Gene
KWMTBOMO05715
Pre Gene Modal
BGIBMGA006822
Annotation
PREDICTED:_lys-63-specific_deubiquitinase_BRCC36-like_isoform_X1_[Amyelois_transitella]
Full name
Lys-63-specific deubiquitinase BRCC36-like
+ More
Lys-63-specific deubiquitinase BRCC36
Lys-63-specific deubiquitinase BRCC36
Alternative Name
BRCA1-A complex subunit BRCC36
BRCA1/BRCA2-containing complex subunit 3
BRCA1/BRCA2-containing complex subunit 36
BRISC complex subunit BRCC36
BRCA1/BRCA2-containing complex subunit 3
BRCA1/BRCA2-containing complex subunit 36
BRISC complex subunit BRCC36
Location in the cell
Nuclear Reliability : 1.906
Sequence
CDS
ATGCTACAAAAGGTCCGTTTATCGTCTGATGTTGCTTTGGTCTGTATGCAACATGCGTTGTCGACAGAGAAAGAAGAAATCATGGGCTTACTTATAGGCGAGGTTCATGATAATGGTGCACTTGTTTCAATAGTGTCATCAGTAATACTTCGCCGTTTGGATAAAAAACCTGACCGTGTTGAAATATCAGAAGAACAACTGGTTCAAGCAACTGTTAGAGCTGAAGAATTAGCTGCAGAAGTTGGCCAACCTCTTAGAGTTGTTGGATGGTACCATTCGCATCCTCATATAACAGTGTGGCCATCCCATGTTGATTTGGCTACTCAATCAATGTATCAAAGGATGGATGCTAGTTTTGTTGGAATTATTTTTGCAGTATTTCTTACAGACCAATCAACAAAGGCCCCTTCAGTTCAAATTACTTGTTTTCAATCAATTAATGAAGGAGCTAGTCAAAGTCGGATTGAAATAGAAATGGAAATTGTAACTAACACTGATTCTTTGTTAACAAACAATTTCGAGACACTAACTCAGCTTCCAACAATTTTAAAAGAGGAAGAAGATGAAGCCTTTAATAATGAAATTAGTTATGATGATACTGATGACATTGTCACTAAGCAACATAATGCTGCAGTAAGGACTATTGCTATTGGCCACATTGTTGATAAGATGTCCCGACCAATGCTAGAAGGTTTAGTGGCCAGAAATTTATTAAACAGTATACGCTTAAAAGCATTGAAGAAACAGCATCAGCAGATGATGTCTAAATTAGAAAATATGACATGCTTGACCTAA
Protein
MLQKVRLSSDVALVCMQHALSTEKEEIMGLLIGEVHDNGALVSIVSSVILRRLDKKPDRVEISEEQLVQATVRAEELAAEVGQPLRVVGWYHSHPHITVWPSHVDLATQSMYQRMDASFVGIIFAVFLTDQSTKAPSVQITCFQSINEGASQSRIEIEMEIVTNTDSLLTNNFETLTQLPTILKEEEDEAFNNEISYDDTDDIVTKQHNAAVRTIAIGHIVDKMSRPMLEGLVARNLLNSIRLKALKKQHQQMMSKLENMTCLT
Summary
Description
Metalloprotease that specifically cleaves 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains.
Metalloprotease that specifically cleaves 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains. Does not have activity toward 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitin chains. Component of the BRCA1-A complex, a complex that specifically recognizes 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitinated histones H2A and H2AX at DNA lesions sites, leading to target the brca1-bard1 heterodimer to sites of DNA damage at double-strand breaks (DSBs). In the BRCA1-A complex, it specifically removes 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitin on histones H2A and H2AX, antagonizing the rnf8-dependent ubiquitination at double-strand breaks (DSBs). Catalytic subunit of the BRISC complex, a multiprotein complex that specifically cleaves 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitin in various substrates. Mediates the specific 'Lys-63'-specific deubiquitination associated with the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), via the interaction of the BRISC complex with the CSN complex. The BRISC complex is required for normal mitotic spindle assembly and microtubule attachment to kinetochores via its role in deubiquitinating numa1. Plays a role in interferon signaling via its role in the deubiquitination of the interferon receptor ifnar1; deubiquitination increases ifnar1 activity by enhancing its stability and cell surface expression. Down-regulates the response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) via its role in ifnar1 deubiquitination.
Metalloprotease that specifically cleaves 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains, leaving the last ubiquitin chain attached to its substrates. Catalytic subunit of the BRISC complex; does not have activity by itself, but needs to be associated into a heterotetramer with ABRAXAS2 for minimal in vitro activity (PubMed:26344097). Plays a role in regulating the onset of apoptosis via its role in modulating 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitination of target proteins (By similarity). Required for normal mitotic spindle assembly and microtubule attachment to kinetochores via its role in deubiquitinating spindle assembly factors (By similarity).
Metalloprotease that specifically cleaves 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains. Does not have activity toward 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitin chains. Component of the BRCA1-A complex, a complex that specifically recognizes 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitinated histones H2A and H2AX at DNA lesions sites, leading to target the brca1-bard1 heterodimer to sites of DNA damage at double-strand breaks (DSBs). In the BRCA1-A complex, it specifically removes 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitin on histones H2A and H2AX, antagonizing the rnf8-dependent ubiquitination at double-strand breaks (DSBs). Catalytic subunit of the BRISC complex, a multiprotein complex that specifically cleaves 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitin in various substrates. Mediates the specific 'Lys-63'-specific deubiquitination associated with the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), via the interaction of the BRISC complex with the CSN complex. The BRISC complex is required for normal mitotic spindle assembly and microtubule attachment to kinetochores via its role in deubiquitinating numa1. Plays a role in interferon signaling via its role in the deubiquitination of the interferon receptor ifnar1; deubiquitination increases ifnar1 activity by enhancing its stability and cell surface expression. Down-regulates the response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) via its role in ifnar1 deubiquitination.
Metalloprotease that specifically cleaves 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains, leaving the last ubiquitin chain attached to its substrates. Catalytic subunit of the BRISC complex; does not have activity by itself, but needs to be associated into a heterotetramer with ABRAXAS2 for minimal in vitro activity (PubMed:26344097). Plays a role in regulating the onset of apoptosis via its role in modulating 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitination of target proteins (By similarity). Required for normal mitotic spindle assembly and microtubule attachment to kinetochores via its role in deubiquitinating spindle assembly factors (By similarity).
Cofactor
Zn(2+)
Subunit
Component of the BRCA1-A complex, at least composed of brca1, bard1, uimc1/rap80, abraxas1, brcc3/brcc36, babam2 and babam1/nba1. In the BRCA1-A complex, interacts directly with ABRAXAS1 and babam2. Component of the BRISC complex, at least composed of ABRAXAS2, brcc3/brcc36, babam2 and babam1/nba1. Within the complex, interacts directly with abraxas2. Both the BRCA1-A complex and the BRISC complex bind polyubiquitin (By similarity).
Component of the BRISC complex, at least composed of ABRAXAS2, BRCC3/BRCC36, BABAM2 and BABAM1/NBA1. Within the complex, interacts directly with ABRAXAS2. The heterodimer with ABRAXAS2 assembles into a heterotetramer. The BRISC complex binds polyubiquitin.
Component of the BRCA1-A complex, at least composed of brca1, bard1, uimc1/rap80, abraxas1, brcc3/brcc36, babam2 and babam1/nba1. In the BRCA1-A complex, interacts directly with abraxas1 and babam2. Component of the BRISC complex, at least composed of abraxas2, brcc3/brcc36, babam2 and babam1/nba1. Within the complex, interacts directly with abraxas2. Both the BRCA1-A complex and the BRISC complex bind polyubiquitin (By similarity).
Component of the BRISC complex, at least composed of ABRAXAS2, BRCC3/BRCC36, BABAM2 and BABAM1/NBA1. Within the complex, interacts directly with ABRAXAS2. The heterodimer with ABRAXAS2 assembles into a heterotetramer. The BRISC complex binds polyubiquitin.
Component of the BRCA1-A complex, at least composed of brca1, bard1, uimc1/rap80, abraxas1, brcc3/brcc36, babam2 and babam1/nba1. In the BRCA1-A complex, interacts directly with abraxas1 and babam2. Component of the BRISC complex, at least composed of abraxas2, brcc3/brcc36, babam2 and babam1/nba1. Within the complex, interacts directly with abraxas2. Both the BRCA1-A complex and the BRISC complex bind polyubiquitin (By similarity).
Similarity
Belongs to the peptidase M67A family. BRCC36 subfamily.
Keywords
Complete proteome
Hydrolase
Metal-binding
Metalloprotease
Protease
Reference proteome
Ubl conjugation pathway
Zinc
Cell cycle
Cell division
Chromatin regulator
Cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton
DNA damage
DNA repair
Mitosis
Nucleus
3D-structure
Coiled coil
Feature
chain Lys-63-specific deubiquitinase BRCC36-like
Uniprot
A0A2A4JWK8
A0A2H1W977
A0A212F6W2
S4PCT1
A0A3S2LVC6
H9JBC7
+ More
A0A194RB77 A0A0L7LE60 A0A194PDN5 A0A2A4JWZ6 A0A2T7NCK8 V4BG98 K1R0R3 A0A2P8YAA1 A0A2Z5TRJ1 V5IIZ7 A0A067QVS0 A0A2C9JF56 A0A210Q288 J3JYU2 K7IXJ9 A0A232EU46 N6ULW8 A0A293MEP4 A0A2A3E4J7 H3B4B8 A0A088A6H9 A0A151P8N4 A0A1U7RSM1 U3KAZ1 E1C8A6 A0A3B3S5D8 A0A1V4KYT2 A0A1W4WE61 R7U6V1 A0A218ULT7 V9KKD3 G3WEK8 A0A131XF68 A7SM50 A0A1W7RJ19 A0A3B1JQJ3 L7LX65 A0A3B4EJ64 H9G3Q5 A0A1W5A3I6 C3YJQ0 A0A2G8LBW4 A0A023GHH5 Q7M757 W5U945 A0A1L8F6Q4 Q66GV6 A0A224YTE2 A0A158NP23 A0A131YRF4 A0A195BXN5 A0A0R4IER2 A0A0M3KL72 A0A1S3RI09 W4YQI3 E2AXC7 A0A026W0T1 A0A1S2X2R6 B5X8M4 A0A0L7R8R7 A0A3Q1MRN1 Q4VA72 W5N8N8 F4WGK0 A0A195F0Z0 G3Q168 A0A151XDS1 A0A2U9CGR9 A0A3Q3M5N8 A0A0B8RYD9 J3SE22 T1E6E6 A0A098M1J7 U3EU66 A0A195DWS2 Q4SEG4 H3CY97 I3KZ08 A0A1W3JPW0 H2S9G6 A0A3B3ZNQ4 E9IEC0 A0A3P8YE19 A0A3Q3N217 A0A3B3ZMV5 A0A3B4ZYJ1 G3TUL5 A0A3Q1AK21 A0A3P8TRF8 A0A1S3GPJ2 A0A087YRW0 A0A0S7I0I1 H9H8T2
A0A194RB77 A0A0L7LE60 A0A194PDN5 A0A2A4JWZ6 A0A2T7NCK8 V4BG98 K1R0R3 A0A2P8YAA1 A0A2Z5TRJ1 V5IIZ7 A0A067QVS0 A0A2C9JF56 A0A210Q288 J3JYU2 K7IXJ9 A0A232EU46 N6ULW8 A0A293MEP4 A0A2A3E4J7 H3B4B8 A0A088A6H9 A0A151P8N4 A0A1U7RSM1 U3KAZ1 E1C8A6 A0A3B3S5D8 A0A1V4KYT2 A0A1W4WE61 R7U6V1 A0A218ULT7 V9KKD3 G3WEK8 A0A131XF68 A7SM50 A0A1W7RJ19 A0A3B1JQJ3 L7LX65 A0A3B4EJ64 H9G3Q5 A0A1W5A3I6 C3YJQ0 A0A2G8LBW4 A0A023GHH5 Q7M757 W5U945 A0A1L8F6Q4 Q66GV6 A0A224YTE2 A0A158NP23 A0A131YRF4 A0A195BXN5 A0A0R4IER2 A0A0M3KL72 A0A1S3RI09 W4YQI3 E2AXC7 A0A026W0T1 A0A1S2X2R6 B5X8M4 A0A0L7R8R7 A0A3Q1MRN1 Q4VA72 W5N8N8 F4WGK0 A0A195F0Z0 G3Q168 A0A151XDS1 A0A2U9CGR9 A0A3Q3M5N8 A0A0B8RYD9 J3SE22 T1E6E6 A0A098M1J7 U3EU66 A0A195DWS2 Q4SEG4 H3CY97 I3KZ08 A0A1W3JPW0 H2S9G6 A0A3B3ZNQ4 E9IEC0 A0A3P8YE19 A0A3Q3N217 A0A3B3ZMV5 A0A3B4ZYJ1 G3TUL5 A0A3Q1AK21 A0A3P8TRF8 A0A1S3GPJ2 A0A087YRW0 A0A0S7I0I1 H9H8T2
EC Number
3.4.19.-
Pubmed
22118469
23622113
19121390
26354079
26227816
23254933
+ More
22992520 29403074 26760975 25765539 24845553 15562597 28812685 22516182 20075255 28648823 23537049 9215903 22293439 15592404 29240929 24402279 21709235 28049606 17615350 26358130 25329095 25576852 21881562 18563158 29023486 15489334 16141072 12838346 23127152 27762356 28797301 21347285 26830274 23594743 26344097 20798317 24508170 30249741 20433749 19393038 21719571 25476704 23025625 23758969 25727380 23915248 15496914 25186727 21551351 25463417 21282665 25069045 17495919
22992520 29403074 26760975 25765539 24845553 15562597 28812685 22516182 20075255 28648823 23537049 9215903 22293439 15592404 29240929 24402279 21709235 28049606 17615350 26358130 25329095 25576852 21881562 18563158 29023486 15489334 16141072 12838346 23127152 27762356 28797301 21347285 26830274 23594743 26344097 20798317 24508170 30249741 20433749 19393038 21719571 25476704 23025625 23758969 25727380 23915248 15496914 25186727 21551351 25463417 21282665 25069045 17495919
EMBL
NWSH01000473
PCG76166.1
ODYU01007140
SOQ49655.1
AGBW02009960
OWR49486.1
+ More
GAIX01003996 JAA88564.1 RSAL01000172 RVE45138.1 BABH01030887 BABH01030888 KQ460398 KPJ15078.1 JTDY01001517 KOB73675.1 KQ459606 KPI91461.1 PCG76164.1 PZQS01000014 PVD18887.1 KB199651 ESP04837.1 JH817038 EKC34695.1 PYGN01000758 PSN41186.1 FX985822 BBA93709.1 GANP01002317 JAB82151.1 KK852954 KDR13285.1 NEDP02005212 OWF42851.1 BT128423 AEE63380.1 AAZX01004642 NNAY01002185 OXU21854.1 APGK01018457 KB740076 ENN81646.1 GFWV01013910 MAA38639.1 KZ288405 PBC26186.1 AFYH01058937 AFYH01058938 AFYH01058939 AFYH01058940 AKHW03000635 KYO45095.1 AGTO01010937 AC172026 LSYS01001150 OPJ89585.1 AMQN01010051 KB306898 ELT99386.1 MUZQ01000241 OWK54322.1 JW865884 AFO98401.1 AEFK01176309 GEFH01003813 JAP64768.1 DS469705 EDO35207.1 GDAY02000284 JAV51129.1 GACK01008852 JAA56182.1 AAWZ02029747 GG666520 EEN59357.1 MRZV01000133 PIK57741.1 GBBM01002002 JAC33416.1 BC120506 BC120508 AK134982 BN000130 JT408378 JT415653 AHH38325.1 CM004480 OCT67266.1 BC082208 GFPF01006387 MAA17533.1 ADTU01022128 GEDV01007871 JAP80686.1 KQ976394 KYM93352.1 CU539056 CU855912 AAGJ04049580 AAGJ04049581 GL443548 EFN61907.1 KK107536 QOIP01000008 EZA49191.1 RLU19806.1 BT047393 KQ414632 KOC67223.1 CR760965 BC096514 AHAT01007363 GL888137 EGI66665.1 KQ981891 KYN33822.1 KQ982268 KYQ58503.1 CP026258 AWP14906.1 GBSH01000432 JAG68592.1 JU173990 GBEX01000397 AFJ49516.1 JAI14163.1 GAAZ01000295 GBKC01000407 GBKD01000273 JAA97648.1 JAG45663.1 JAG47345.1 GBSI01000353 GBSI01000351 JAC96142.1 JAC96144.1 GAEP01000213 GBEW01000143 JAB54608.1 JAI10222.1 KQ980167 KYN17338.1 CAAE01014621 CAG00968.1 AERX01004656 GL762576 EFZ21081.1 AYCK01025600 GBYX01435653 JAO45682.1
GAIX01003996 JAA88564.1 RSAL01000172 RVE45138.1 BABH01030887 BABH01030888 KQ460398 KPJ15078.1 JTDY01001517 KOB73675.1 KQ459606 KPI91461.1 PCG76164.1 PZQS01000014 PVD18887.1 KB199651 ESP04837.1 JH817038 EKC34695.1 PYGN01000758 PSN41186.1 FX985822 BBA93709.1 GANP01002317 JAB82151.1 KK852954 KDR13285.1 NEDP02005212 OWF42851.1 BT128423 AEE63380.1 AAZX01004642 NNAY01002185 OXU21854.1 APGK01018457 KB740076 ENN81646.1 GFWV01013910 MAA38639.1 KZ288405 PBC26186.1 AFYH01058937 AFYH01058938 AFYH01058939 AFYH01058940 AKHW03000635 KYO45095.1 AGTO01010937 AC172026 LSYS01001150 OPJ89585.1 AMQN01010051 KB306898 ELT99386.1 MUZQ01000241 OWK54322.1 JW865884 AFO98401.1 AEFK01176309 GEFH01003813 JAP64768.1 DS469705 EDO35207.1 GDAY02000284 JAV51129.1 GACK01008852 JAA56182.1 AAWZ02029747 GG666520 EEN59357.1 MRZV01000133 PIK57741.1 GBBM01002002 JAC33416.1 BC120506 BC120508 AK134982 BN000130 JT408378 JT415653 AHH38325.1 CM004480 OCT67266.1 BC082208 GFPF01006387 MAA17533.1 ADTU01022128 GEDV01007871 JAP80686.1 KQ976394 KYM93352.1 CU539056 CU855912 AAGJ04049580 AAGJ04049581 GL443548 EFN61907.1 KK107536 QOIP01000008 EZA49191.1 RLU19806.1 BT047393 KQ414632 KOC67223.1 CR760965 BC096514 AHAT01007363 GL888137 EGI66665.1 KQ981891 KYN33822.1 KQ982268 KYQ58503.1 CP026258 AWP14906.1 GBSH01000432 JAG68592.1 JU173990 GBEX01000397 AFJ49516.1 JAI14163.1 GAAZ01000295 GBKC01000407 GBKD01000273 JAA97648.1 JAG45663.1 JAG47345.1 GBSI01000353 GBSI01000351 JAC96142.1 JAC96144.1 GAEP01000213 GBEW01000143 JAB54608.1 JAI10222.1 KQ980167 KYN17338.1 CAAE01014621 CAG00968.1 AERX01004656 GL762576 EFZ21081.1 AYCK01025600 GBYX01435653 JAO45682.1
Proteomes
UP000218220
UP000007151
UP000283053
UP000005204
UP000053240
UP000037510
+ More
UP000053268 UP000245119 UP000030746 UP000005408 UP000245037 UP000027135 UP000076420 UP000242188 UP000002358 UP000215335 UP000019118 UP000242457 UP000008672 UP000005203 UP000050525 UP000189705 UP000016665 UP000000539 UP000261540 UP000190648 UP000192223 UP000014760 UP000197619 UP000007648 UP000001593 UP000018467 UP000261440 UP000001646 UP000192224 UP000001554 UP000230750 UP000000589 UP000221080 UP000186698 UP000005205 UP000078540 UP000000437 UP000087266 UP000007110 UP000000311 UP000053097 UP000279307 UP000053825 UP000009136 UP000008143 UP000018468 UP000007755 UP000078541 UP000007635 UP000075809 UP000246464 UP000261660 UP000078492 UP000007303 UP000005207 UP000005226 UP000261520 UP000265140 UP000261640 UP000261400 UP000007646 UP000257160 UP000265080 UP000081671 UP000028760 UP000002280
UP000053268 UP000245119 UP000030746 UP000005408 UP000245037 UP000027135 UP000076420 UP000242188 UP000002358 UP000215335 UP000019118 UP000242457 UP000008672 UP000005203 UP000050525 UP000189705 UP000016665 UP000000539 UP000261540 UP000190648 UP000192223 UP000014760 UP000197619 UP000007648 UP000001593 UP000018467 UP000261440 UP000001646 UP000192224 UP000001554 UP000230750 UP000000589 UP000221080 UP000186698 UP000005205 UP000078540 UP000000437 UP000087266 UP000007110 UP000000311 UP000053097 UP000279307 UP000053825 UP000009136 UP000008143 UP000018468 UP000007755 UP000078541 UP000007635 UP000075809 UP000246464 UP000261660 UP000078492 UP000007303 UP000005207 UP000005226 UP000261520 UP000265140 UP000261640 UP000261400 UP000007646 UP000257160 UP000265080 UP000081671 UP000028760 UP000002280
ProteinModelPortal
A0A2A4JWK8
A0A2H1W977
A0A212F6W2
S4PCT1
A0A3S2LVC6
H9JBC7
+ More
A0A194RB77 A0A0L7LE60 A0A194PDN5 A0A2A4JWZ6 A0A2T7NCK8 V4BG98 K1R0R3 A0A2P8YAA1 A0A2Z5TRJ1 V5IIZ7 A0A067QVS0 A0A2C9JF56 A0A210Q288 J3JYU2 K7IXJ9 A0A232EU46 N6ULW8 A0A293MEP4 A0A2A3E4J7 H3B4B8 A0A088A6H9 A0A151P8N4 A0A1U7RSM1 U3KAZ1 E1C8A6 A0A3B3S5D8 A0A1V4KYT2 A0A1W4WE61 R7U6V1 A0A218ULT7 V9KKD3 G3WEK8 A0A131XF68 A7SM50 A0A1W7RJ19 A0A3B1JQJ3 L7LX65 A0A3B4EJ64 H9G3Q5 A0A1W5A3I6 C3YJQ0 A0A2G8LBW4 A0A023GHH5 Q7M757 W5U945 A0A1L8F6Q4 Q66GV6 A0A224YTE2 A0A158NP23 A0A131YRF4 A0A195BXN5 A0A0R4IER2 A0A0M3KL72 A0A1S3RI09 W4YQI3 E2AXC7 A0A026W0T1 A0A1S2X2R6 B5X8M4 A0A0L7R8R7 A0A3Q1MRN1 Q4VA72 W5N8N8 F4WGK0 A0A195F0Z0 G3Q168 A0A151XDS1 A0A2U9CGR9 A0A3Q3M5N8 A0A0B8RYD9 J3SE22 T1E6E6 A0A098M1J7 U3EU66 A0A195DWS2 Q4SEG4 H3CY97 I3KZ08 A0A1W3JPW0 H2S9G6 A0A3B3ZNQ4 E9IEC0 A0A3P8YE19 A0A3Q3N217 A0A3B3ZMV5 A0A3B4ZYJ1 G3TUL5 A0A3Q1AK21 A0A3P8TRF8 A0A1S3GPJ2 A0A087YRW0 A0A0S7I0I1 H9H8T2
A0A194RB77 A0A0L7LE60 A0A194PDN5 A0A2A4JWZ6 A0A2T7NCK8 V4BG98 K1R0R3 A0A2P8YAA1 A0A2Z5TRJ1 V5IIZ7 A0A067QVS0 A0A2C9JF56 A0A210Q288 J3JYU2 K7IXJ9 A0A232EU46 N6ULW8 A0A293MEP4 A0A2A3E4J7 H3B4B8 A0A088A6H9 A0A151P8N4 A0A1U7RSM1 U3KAZ1 E1C8A6 A0A3B3S5D8 A0A1V4KYT2 A0A1W4WE61 R7U6V1 A0A218ULT7 V9KKD3 G3WEK8 A0A131XF68 A7SM50 A0A1W7RJ19 A0A3B1JQJ3 L7LX65 A0A3B4EJ64 H9G3Q5 A0A1W5A3I6 C3YJQ0 A0A2G8LBW4 A0A023GHH5 Q7M757 W5U945 A0A1L8F6Q4 Q66GV6 A0A224YTE2 A0A158NP23 A0A131YRF4 A0A195BXN5 A0A0R4IER2 A0A0M3KL72 A0A1S3RI09 W4YQI3 E2AXC7 A0A026W0T1 A0A1S2X2R6 B5X8M4 A0A0L7R8R7 A0A3Q1MRN1 Q4VA72 W5N8N8 F4WGK0 A0A195F0Z0 G3Q168 A0A151XDS1 A0A2U9CGR9 A0A3Q3M5N8 A0A0B8RYD9 J3SE22 T1E6E6 A0A098M1J7 U3EU66 A0A195DWS2 Q4SEG4 H3CY97 I3KZ08 A0A1W3JPW0 H2S9G6 A0A3B3ZNQ4 E9IEC0 A0A3P8YE19 A0A3Q3N217 A0A3B3ZMV5 A0A3B4ZYJ1 G3TUL5 A0A3Q1AK21 A0A3P8TRF8 A0A1S3GPJ2 A0A087YRW0 A0A0S7I0I1 H9H8T2
PDB
5CW6
E-value=1.46813e-53,
Score=528
Ontologies
GO
GO:0070536
GO:0006281
GO:0070552
GO:0004843
GO:0070531
GO:0070537
GO:0000152
GO:0045739
GO:0072425
GO:0010165
GO:0031593
GO:0005737
GO:0006302
GO:0005654
GO:0030234
GO:0008237
GO:0036459
GO:0001525
GO:0005634
GO:0046872
GO:0010212
GO:0000922
GO:0051301
GO:0007049
GO:0016021
GO:0005515
GO:0003867
GO:0009448
GO:0019226
GO:0042065
GO:0042066
GO:0003707
GO:0043565
Topology
Subcellular location
Nucleus
Localizes at sites of DNA damage at double-strand breaks (DSBs). Interaction with abraxas2 retains brcc3 in the cytoplasm. With evidence from 2 publications.
Cytoplasm Localizes at sites of DNA damage at double-strand breaks (DSBs). Interaction with abraxas2 retains brcc3 in the cytoplasm. With evidence from 2 publications.
Cytoskeleton Localizes at sites of DNA damage at double-strand breaks (DSBs). Interaction with abraxas2 retains brcc3 in the cytoplasm. With evidence from 2 publications.
Spindle pole Localizes at sites of DNA damage at double-strand breaks (DSBs). Interaction with abraxas2 retains brcc3 in the cytoplasm. With evidence from 2 publications.
Cytoplasm Localizes at sites of DNA damage at double-strand breaks (DSBs). Interaction with abraxas2 retains brcc3 in the cytoplasm. With evidence from 2 publications.
Cytoskeleton Localizes at sites of DNA damage at double-strand breaks (DSBs). Interaction with abraxas2 retains brcc3 in the cytoplasm. With evidence from 2 publications.
Spindle pole Localizes at sites of DNA damage at double-strand breaks (DSBs). Interaction with abraxas2 retains brcc3 in the cytoplasm. With evidence from 2 publications.
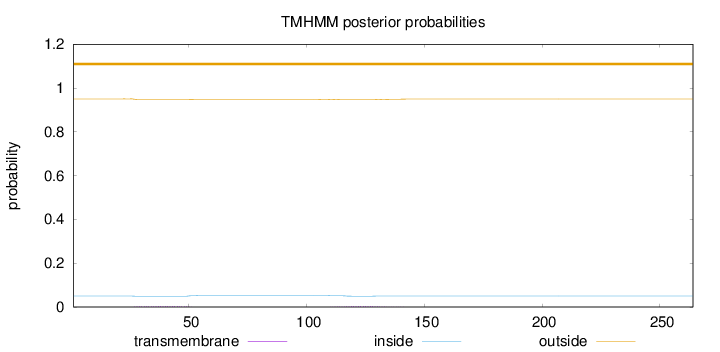
Length:
264
Number of predicted TMHs:
0
Exp number of AAs in TMHs:
0.15321
Exp number, first 60 AAs:
0.08105
Total prob of N-in:
0.04976
outside
1 - 264
Population Genetic Test Statistics
Pi
333.04527
Theta
212.310272
Tajima's D
1.661296
CLR
0.013715
CSRT
0.821258937053147
Interpretation
Uncertain
