Pre Gene Modal
BGIBMGA009473
Annotation
PREDICTED:_apoptosis-inducing_factor_1?_mitochondrial-like_[Bombyx_mori]
Full name
Apoptosis-inducing factor 1, mitochondrial
Alternative Name
Programmed cell death protein 8
Location in the cell
Cytoplasmic Reliability : 1.791
Sequence
CDS
ATGCTGGGCACCGCGCCCGCGCCCTACACGCACCCGCACATGTTCTGGACCGACCTCGGGCCCGACCTCGGATACGAGGCCATCGGCACCATCGACTCAAAACTAAAGACCGTCGGAGTGTTCTCTGAGGACGCCGTCACGGAGCTCCGGGCCCACGCCGCCGCCGCCGGGGAGGGGGACGCGGGGGGGCCGGGGGAGGGCGCGGCCGGGGCGGCGGTGAGGCTGGAGGGGGGCGCGGCGGGGGGCCGGCGGTACGAGCGCGGCGTGGTGTTCTACCTGGAGGGCCGGCGCGTGGTGGGCGTGCTGCTGTGGAACCTCTTCAACCGGATGCACGTGGCCAGGCAGGTGCTGGCGCAGGCGGAGTTCGAGGACCTGTTCGAGGTGGCCAAGCTGTTCGCGCTCCACGAAGACGAATAG
Protein
MLGTAPAPYTHPHMFWTDLGPDLGYEAIGTIDSKLKTVGVFSEDAVTELRAHAAAAGEGDAGGPGEGAAGAAVRLEGGAAGGRRYERGVVFYLEGRRVVGVLLWNLFNRMHVARQVLAQAEFEDLFEVAKLFALHEDE
Summary
Description
Functions both as NADH oxidoreductase and as regulator of apoptosis. In response to apoptotic stimuli, it is released from the mitochondrion intermembrane space into the cytosol and to the nucleus, where it functions as a proapoptotic factor in a caspase-independent pathway. In contrast, functions as an antiapoptotic factor in normal mitochondria via its NADH oxidoreductase activity. The soluble form (AIFsol) found in the nucleus induces 'parthanatos' i.e. caspase-independent fragmentation of chromosomal DNA. Interacts with EIF3G,and thereby inhibits the EIF3 machinery and protein synthesis, and activates casapse-7 to amplify apoptosis. Plays a critical role in caspase-independent, pyknotic cell death in hydrogen peroxide-exposed cells. Binds to DNA in a sequence-independent manner.
Cofactor
FAD
Biophysicochemical Properties
1.53 mM for NADH
26 uM for cytochrome c
26 uM for cytochrome c
Subunit
Monomer (oxidized form). Homodimer (reduced form). Also dimerizes with isoform 3 preventing its release from mitochondria. Interacts with XIAP/BIRC4. Interacts (via N-terminus) with EIF3G (via C-terminus). Interacts with PRELID1.
Similarity
Belongs to the FAD-dependent oxidoreductase family.
Keywords
3D-structure
Acetylation
Alternative splicing
Apoptosis
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
Complete proteome
Cytoplasm
Deafness
Direct protein sequencing
Disease mutation
DNA-binding
FAD
Flavoprotein
Isopeptide bond
Membrane
Mental retardation
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion inner membrane
NAD
Neurodegeneration
Neuropathy
Nucleus
Oxidoreductase
Phosphoprotein
Primary mitochondrial disease
Reference proteome
Transit peptide
Ubl conjugation
Feature
propeptide Removed in mature form
chain Apoptosis-inducing factor 1, mitochondrial
splice variant In isoform 5.
sequence variant In COXPD6; higher DNA binding affinity, partially impaired flavin binding and association with increased parthanatos-linked cell death.
chain Apoptosis-inducing factor 1, mitochondrial
splice variant In isoform 5.
sequence variant In COXPD6; higher DNA binding affinity, partially impaired flavin binding and association with increased parthanatos-linked cell death.
Uniprot
H9JIX2
A0A212FC61
A0A2H1W831
A0A194PZ37
A0A2P2HWW7
A0A0C9QS22
+ More
A0A2U3XUU4 A0A0Q9X3C3 B4KGB9 A0A2D4PTB4 A0A1S3A118 A0A401PLL5 A0A2Y9KMD9 A0A2R9ASH6 O95831-5 A0A140VK04 A0A2Y9KK59 A0A337S4Y7 A0A2U3ZGK2 A0A2I3T1Z5 A0A0E9X1B5 A0A2J8WWS8 E9PMA0 A0A1B6J809 A0A2J8JBB9 A0A2K6QE09 A0A1B6EI32 A0A2K6EP57 O95831-2 A0A2J8WWP9 A0A2I3N3Q0 A0A2K6DRL2 A0A2K5X6R6 F7C728 A0A2K6UVT3 A0A2K5RPH7 A0A2U3VXV0 A0A2J8JBC3 A0A3Q0DXU3 A0A2I3FRD9 A0A2K6UVY6 A0A1B6HC81 A0A2K5EDF8 F7C333 Q2QKE3 A0A2K5RPW3 A0A3B4UMM2 A0A2J7RG21 A0A2K5XDQ2 A0A2K5L4G4 A0A0V0YLQ4 U3KP10 A0A1U8DHQ1 G1SIM3 G1Q8W8 A0A3P9IWE7 A0A401SL88 A0A1B0CTJ1 A0A3B3RGD9 K7J4K5 T1J3Z2 A0A3Q3AM59 A0A0B4KJP5 A0A0B8RTX7 F1RTH3 A0A068CA64 G5B2Q8 A0A3B3RGH1 A0A0N8EUC8 A0A1S3A121 A0A1S3A140 M1EC95 H2ZVB2 H2ZVB3 J3S402 A0A3T0JLN2 A0A1L8DK09 A0A3Q2NRH5 A0A1I8NNT6 G3WTU3 A0A1I8NNT5 G3QAE4 K7FFA3 A0A1L8DJS3 K7FF97 M7BJ62 A0A2K6JYL8 A0A1Y1LHD2 A0A165NNH9 A0A0M8ZRB3 A0A2K5XDM0 A0A2K5L4D7 A0A2K5XDP8 A0A2K5L4B7 A0A2Y9DRB2 A0A1U7QXN0 A0A287D6C8 A0A1U7QM98 I3MBI5
A0A2U3XUU4 A0A0Q9X3C3 B4KGB9 A0A2D4PTB4 A0A1S3A118 A0A401PLL5 A0A2Y9KMD9 A0A2R9ASH6 O95831-5 A0A140VK04 A0A2Y9KK59 A0A337S4Y7 A0A2U3ZGK2 A0A2I3T1Z5 A0A0E9X1B5 A0A2J8WWS8 E9PMA0 A0A1B6J809 A0A2J8JBB9 A0A2K6QE09 A0A1B6EI32 A0A2K6EP57 O95831-2 A0A2J8WWP9 A0A2I3N3Q0 A0A2K6DRL2 A0A2K5X6R6 F7C728 A0A2K6UVT3 A0A2K5RPH7 A0A2U3VXV0 A0A2J8JBC3 A0A3Q0DXU3 A0A2I3FRD9 A0A2K6UVY6 A0A1B6HC81 A0A2K5EDF8 F7C333 Q2QKE3 A0A2K5RPW3 A0A3B4UMM2 A0A2J7RG21 A0A2K5XDQ2 A0A2K5L4G4 A0A0V0YLQ4 U3KP10 A0A1U8DHQ1 G1SIM3 G1Q8W8 A0A3P9IWE7 A0A401SL88 A0A1B0CTJ1 A0A3B3RGD9 K7J4K5 T1J3Z2 A0A3Q3AM59 A0A0B4KJP5 A0A0B8RTX7 F1RTH3 A0A068CA64 G5B2Q8 A0A3B3RGH1 A0A0N8EUC8 A0A1S3A121 A0A1S3A140 M1EC95 H2ZVB2 H2ZVB3 J3S402 A0A3T0JLN2 A0A1L8DK09 A0A3Q2NRH5 A0A1I8NNT6 G3WTU3 A0A1I8NNT5 G3QAE4 K7FFA3 A0A1L8DJS3 K7FF97 M7BJ62 A0A2K6JYL8 A0A1Y1LHD2 A0A165NNH9 A0A0M8ZRB3 A0A2K5XDM0 A0A2K5L4D7 A0A2K5XDP8 A0A2K5L4B7 A0A2Y9DRB2 A0A1U7QXN0 A0A287D6C8 A0A1U7QM98 I3MBI5
EC Number
1.1.1.-
Pubmed
19121390
22118469
26354079
17994087
30297745
22722832
+ More
9989411 16365034 16644725 14702039 15772651 15489334 15775970 10913597 17094969 18691976 17967870 18669648 19418225 20111043 21364629 21269460 22103349 23186163 24275569 25944712 12198487 23217327 20362274 22019070 25986071 25583628 17975172 16136131 25613341 25362486 17431167 21993624 17554307 29240929 20075255 24792819 24901321 21993625 23236062 9215903 23025625 21709235 17381049 23624526 28004739
9989411 16365034 16644725 14702039 15772651 15489334 15775970 10913597 17094969 18691976 17967870 18669648 19418225 20111043 21364629 21269460 22103349 23186163 24275569 25944712 12198487 23217327 20362274 22019070 25986071 25583628 17975172 16136131 25613341 25362486 17431167 21993624 17554307 29240929 20075255 24792819 24901321 21993625 23236062 9215903 23025625 21709235 17381049 23624526 28004739
EMBL
BABH01023033
BABH01023034
BABH01023035
BABH01023036
BABH01023037
AGBW02009223
+ More
OWR51313.1 ODYU01006927 SOQ49207.1 KQ459585 KPI98303.1 IACF01000468 LAB66242.1 GBYB01003442 JAG73209.1 CH933807 KRG02527.1 EDW11106.2 IACN01097649 LAB60496.1 BFAA01000829 GCB74034.1 AJFE02064709 AJFE02064710 AJFE02064711 AJFE02064712 AF100928 DQ016496 DQ016498 DQ016500 AL049703 AL049704 AK314446 CR457379 AL139234 CH471107 BC111065 BC139738 AF131759 HM005544 AEE61141.1 AANG04002924 AACZ04057131 AACZ04057132 AACZ04057133 AACZ04057134 AACZ04057135 GBXM01012882 JAH95695.1 NDHI03003376 PNJ74200.1 KF459397 KF510638 GECU01012397 JAS95309.1 NBAG03000486 PNI20061.1 GECZ01032172 JAS37597.1 PNJ74202.1 AHZZ02038749 AQIA01087003 AQIA01087004 JSUE03046784 JSUE03046785 JSUE03046786 PNI20060.1 ADFV01009262 ADFV01009263 ADFV01009264 GECU01035382 JAS72324.1 DQ016497 AAY84738.1 NEVH01004406 PNF39781.1 JYDU01000004 KRY01278.1 AAGW02046665 AAGW02046666 AAGW02046667 AAGW02046668 AAGW02046669 AAPE02002264 AAPE02002265 AAPE02002266 AAPE02002267 BEZZ01000345 GCC31142.1 AJWK01027683 AAZX01002348 JH431832 JX975255 GAAL01000001 AGU38818.1 JAT78663.1 GBZA01000033 JAG69735.1 AEMK02000122 KF941299 AID16308.1 JH168143 EHB03571.1 GEBF01001939 JAO01694.1 JP005347 AER93944.1 AFYH01037266 AFYH01037267 AFYH01037268 AFYH01037269 AFYH01037270 JU173911 GBEX01000255 AFJ49437.1 JAI14305.1 MH393923 AZV23876.1 GFDF01007379 JAV06705.1 AEFK01230020 AEFK01230021 AGCU01052110 AGCU01052111 AGCU01052112 GFDF01007382 JAV06702.1 KB542241 EMP32088.1 GEZM01061487 JAV70437.1 KU948202 AMY56536.1 KQ435966 KOX67939.1 AGTP01013067 AGTP01013068
OWR51313.1 ODYU01006927 SOQ49207.1 KQ459585 KPI98303.1 IACF01000468 LAB66242.1 GBYB01003442 JAG73209.1 CH933807 KRG02527.1 EDW11106.2 IACN01097649 LAB60496.1 BFAA01000829 GCB74034.1 AJFE02064709 AJFE02064710 AJFE02064711 AJFE02064712 AF100928 DQ016496 DQ016498 DQ016500 AL049703 AL049704 AK314446 CR457379 AL139234 CH471107 BC111065 BC139738 AF131759 HM005544 AEE61141.1 AANG04002924 AACZ04057131 AACZ04057132 AACZ04057133 AACZ04057134 AACZ04057135 GBXM01012882 JAH95695.1 NDHI03003376 PNJ74200.1 KF459397 KF510638 GECU01012397 JAS95309.1 NBAG03000486 PNI20061.1 GECZ01032172 JAS37597.1 PNJ74202.1 AHZZ02038749 AQIA01087003 AQIA01087004 JSUE03046784 JSUE03046785 JSUE03046786 PNI20060.1 ADFV01009262 ADFV01009263 ADFV01009264 GECU01035382 JAS72324.1 DQ016497 AAY84738.1 NEVH01004406 PNF39781.1 JYDU01000004 KRY01278.1 AAGW02046665 AAGW02046666 AAGW02046667 AAGW02046668 AAGW02046669 AAPE02002264 AAPE02002265 AAPE02002266 AAPE02002267 BEZZ01000345 GCC31142.1 AJWK01027683 AAZX01002348 JH431832 JX975255 GAAL01000001 AGU38818.1 JAT78663.1 GBZA01000033 JAG69735.1 AEMK02000122 KF941299 AID16308.1 JH168143 EHB03571.1 GEBF01001939 JAO01694.1 JP005347 AER93944.1 AFYH01037266 AFYH01037267 AFYH01037268 AFYH01037269 AFYH01037270 JU173911 GBEX01000255 AFJ49437.1 JAI14305.1 MH393923 AZV23876.1 GFDF01007379 JAV06705.1 AEFK01230020 AEFK01230021 AGCU01052110 AGCU01052111 AGCU01052112 GFDF01007382 JAV06702.1 KB542241 EMP32088.1 GEZM01061487 JAV70437.1 KU948202 AMY56536.1 KQ435966 KOX67939.1 AGTP01013067 AGTP01013068
Proteomes
UP000005204
UP000007151
UP000053268
UP000245341
UP000009192
UP000079721
+ More
UP000288216 UP000248482 UP000240080 UP000005640 UP000011712 UP000245340 UP000002277 UP000233200 UP000233160 UP000028761 UP000233120 UP000233100 UP000006718 UP000233220 UP000233040 UP000189704 UP000001073 UP000233020 UP000008225 UP000261420 UP000235965 UP000233140 UP000233060 UP000054815 UP000001811 UP000189705 UP000001074 UP000265200 UP000287033 UP000092461 UP000261540 UP000002358 UP000264800 UP000008227 UP000006813 UP000008672 UP000265000 UP000095300 UP000007648 UP000007635 UP000007267 UP000031443 UP000233180 UP000053105 UP000248480 UP000189706 UP000005215
UP000288216 UP000248482 UP000240080 UP000005640 UP000011712 UP000245340 UP000002277 UP000233200 UP000233160 UP000028761 UP000233120 UP000233100 UP000006718 UP000233220 UP000233040 UP000189704 UP000001073 UP000233020 UP000008225 UP000261420 UP000235965 UP000233140 UP000233060 UP000054815 UP000001811 UP000189705 UP000001074 UP000265200 UP000287033 UP000092461 UP000261540 UP000002358 UP000264800 UP000008227 UP000006813 UP000008672 UP000265000 UP000095300 UP000007648 UP000007635 UP000007267 UP000031443 UP000233180 UP000053105 UP000248480 UP000189706 UP000005215
Interpro
Gene 3D
ProteinModelPortal
H9JIX2
A0A212FC61
A0A2H1W831
A0A194PZ37
A0A2P2HWW7
A0A0C9QS22
+ More
A0A2U3XUU4 A0A0Q9X3C3 B4KGB9 A0A2D4PTB4 A0A1S3A118 A0A401PLL5 A0A2Y9KMD9 A0A2R9ASH6 O95831-5 A0A140VK04 A0A2Y9KK59 A0A337S4Y7 A0A2U3ZGK2 A0A2I3T1Z5 A0A0E9X1B5 A0A2J8WWS8 E9PMA0 A0A1B6J809 A0A2J8JBB9 A0A2K6QE09 A0A1B6EI32 A0A2K6EP57 O95831-2 A0A2J8WWP9 A0A2I3N3Q0 A0A2K6DRL2 A0A2K5X6R6 F7C728 A0A2K6UVT3 A0A2K5RPH7 A0A2U3VXV0 A0A2J8JBC3 A0A3Q0DXU3 A0A2I3FRD9 A0A2K6UVY6 A0A1B6HC81 A0A2K5EDF8 F7C333 Q2QKE3 A0A2K5RPW3 A0A3B4UMM2 A0A2J7RG21 A0A2K5XDQ2 A0A2K5L4G4 A0A0V0YLQ4 U3KP10 A0A1U8DHQ1 G1SIM3 G1Q8W8 A0A3P9IWE7 A0A401SL88 A0A1B0CTJ1 A0A3B3RGD9 K7J4K5 T1J3Z2 A0A3Q3AM59 A0A0B4KJP5 A0A0B8RTX7 F1RTH3 A0A068CA64 G5B2Q8 A0A3B3RGH1 A0A0N8EUC8 A0A1S3A121 A0A1S3A140 M1EC95 H2ZVB2 H2ZVB3 J3S402 A0A3T0JLN2 A0A1L8DK09 A0A3Q2NRH5 A0A1I8NNT6 G3WTU3 A0A1I8NNT5 G3QAE4 K7FFA3 A0A1L8DJS3 K7FF97 M7BJ62 A0A2K6JYL8 A0A1Y1LHD2 A0A165NNH9 A0A0M8ZRB3 A0A2K5XDM0 A0A2K5L4D7 A0A2K5XDP8 A0A2K5L4B7 A0A2Y9DRB2 A0A1U7QXN0 A0A287D6C8 A0A1U7QM98 I3MBI5
A0A2U3XUU4 A0A0Q9X3C3 B4KGB9 A0A2D4PTB4 A0A1S3A118 A0A401PLL5 A0A2Y9KMD9 A0A2R9ASH6 O95831-5 A0A140VK04 A0A2Y9KK59 A0A337S4Y7 A0A2U3ZGK2 A0A2I3T1Z5 A0A0E9X1B5 A0A2J8WWS8 E9PMA0 A0A1B6J809 A0A2J8JBB9 A0A2K6QE09 A0A1B6EI32 A0A2K6EP57 O95831-2 A0A2J8WWP9 A0A2I3N3Q0 A0A2K6DRL2 A0A2K5X6R6 F7C728 A0A2K6UVT3 A0A2K5RPH7 A0A2U3VXV0 A0A2J8JBC3 A0A3Q0DXU3 A0A2I3FRD9 A0A2K6UVY6 A0A1B6HC81 A0A2K5EDF8 F7C333 Q2QKE3 A0A2K5RPW3 A0A3B4UMM2 A0A2J7RG21 A0A2K5XDQ2 A0A2K5L4G4 A0A0V0YLQ4 U3KP10 A0A1U8DHQ1 G1SIM3 G1Q8W8 A0A3P9IWE7 A0A401SL88 A0A1B0CTJ1 A0A3B3RGD9 K7J4K5 T1J3Z2 A0A3Q3AM59 A0A0B4KJP5 A0A0B8RTX7 F1RTH3 A0A068CA64 G5B2Q8 A0A3B3RGH1 A0A0N8EUC8 A0A1S3A121 A0A1S3A140 M1EC95 H2ZVB2 H2ZVB3 J3S402 A0A3T0JLN2 A0A1L8DK09 A0A3Q2NRH5 A0A1I8NNT6 G3WTU3 A0A1I8NNT5 G3QAE4 K7FFA3 A0A1L8DJS3 K7FF97 M7BJ62 A0A2K6JYL8 A0A1Y1LHD2 A0A165NNH9 A0A0M8ZRB3 A0A2K5XDM0 A0A2K5L4D7 A0A2K5XDP8 A0A2K5L4B7 A0A2Y9DRB2 A0A1U7QXN0 A0A287D6C8 A0A1U7QM98 I3MBI5
PDB
5FS8
E-value=8.94921e-21,
Score=240
Ontologies
GO
GO:0046983
GO:0016491
GO:0050660
GO:0016021
GO:0042775
GO:0050832
GO:0005758
GO:0010623
GO:0016651
GO:0090650
GO:0043065
GO:0070301
GO:0048471
GO:0071392
GO:0051402
GO:0071949
GO:0006915
GO:1902065
GO:1902510
GO:0030261
GO:0002931
GO:0016174
GO:0070059
GO:0006919
GO:0003677
GO:0071732
GO:0005829
GO:1904045
GO:0043525
GO:0005739
GO:0032981
GO:0030182
GO:0005743
GO:0005634
GO:0045454
GO:0005515
GO:0030145
GO:0006412
GO:0016876
GO:0043039
GO:0055114
Topology
Subcellular location
Mitochondrion intermembrane space
Mitochondrion inner membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Perinuclear region
Mitochondrion inner membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Perinuclear region
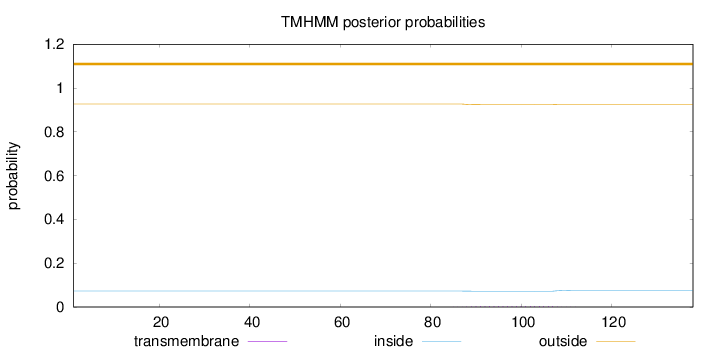
Length:
138
Number of predicted TMHs:
0
Exp number of AAs in TMHs:
0.08735
Exp number, first 60 AAs:
0.000620000000000001
Total prob of N-in:
0.07283
outside
1 - 138
Population Genetic Test Statistics
Pi
301.829604
Theta
177.583244
Tajima's D
2.139703
CLR
0.418584
CSRT
0.901904904754762
Interpretation
Uncertain
