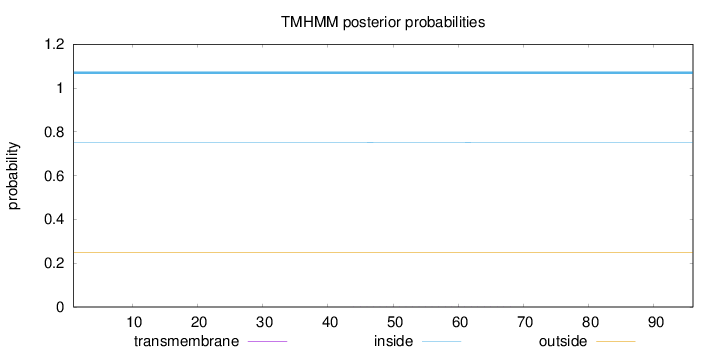
Length:
96
Number of predicted TMHs:
0
Exp number of AAs in TMHs:
0.00943
Exp number, first 60 AAs:
0.0072
Total prob of N-in:
0.75218
inside
1 - 96
Population Genetic Test Statistics
Pi
280.525274
Theta
202.028499
Tajima's D
1.321692
CLR
0
CSRT
0.744512774361282
Interpretation
Uncertain
