Gene
KWMTBOMO07940
Pre Gene Modal
BGIBMGA001163
Annotation
PREDICTED:_cAMP-dependent_protein_kinase_catalytic_subunit_alpha-like_[Papilio_xuthus]
Full name
cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit
+ More
cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha
cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha
Location in the cell
Cytoplasmic Reliability : 3.429
Sequence
CDS
ATGGCAGATAGTGAAATTAAAAGGCATATAAATTCACCACGTGGTGATTTGATACAACACGGTGGCTATTCTCCTGCAAAACAAGAACAATACTCTCAATATTTAAAGAAACTCCGTCAAGATTTTGTTGAGTCATGGGATGATAAATCTGAAAGTAATGCAAAGTTGAATGATTTTGAAAGACAAAAAGTTTTAGGAACAGGAGCATTTGGCATTGTTTTTCTTGTAAAGCATATTGTAACAGGTAAATATTATGCTATGAAAATGCTCGAAAAAGAGAAAATTGTTAGATTGAAACAAATTGAGCACAGCTACTACGAAAAAAAGATTCTATGTGGCTTAAATTTTCCTTTTGTTGTTTACATGAAATACTATTTTAAGGATAACGTTTATCTTTATTACGTTCTACCTTTCATAGCCGGTGGGGAAATGTTTTCACATTTACGTAAAATGGGCAAGTTTGAAGAAACTTCTGCAAAATTTTACGGAGCACAAGTTATACTAGCATTGGAATATCTGCACGCTTGTGAATTAGTATATCGAGATCTAAAGCCCGAGAATATATTAATAGATCGTACAGGTTATATCAAAATTACTGACTTCGGTTTCTGTAAGCTTATCCGCGGTAGGACTTGGACACTTTGCGGTACTCCAGAATATTTAGCACCTGAAATCATTCTAAGCAAAGGCTATGGAATGTCAGTCGACTGGTGGTCCCTAGGGGTATTACTTTTCGAAATGAGTGCCGGGCATCCACCATTTTTTGCTTCGGATCCAATGAGAATTTATGAAAAAATTGTGGCAGGAAAATATAGATGTCCATCACATTTTTCTGTTGAATTAAAAGATATAATAGGACATGTTTTACAAGTCGACACAACAAGACGTTACGGAACTCTTAAAGATGGCGTGTTGGATTTTAAAAATCATAAATGGTTTAGAGAAATCGATTGGGATAGTATTTTGAATAGTCGCATACATCCGCCGTTTTTTCCAAAGATACGTTCACCAGGCGACACCACTAATTTCGATGTTTTTGATGAAGAAAAAATTAAAGACAGTCCAGTATGTCTTTATGAAGAAGAATTTGCTGATTTTTAA
Protein
MADSEIKRHINSPRGDLIQHGGYSPAKQEQYSQYLKKLRQDFVESWDDKSESNAKLNDFERQKVLGTGAFGIVFLVKHIVTGKYYAMKMLEKEKIVRLKQIEHSYYEKKILCGLNFPFVVYMKYYFKDNVYLYYVLPFIAGGEMFSHLRKMGKFEETSAKFYGAQVILALEYLHACELVYRDLKPENILIDRTGYIKITDFGFCKLIRGRTWTLCGTPEYLAPEIILSKGYGMSVDWWSLGVLLFEMSAGHPPFFASDPMRIYEKIVAGKYRCPSHFSVELKDIIGHVLQVDTTRRYGTLKDGVLDFKNHKWFREIDWDSILNSRIHPPFFPKIRSPGDTTNFDVFDEEKIKDSPVCLYEEEFADF
Summary
Description
Essential for larval development (PubMed:22887816). Controls the rhythmic contraction of enteric muscles probably by regulating G-protein coupled receptor aex-2-mediated calcium influx in GABAergic DVB neurons (PubMed:24086161). Plays a role in the control of oocyte meiotic maturation by gonadal sheath cells (PubMed:22887816).
Isoforms a and b: May play a role in the regulation of neuromuscular junctions.
Phosphorylates a large number of substrates in the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Regulates the abundance of compartmentalized pools of its regulatory subunits through phosphorylation of PJA2 which binds and ubiquitinates these subunits, leading to their subsequent proteolysis. Phosphorylates CDC25B, ABL1, NFKB1, CLDN3, PSMC5/RPT6, PJA2, RYR2, RORA and VASP. RORA is activated by phosphorylation. Required for glucose-mediated adipogenic differentiation increase and osteogenic differentiation inhibition from osteoblasts. Involved in the regulation of platelets in response to thrombin and collagen; maintains circulating platelets in a resting state by phosphorylating proteins in numerous platelet inhibitory pathways when in complex with NF-kappa-B (NFKB1 and NFKB2) and I-kappa-B-alpha (NFKBIA), but thrombin and collagen disrupt these complexes and free active PRKACA stimulates platelets and leads to platelet aggregation by phosphorylating VASP. Prevents the antiproliferative and anti-invasive effects of alpha-difluoromethylornithine in breast cancer cells when activated. RYR2 channel activity is potentiated by phosphorylation in presence of luminal Ca(2+), leading to reduced amplitude and increased frequency of store overload-induced Ca(2+) release (SOICR) characterized by an increased rate of Ca(2+) release and propagation velocity of spontaneous Ca(2+) waves, despite reduced wave amplitude and resting cytosolic Ca(2+). PSMC5/RPT6 activation by phosphorylation stimulates proteasome. Negatively regulates tight junctions (TJs) in ovarian cancer cells via CLDN3 phosphorylation. NFKB1 phosphorylation promotes NF-kappa-B p50-p50 DNA binding. Involved in embryonic development by down-regulating the Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway that determines embryo pattern formation and morphogenesis. Prevents meiosis resumption in prophase-arrested oocytes via CDC25B inactivation by phosphorylation. May also regulate rapid eye movement (REM) sleep in the pedunculopontine tegmental (PPT) (By similarity). Phosphorylates APOBEC3G and AICDA (By similarity). Phosphorylates HSF1; this phosphorylation promotes HSF1 nuclear localization and transcriptional activity upon heat shock (By similarity).
Isoforms a and b: May play a role in the regulation of neuromuscular junctions.
Phosphorylates a large number of substrates in the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Regulates the abundance of compartmentalized pools of its regulatory subunits through phosphorylation of PJA2 which binds and ubiquitinates these subunits, leading to their subsequent proteolysis. Phosphorylates CDC25B, ABL1, NFKB1, CLDN3, PSMC5/RPT6, PJA2, RYR2, RORA and VASP. RORA is activated by phosphorylation. Required for glucose-mediated adipogenic differentiation increase and osteogenic differentiation inhibition from osteoblasts. Involved in the regulation of platelets in response to thrombin and collagen; maintains circulating platelets in a resting state by phosphorylating proteins in numerous platelet inhibitory pathways when in complex with NF-kappa-B (NFKB1 and NFKB2) and I-kappa-B-alpha (NFKBIA), but thrombin and collagen disrupt these complexes and free active PRKACA stimulates platelets and leads to platelet aggregation by phosphorylating VASP. Prevents the antiproliferative and anti-invasive effects of alpha-difluoromethylornithine in breast cancer cells when activated. RYR2 channel activity is potentiated by phosphorylation in presence of luminal Ca(2+), leading to reduced amplitude and increased frequency of store overload-induced Ca(2+) release (SOICR) characterized by an increased rate of Ca(2+) release and propagation velocity of spontaneous Ca(2+) waves, despite reduced wave amplitude and resting cytosolic Ca(2+). PSMC5/RPT6 activation by phosphorylation stimulates proteasome. Negatively regulates tight junctions (TJs) in ovarian cancer cells via CLDN3 phosphorylation. NFKB1 phosphorylation promotes NF-kappa-B p50-p50 DNA binding. Involved in embryonic development by down-regulating the Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway that determines embryo pattern formation and morphogenesis. Prevents meiosis resumption in prophase-arrested oocytes via CDC25B inactivation by phosphorylation. May also regulate rapid eye movement (REM) sleep in the pedunculopontine tegmental (PPT) (By similarity). Phosphorylates APOBEC3G and AICDA (By similarity). Phosphorylates HSF1; this phosphorylation promotes HSF1 nuclear localization and transcriptional activity upon heat shock (By similarity).
Catalytic Activity
ATP + L-seryl-[protein] = ADP + H(+) + O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein]
ATP + L-threonyl-[protein] = ADP + H(+) + O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein]
ATP + L-threonyl-[protein] = ADP + H(+) + O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein]
Subunit
Heterotetramer composed of two regulatory subunits and two catalytic subunits.
A number of inactive tetrameric holoenzymes are produced by the combination of homo- or heterodimers of the different regulatory subunits associated with two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Activates cAMP-sensitive PKAI and PKAII holoenzymes by interacting with regulatory subunit (R) of PKA, PRKAR1A/PKR1 and PRKAR2A/PKR2, respectively. Interacts with NFKB1, NFKB2 and NFKBIA in platelets; these interactions are disrupted by thrombin and collagen. Binds to ABL1 in spermatozoa and with CDC25B in oocytes (By similarity). Interacts with APOBEC3G and AICDA (By similarity). Interacts with RAB13; downstream effector of RAB13 involved in tight junction assembly. Found in a complex at least composed of MROH2B, PRKACA and TCP11 (By similarity). Interacts with MROH2B (By similarity). Interacts with TCP11 (By similarity). Interacts with HSF1 (By similarity).
A number of inactive tetrameric holoenzymes are produced by the combination of homo- or heterodimers of the different regulatory subunits associated with two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Activates cAMP-sensitive PKAI and PKAII holoenzymes by interacting with regulatory subunit (R) of PKA, PRKAR1A/PKR1 and PRKAR2A/PKR2, respectively. Interacts with NFKB1, NFKB2 and NFKBIA in platelets; these interactions are disrupted by thrombin and collagen. Binds to ABL1 in spermatozoa and with CDC25B in oocytes (By similarity). Interacts with APOBEC3G and AICDA (By similarity). Interacts with RAB13; downstream effector of RAB13 involved in tight junction assembly. Found in a complex at least composed of MROH2B, PRKACA and TCP11 (By similarity). Interacts with MROH2B (By similarity). Interacts with TCP11 (By similarity). Interacts with HSF1 (By similarity).
Similarity
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. cAMP subfamily.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. cAMP subfamily.
Keywords
Alternative splicing
ATP-binding
cAMP
Complete proteome
Kinase
Lipoprotein
Myristate
Nucleotide-binding
Phosphoprotein
Reference proteome
Transferase
3D-structure
Cell membrane
Cell projection
Cilium
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasmic vesicle
Direct protein sequencing
Flagellum
Membrane
Mitochondrion
Nucleus
Feature
chain cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit
splice variant In isoform c.
splice variant In isoform c.
Uniprot
H9IV83
A0A194Q915
A0A0N1IPW6
A0A0L7LC89
A0A212ER70
A0A212EWD5
+ More
A0A0L7LQB0 A0A194R2E1 A0A194PZ30 E0VEQ2 A0A0C9RV13 A0A0L7R855 A0A1D5P0J5 A0A218VET5 A0A2A2J6C5 A0A1Y1N4Z4 U3JU00 A0A1D5NW04 A0A094KSF4 A0A2I0MEC8 A0A091TYR0 A0A091T8G2 A0A1D5PLV3 A0A0Q3LUM3 A0A091HTZ5 A0A151NJ57 A0A1U7SDV1 A0A091VJW1 H3AXE1 V9KQ53 A0A0B8RRH8 A0A1W7RIS1 J3SBX2 T1E718 U3F901 A0A094L3Q4 A0A151NJ10 A0A3Q0HA31 G1N3V9 A0A087V9U4 A0A091NAU9 A0A1U7SGF3 A0A2A2J6B5 A0A093CTL8 A0A1V4JYX0 A0A091H3Y8 A0A3L8SQJ8 A0A151NJ28 A0A091JZS9 A0A091GF94 P21137-12 A0A091EJ36 A0A093NJS6 A0A087QHL7 A0A091WFF0 A0A091MDI6 A0A091LYA7 A0A0A0AFY6 A0A226PKL4 P21137-6 A0A2I0MED5 K7FHV7 A0A3Q0H5E5 R0JPM8 P21137-8 A0A3Q0HA50 H0Z8E2 A0A1U7S2J4 P21137-13 R4GIN8 A0A2A2J6Y2 A0A3Q0H6Q6 A0A2A2J6X7 A0A091RLQ8 A0A091QAC2 A0A093HF97 P21137-2 A0A093GDJ5 A0A093Q3X5 A0A091IX21 A0A098M014 A0A091PTQ1 H9GAL8 R4GCW7 A0A1I7VJD7 A0A3L8DY06 P21137-7 V9KWZ2 F6UP78 A0A0K0JSZ6 A0A170RC44 K7FHX4 A0A2K6D6Z3 A0A2K6MG58 A0A2K5VKF2 A0A2K5ZY03 A0A2K6NMP1 A0A2K5NNF3 H9FWY1 P00517
A0A0L7LQB0 A0A194R2E1 A0A194PZ30 E0VEQ2 A0A0C9RV13 A0A0L7R855 A0A1D5P0J5 A0A218VET5 A0A2A2J6C5 A0A1Y1N4Z4 U3JU00 A0A1D5NW04 A0A094KSF4 A0A2I0MEC8 A0A091TYR0 A0A091T8G2 A0A1D5PLV3 A0A0Q3LUM3 A0A091HTZ5 A0A151NJ57 A0A1U7SDV1 A0A091VJW1 H3AXE1 V9KQ53 A0A0B8RRH8 A0A1W7RIS1 J3SBX2 T1E718 U3F901 A0A094L3Q4 A0A151NJ10 A0A3Q0HA31 G1N3V9 A0A087V9U4 A0A091NAU9 A0A1U7SGF3 A0A2A2J6B5 A0A093CTL8 A0A1V4JYX0 A0A091H3Y8 A0A3L8SQJ8 A0A151NJ28 A0A091JZS9 A0A091GF94 P21137-12 A0A091EJ36 A0A093NJS6 A0A087QHL7 A0A091WFF0 A0A091MDI6 A0A091LYA7 A0A0A0AFY6 A0A226PKL4 P21137-6 A0A2I0MED5 K7FHV7 A0A3Q0H5E5 R0JPM8 P21137-8 A0A3Q0HA50 H0Z8E2 A0A1U7S2J4 P21137-13 R4GIN8 A0A2A2J6Y2 A0A3Q0H6Q6 A0A2A2J6X7 A0A091RLQ8 A0A091QAC2 A0A093HF97 P21137-2 A0A093GDJ5 A0A093Q3X5 A0A091IX21 A0A098M014 A0A091PTQ1 H9GAL8 R4GCW7 A0A1I7VJD7 A0A3L8DY06 P21137-7 V9KWZ2 F6UP78 A0A0K0JSZ6 A0A170RC44 K7FHX4 A0A2K6D6Z3 A0A2K6MG58 A0A2K5VKF2 A0A2K5ZY03 A0A2K6NMP1 A0A2K5NNF3 H9FWY1 P00517
EC Number
2.7.11.11
Pubmed
19121390
26354079
26227816
22118469
20566863
15592404
+ More
28004739 23371554 22293439 9215903 24402279 25476704 26358130 23025625 23758969 25727380 23915248 20838655 30282656 2324104 9851916 10085246 9299544 16806821 18077108 22286028 22887816 24086161 24621616 17381049 20360741 21881562 25217238 30249741 20431018 17885136 25362486 25319552 1420367 6262777 6311252 6286662 9521123 10684253 11152138 15096524 8824261 9438863
28004739 23371554 22293439 9215903 24402279 25476704 26358130 23025625 23758969 25727380 23915248 20838655 30282656 2324104 9851916 10085246 9299544 16806821 18077108 22286028 22887816 24086161 24621616 17381049 20360741 21881562 25217238 30249741 20431018 17885136 25362486 25319552 1420367 6262777 6311252 6286662 9521123 10684253 11152138 15096524 8824261 9438863
EMBL
BABH01000681
KQ459299
KPJ01909.1
KQ460202
KPJ17176.1
JTDY01001711
+ More
KOB73103.1 AGBW02013095 OWR43992.1 AGBW02012010 OWR45805.1 JTDY01000340 KOB77630.1 KQ460855 KPJ11867.1 KQ459584 KPI98576.1 AAZO01001585 DS235093 EEB11858.1 GBYB01011506 JAG81273.1 KQ414637 KOC66936.1 AADN05000647 MUZQ01000002 OWK64503.1 LIAE01010642 PAV57368.1 GEZM01015981 JAV91396.1 AGTO01021089 KL262375 KFZ60277.1 AKCR02000018 PKK28038.1 KK408331 KFQ83376.1 KK945962 KFQ54356.1 LMAW01003072 KQK74224.1 KL217788 KFO98612.1 AKHW03002907 KYO36790.1 KK734081 KFR03712.1 AFYH01051841 AFYH01051842 AFYH01051843 AFYH01051844 AFYH01051845 AFYH01051846 AFYH01051847 AFYH01051848 AFYH01051849 AFYH01051850 JW867900 AFP00418.1 GBSH01000536 JAG68489.1 GDAY02000383 JAV51030.1 JU174069 GBEX01000552 AFJ49595.1 JAI14008.1 GAAZ01000411 GBKC01000571 JAA97532.1 JAG45499.1 GAEP01000269 GBEW01000184 JAB54552.1 JAI10181.1 KL350738 KFZ58739.1 KYO36791.1 KL485232 KFO09386.1 KL380329 KFP86838.1 PAV57358.1 KL248304 KFV16254.1 LSYS01005497 OPJ77408.1 KL520265 KFO89395.1 QUSF01000010 RLW06015.1 KYO36792.1 KK540411 KFP30707.1 KL447384 KFO72782.1 M37119 M37114 M37115 M37116 M37117 M37118 Z82096 Z81511 AJ011936 AJ011937 AJ011938 AJ012354 AJ012355 AJ012356 KK718445 KFO56612.1 KL224623 KFW62215.1 KL225597 KFM00721.1 KL410872 KFR00341.1 KK527473 KFP68664.1 KL300969 KFP51276.1 KL871737 KGL93061.1 AWGT02000057 OXB80050.1 PKK28039.1 AGCU01066600 AGCU01066601 AGCU01066602 AGCU01066603 AGCU01066604 AGCU01066605 AGCU01066606 AGCU01066607 AGCU01066608 AGCU01066609 KB743342 EOA99300.1 ABQF01041419 ABQF01041420 ABQF01041421 ABQF01041422 ABQF01041423 PAV57363.1 PAV57369.1 KK802033 KFQ29452.1 KK692017 KFQ22039.1 KL206233 KFV80346.1 KL215901 KFV67258.1 KL670376 KFW78932.1 KK501110 KFP12867.1 GBSI01000439 JAC96057.1 KK678206 KFQ10696.1 AAWZ02004438 QOIP01000003 RLU25256.1 JW871135 AFP03653.1 AAMC01003225 AAMC01003226 AAMC01003227 AAMC01003228 AAMC01003229 AAMC01003230 KU193794 ANB82449.1 AQIA01003548 AQIA01003549 AQIA01003550 AQIA01003551 JU335387 JV043888 AFE79140.1 AFI33959.1 X67154
KOB73103.1 AGBW02013095 OWR43992.1 AGBW02012010 OWR45805.1 JTDY01000340 KOB77630.1 KQ460855 KPJ11867.1 KQ459584 KPI98576.1 AAZO01001585 DS235093 EEB11858.1 GBYB01011506 JAG81273.1 KQ414637 KOC66936.1 AADN05000647 MUZQ01000002 OWK64503.1 LIAE01010642 PAV57368.1 GEZM01015981 JAV91396.1 AGTO01021089 KL262375 KFZ60277.1 AKCR02000018 PKK28038.1 KK408331 KFQ83376.1 KK945962 KFQ54356.1 LMAW01003072 KQK74224.1 KL217788 KFO98612.1 AKHW03002907 KYO36790.1 KK734081 KFR03712.1 AFYH01051841 AFYH01051842 AFYH01051843 AFYH01051844 AFYH01051845 AFYH01051846 AFYH01051847 AFYH01051848 AFYH01051849 AFYH01051850 JW867900 AFP00418.1 GBSH01000536 JAG68489.1 GDAY02000383 JAV51030.1 JU174069 GBEX01000552 AFJ49595.1 JAI14008.1 GAAZ01000411 GBKC01000571 JAA97532.1 JAG45499.1 GAEP01000269 GBEW01000184 JAB54552.1 JAI10181.1 KL350738 KFZ58739.1 KYO36791.1 KL485232 KFO09386.1 KL380329 KFP86838.1 PAV57358.1 KL248304 KFV16254.1 LSYS01005497 OPJ77408.1 KL520265 KFO89395.1 QUSF01000010 RLW06015.1 KYO36792.1 KK540411 KFP30707.1 KL447384 KFO72782.1 M37119 M37114 M37115 M37116 M37117 M37118 Z82096 Z81511 AJ011936 AJ011937 AJ011938 AJ012354 AJ012355 AJ012356 KK718445 KFO56612.1 KL224623 KFW62215.1 KL225597 KFM00721.1 KL410872 KFR00341.1 KK527473 KFP68664.1 KL300969 KFP51276.1 KL871737 KGL93061.1 AWGT02000057 OXB80050.1 PKK28039.1 AGCU01066600 AGCU01066601 AGCU01066602 AGCU01066603 AGCU01066604 AGCU01066605 AGCU01066606 AGCU01066607 AGCU01066608 AGCU01066609 KB743342 EOA99300.1 ABQF01041419 ABQF01041420 ABQF01041421 ABQF01041422 ABQF01041423 PAV57363.1 PAV57369.1 KK802033 KFQ29452.1 KK692017 KFQ22039.1 KL206233 KFV80346.1 KL215901 KFV67258.1 KL670376 KFW78932.1 KK501110 KFP12867.1 GBSI01000439 JAC96057.1 KK678206 KFQ10696.1 AAWZ02004438 QOIP01000003 RLU25256.1 JW871135 AFP03653.1 AAMC01003225 AAMC01003226 AAMC01003227 AAMC01003228 AAMC01003229 AAMC01003230 KU193794 ANB82449.1 AQIA01003548 AQIA01003549 AQIA01003550 AQIA01003551 JU335387 JV043888 AFE79140.1 AFI33959.1 X67154
Proteomes
UP000005204
UP000053268
UP000053240
UP000037510
UP000007151
UP000009046
+ More
UP000053825 UP000000539 UP000197619 UP000218231 UP000016665 UP000053872 UP000051836 UP000054308 UP000050525 UP000189705 UP000053605 UP000008672 UP000001645 UP000190648 UP000276834 UP000053760 UP000001940 UP000052976 UP000054081 UP000053286 UP000053283 UP000053858 UP000198419 UP000007267 UP000007754 UP000053584 UP000053875 UP000053258 UP000053119 UP000001646 UP000095285 UP000279307 UP000008143 UP000006672 UP000233120 UP000233180 UP000233100 UP000233140 UP000233200 UP000233060 UP000009136
UP000053825 UP000000539 UP000197619 UP000218231 UP000016665 UP000053872 UP000051836 UP000054308 UP000050525 UP000189705 UP000053605 UP000008672 UP000001645 UP000190648 UP000276834 UP000053760 UP000001940 UP000052976 UP000054081 UP000053286 UP000053283 UP000053858 UP000198419 UP000007267 UP000007754 UP000053584 UP000053875 UP000053258 UP000053119 UP000001646 UP000095285 UP000279307 UP000008143 UP000006672 UP000233120 UP000233180 UP000233100 UP000233140 UP000233200 UP000233060 UP000009136
Pfam
PF00069 Pkinase
Interpro
SUPFAM
SSF56112
SSF56112
ProteinModelPortal
H9IV83
A0A194Q915
A0A0N1IPW6
A0A0L7LC89
A0A212ER70
A0A212EWD5
+ More
A0A0L7LQB0 A0A194R2E1 A0A194PZ30 E0VEQ2 A0A0C9RV13 A0A0L7R855 A0A1D5P0J5 A0A218VET5 A0A2A2J6C5 A0A1Y1N4Z4 U3JU00 A0A1D5NW04 A0A094KSF4 A0A2I0MEC8 A0A091TYR0 A0A091T8G2 A0A1D5PLV3 A0A0Q3LUM3 A0A091HTZ5 A0A151NJ57 A0A1U7SDV1 A0A091VJW1 H3AXE1 V9KQ53 A0A0B8RRH8 A0A1W7RIS1 J3SBX2 T1E718 U3F901 A0A094L3Q4 A0A151NJ10 A0A3Q0HA31 G1N3V9 A0A087V9U4 A0A091NAU9 A0A1U7SGF3 A0A2A2J6B5 A0A093CTL8 A0A1V4JYX0 A0A091H3Y8 A0A3L8SQJ8 A0A151NJ28 A0A091JZS9 A0A091GF94 P21137-12 A0A091EJ36 A0A093NJS6 A0A087QHL7 A0A091WFF0 A0A091MDI6 A0A091LYA7 A0A0A0AFY6 A0A226PKL4 P21137-6 A0A2I0MED5 K7FHV7 A0A3Q0H5E5 R0JPM8 P21137-8 A0A3Q0HA50 H0Z8E2 A0A1U7S2J4 P21137-13 R4GIN8 A0A2A2J6Y2 A0A3Q0H6Q6 A0A2A2J6X7 A0A091RLQ8 A0A091QAC2 A0A093HF97 P21137-2 A0A093GDJ5 A0A093Q3X5 A0A091IX21 A0A098M014 A0A091PTQ1 H9GAL8 R4GCW7 A0A1I7VJD7 A0A3L8DY06 P21137-7 V9KWZ2 F6UP78 A0A0K0JSZ6 A0A170RC44 K7FHX4 A0A2K6D6Z3 A0A2K6MG58 A0A2K5VKF2 A0A2K5ZY03 A0A2K6NMP1 A0A2K5NNF3 H9FWY1 P00517
A0A0L7LQB0 A0A194R2E1 A0A194PZ30 E0VEQ2 A0A0C9RV13 A0A0L7R855 A0A1D5P0J5 A0A218VET5 A0A2A2J6C5 A0A1Y1N4Z4 U3JU00 A0A1D5NW04 A0A094KSF4 A0A2I0MEC8 A0A091TYR0 A0A091T8G2 A0A1D5PLV3 A0A0Q3LUM3 A0A091HTZ5 A0A151NJ57 A0A1U7SDV1 A0A091VJW1 H3AXE1 V9KQ53 A0A0B8RRH8 A0A1W7RIS1 J3SBX2 T1E718 U3F901 A0A094L3Q4 A0A151NJ10 A0A3Q0HA31 G1N3V9 A0A087V9U4 A0A091NAU9 A0A1U7SGF3 A0A2A2J6B5 A0A093CTL8 A0A1V4JYX0 A0A091H3Y8 A0A3L8SQJ8 A0A151NJ28 A0A091JZS9 A0A091GF94 P21137-12 A0A091EJ36 A0A093NJS6 A0A087QHL7 A0A091WFF0 A0A091MDI6 A0A091LYA7 A0A0A0AFY6 A0A226PKL4 P21137-6 A0A2I0MED5 K7FHV7 A0A3Q0H5E5 R0JPM8 P21137-8 A0A3Q0HA50 H0Z8E2 A0A1U7S2J4 P21137-13 R4GIN8 A0A2A2J6Y2 A0A3Q0H6Q6 A0A2A2J6X7 A0A091RLQ8 A0A091QAC2 A0A093HF97 P21137-2 A0A093GDJ5 A0A093Q3X5 A0A091IX21 A0A098M014 A0A091PTQ1 H9GAL8 R4GCW7 A0A1I7VJD7 A0A3L8DY06 P21137-7 V9KWZ2 F6UP78 A0A0K0JSZ6 A0A170RC44 K7FHX4 A0A2K6D6Z3 A0A2K6MG58 A0A2K5VKF2 A0A2K5ZY03 A0A2K6NMP1 A0A2K5NNF3 H9FWY1 P00517
PDB
1YDT
E-value=1.19194e-124,
Score=1142
Ontologies
PATHWAY
GO
GO:0034237
GO:0004691
GO:0007186
GO:0005524
GO:0004674
GO:0016021
GO:1900195
GO:0006468
GO:0005952
GO:0001669
GO:0036126
GO:0004672
GO:0005634
GO:0010737
GO:0005886
GO:0005739
GO:0019904
GO:0005737
GO:0001707
GO:0071333
GO:0048471
GO:0031594
GO:0034605
GO:0018105
GO:0043015
GO:0007169
GO:0016020
GO:0006412
GO:0016876
GO:0043039
PANTHER
Topology
Subcellular location
Cytoplasm
Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Nucleus Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Cell membrane Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Mitochondrion Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Membrane Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Cell projection Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Cilium Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Flagellum Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Cytoplasmic vesicle Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Secretory vesicle Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Acrosome Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Nucleus Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Cell membrane Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Mitochondrion Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Membrane Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Cell projection Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Cilium Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Flagellum Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Cytoplasmic vesicle Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Secretory vesicle Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
Acrosome Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (By similarity). With evidence from 9 publications.
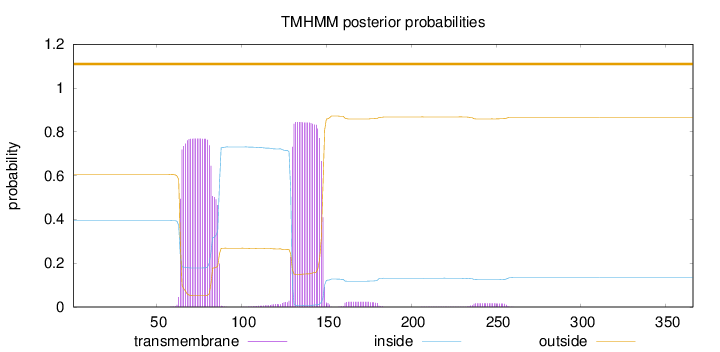
Length:
366
Number of predicted TMHs:
0
Exp number of AAs in TMHs:
32.8859600000001
Exp number, first 60 AAs:
0.00337
Total prob of N-in:
0.39446
outside
1 - 366
Population Genetic Test Statistics
Pi
209.269885
Theta
217.335283
Tajima's D
-0.15855
CLR
0.206851
CSRT
0.327033648317584
Interpretation
Uncertain
