Gene
KWMTBOMO04972
Pre Gene Modal
BGIBMGA007984
Annotation
PREDICTED:_NAD-dependent_protein_deacylase-like_[Papilio_xuthus]
Full name
NAD-dependent protein deacylase
+ More
NAD-dependent protein deacylase sirtuin-5, mitochondrial
NAD-dependent protein deacylase sirtuin-5, mitochondrial
Alternative Name
Regulatory protein SIR2 homolog 5
SIR2-like protein 5
SIR2-like protein 5
Location in the cell
Mitochondrial Reliability : 2.148
Sequence
CDS
ATGTGCCTTAGTTTATTGAAAACACTAAATCAGAGAGTCATTCCTTGTTATATTAATAAAGTCATGAGTTCAAGACAATCTAGTGATTTCTCAAAGTTCAGAGTTGCTTTAAAATCGGCAAAAGAAATAGTTATCTTATCTGGAGCCGGCATTAGTGCAGAATCTGGAATACCTACTTTTCGTGGTGCTGGAGGGCTTTGGAGGAAATATCAAGCTTCGGCCTTAGCAACACCAGGAGCTTTTAGAGAAAGTCCAAGCTTAGTATGGGAATTTTACCACTACAGAAGAGAGGTGGCAGCAAAGGCGAAGCCTAATGCGGGACATTTTGCTATTGCTAAATTCGAAGATAACCATGGATCCCAAAAAAAAATTACAGTAATTACTCAGAATGTGGATGGTTTACATGCAAGAGCAGGAACGAAAAGATTGATAGAGCTTCATGGAAATTTATACAAAACTCGATGTACAAAATGTAAGGAAGTATTGGTGAATAATGACAGCCCTATATGTGAGGCACTTGCAAATAGAGGAGCCCCAGATTCTAATATGGTGGGTTCTGATATTCCTGTGAAATTATTACCACACTGTAAAAAGGCTCATTGTGGAGCCTTGCTAAGACCCCACATTGTGTGGTTCGGTGAAAGTTTAGAACATGATATTTTAGAAGCAGCTGAACATGCAATGTCCACCTGTGATGTATGCCTAGTTGTTGGTACATCATCAGTGGTATATCCTGCGGCAATGTTTGCTCCGCAAGCAGCTTTGAGGGGTGCAATTGTAGCAGAATTTAATATAGAACCAACACCGGCCACACCTGATTTCCATTTTTACTTCGAAGGACCTTGTGGTACAACACTGCCACAAGCACTGGCTGATTAG
Protein
MCLSLLKTLNQRVIPCYINKVMSSRQSSDFSKFRVALKSAKEIVILSGAGISAESGIPTFRGAGGLWRKYQASALATPGAFRESPSLVWEFYHYRREVAAKAKPNAGHFAIAKFEDNHGSQKKITVITQNVDGLHARAGTKRLIELHGNLYKTRCTKCKEVLVNNDSPICEALANRGAPDSNMVGSDIPVKLLPHCKKAHCGALLRPHIVWFGESLEHDILEAAEHAMSTCDVCLVVGTSSVVYPAAMFAPQAALRGAIVAEFNIEPTPATPDFHFYFEGPCGTTLPQALAD
Summary
Description
NAD-dependent lysine demalonylase, desuccinylase and deglutarylase that specifically removes malonyl, succinyl and glutaryl groups on target proteins. Has weak NAD-dependent protein deacetylase activity; however this activity may not be physiologically relevant in vivo.
NAD-dependent lysine demalonylase, desuccinylase and deglutarylase that specifically removes malonyl, succinyl and glutaryl groups on target proteins. Activates CPS1 and contributes to the regulation of blood ammonia levels during prolonged fasting: acts by mediating desuccinylation and deglutarylation of CPS1, thereby increasing CPS1 activity in response to elevated NAD levels during fasting. Activates SOD1 by mediating its desuccinylation, leading to reduced reactive oxygen species. Modulates ketogenesis through the desuccinylation and activation of HMGCS2. Has weak NAD-dependent protein deacetylase activity; however this activity may not be physiologically relevant in vivo. Can deacetylate cytochrome c (CYCS) and a number of other proteins in vitro such as Uox.
NAD-dependent lysine demalonylase, desuccinylase and deglutarylase that specifically removes malonyl, succinyl and glutaryl groups on target proteins. Activates CPS1 and contributes to the regulation of blood ammonia levels during prolonged fasting: acts by mediating desuccinylation and deglutarylation of CPS1, thereby increasing CPS1 activity in response to elevated NAD levels during fasting. Activates SOD1 by mediating its desuccinylation, leading to reduced reactive oxygen species. Activates SHMT2 by mediating its desuccinylation. Modulates ketogenesis through the desuccinylation and activation of HMGCS2. Has weak NAD-dependent protein deacetylase activity; however this activity may not be physiologically relevant in vivo. Can deacetylate cytochrome c (CYCS) and a number of other proteins in vitro such as UOX.
NAD-dependent lysine demalonylase, desuccinylase and deglutarylase that specifically removes malonyl, succinyl and glutaryl groups on target proteins (PubMed:21908771, PubMed:22076378, PubMed:24703693, PubMed:29180469). Activates CPS1 and contributes to the regulation of blood ammonia levels during prolonged fasting: acts by mediating desuccinylation and deglutarylation of CPS1, thereby increasing CPS1 activity in response to elevated NAD levels during fasting (PubMed:22076378, PubMed:24703693). Activates SOD1 by mediating its desuccinylation, leading to reduced reactive oxygen species (PubMed:24140062). Activates SHMT2 by mediating its desuccinylation (PubMed:29180469). Modulates ketogenesis through the desuccinylation and activation of HMGCS2 (By similarity). Has weak NAD-dependent protein deacetylase activity; however this activity may not be physiologically relevant in vivo. Can deacetylate cytochrome c (CYCS) and a number of other proteins in vitro such as UOX.
NAD-dependent lysine demalonylase, desuccinylase and deglutarylase that specifically removes malonyl, succinyl and glutaryl groups on target proteins. Activates CPS1 and contributes to the regulation of blood ammonia levels during prolonged fasting: acts by mediating desuccinylation and deglutarylation of CPS1, thereby increasing CPS1 activity in response to elevated NAD levels during fasting. Activates SOD1 by mediating its desuccinylation, leading to reduced reactive oxygen species. Modulates ketogenesis through the desuccinylation and activation of HMGCS2. Has weak NAD-dependent protein deacetylase activity; however this activity may not be physiologically relevant in vivo. Can deacetylate cytochrome c (CYCS) and a number of other proteins in vitro such as Uox.
NAD-dependent lysine demalonylase, desuccinylase and deglutarylase that specifically removes malonyl, succinyl and glutaryl groups on target proteins. Activates CPS1 and contributes to the regulation of blood ammonia levels during prolonged fasting: acts by mediating desuccinylation and deglutarylation of CPS1, thereby increasing CPS1 activity in response to elevated NAD levels during fasting. Activates SOD1 by mediating its desuccinylation, leading to reduced reactive oxygen species. Activates SHMT2 by mediating its desuccinylation. Modulates ketogenesis through the desuccinylation and activation of HMGCS2. Has weak NAD-dependent protein deacetylase activity; however this activity may not be physiologically relevant in vivo. Can deacetylate cytochrome c (CYCS) and a number of other proteins in vitro such as UOX.
NAD-dependent lysine demalonylase, desuccinylase and deglutarylase that specifically removes malonyl, succinyl and glutaryl groups on target proteins (PubMed:21908771, PubMed:22076378, PubMed:24703693, PubMed:29180469). Activates CPS1 and contributes to the regulation of blood ammonia levels during prolonged fasting: acts by mediating desuccinylation and deglutarylation of CPS1, thereby increasing CPS1 activity in response to elevated NAD levels during fasting (PubMed:22076378, PubMed:24703693). Activates SOD1 by mediating its desuccinylation, leading to reduced reactive oxygen species (PubMed:24140062). Activates SHMT2 by mediating its desuccinylation (PubMed:29180469). Modulates ketogenesis through the desuccinylation and activation of HMGCS2 (By similarity). Has weak NAD-dependent protein deacetylase activity; however this activity may not be physiologically relevant in vivo. Can deacetylate cytochrome c (CYCS) and a number of other proteins in vitro such as UOX.
Catalytic Activity
H2O + N(6)-glutaryl-L-lysyl-[protein] + NAD(+) = 2''-O-glutaryl-ADP-D-ribose + L-lysyl-[protein] + nicotinamide
H2O + N(6)-malonyl-L-lysyl-[protein] + NAD(+) = 2''-O-malonyl-ADP-D-ribose + L-lysyl-[protein] + nicotinamide
H2O + N(6)-succinyl-L-lysyl-[protein] + NAD(+) = 2''-O-succinyl-ADP-D-ribose + L-lysyl-[protein] + nicotinamide
H2O + N(6)-malonyl-L-lysyl-[protein] + NAD(+) = 2''-O-malonyl-ADP-D-ribose + L-lysyl-[protein] + nicotinamide
H2O + N(6)-succinyl-L-lysyl-[protein] + NAD(+) = 2''-O-succinyl-ADP-D-ribose + L-lysyl-[protein] + nicotinamide
Cofactor
Zn(2+)
Biophysicochemical Properties
6.1 uM for a synthetic histone H3K9 malonyllysine peptide
5.8 uM for a synthetic histone H3K9 succinyllysine peptide
8.7 uM for a synthetic GLUD1 peptide malonylated at 'Lys-503'
14 uM for a synthetic GLUD1 peptide succinylated at 'Lys-503'
150 uM for a synthetic ACSS1 peptide malonylated at 'Lys-628'
450 uM for a synthetic ACSS1 peptide succinylated at 'Lys-628'
5.8 uM for a synthetic histone H3K9 succinyllysine peptide
8.7 uM for a synthetic GLUD1 peptide malonylated at 'Lys-503'
14 uM for a synthetic GLUD1 peptide succinylated at 'Lys-503'
150 uM for a synthetic ACSS1 peptide malonylated at 'Lys-628'
450 uM for a synthetic ACSS1 peptide succinylated at 'Lys-628'
Subunit
Monomer. Homodimer. Interacts with CPS1.
Monomer. Homodimer. Interacts with CPS1. Interacts with PCCA (By similarity).
Interacts with CPS1 (By similarity). Interacts with PCCA (PubMed:23438705). Monomer (PubMed:17355872). Homodimer (PubMed:17355872). Forms homodimers upon suramin binding (PubMed:17355872).
Monomer. Homodimer. Interacts with CPS1. Interacts with PCCA (By similarity).
Interacts with CPS1 (By similarity). Interacts with PCCA (PubMed:23438705). Monomer (PubMed:17355872). Homodimer (PubMed:17355872). Forms homodimers upon suramin binding (PubMed:17355872).
Miscellaneous
The mechanism of demalonylation and desuccinylation involves the presence of a 1',2'-cyclic intermediate, suggesting that sirtuins use the ADP-ribose-peptidylamidate mechanism to remove acyl groups from substrate lysine residues.
This protein may be expected to contain an N-terminal transit peptide but none has been predicted.
This protein may be expected to contain an N-terminal transit peptide but none has been predicted.
Similarity
Belongs to the sirtuin family. Class III subfamily.
Keywords
Complete proteome
Cytoplasm
Hydrolase
Metal-binding
Mitochondrion
NAD
Nucleus
Reference proteome
Transit peptide
Zinc
Alternative splicing
3D-structure
Polymorphism
Feature
chain NAD-dependent protein deacylase sirtuin-5, mitochondrial
splice variant In isoform 2.
sequence variant In dbSNP:rs9464003.
splice variant In isoform 2.
sequence variant In dbSNP:rs9464003.
Uniprot
H9JEN7
A0A2A4IU40
A0A2A4J757
A0A194PE30
A0A2W1BLQ1
A0A194QKF9
+ More
A0A212F1S9 A0A2H1W3C4 A0A3S2TCY5 A0A0L7LGG5 A0A2W1B9B8 A0A2A4J4P9 A0A2P8YXP3 T1JM32 A0A0L8FJ96 A0A1S3I9P2 A0A1S3I3K6 A0A384C9F6 A0A3Q7W2D8 G1L0W8 A0A0A9VU74 R7TYG4 A0A347ZJG9 A0A347ZJH0 A0A2K5Z885 U6CSQ7 M3XNN7 G9KNZ1 L8I353 A0A1S3ARI7 A0A2U3ZJM8 A0A2Y9HU99 A0A2Y9KHV5 A0A2A4J8L1 A0A3Q7S747 A0A232EQW5 E2RDZ6 A0A0D9R5A6 A0A2K6EL10 G1SSN2 A0A3B3DLW2 A0A2K5D7U6 A0A1S3WWN1 L5KVZ6 G7MQR7 A0A1B6F0Z9 A0A2H1V7W5 A0A1U7TB08 I3MLJ1 T1FM78 V3ZQA2 A0A2K6KGU3 A0A2J8WN49 Q5R6G3 A0A2K5U3X0 Q3ZBQ0 A0A2A4IVN0 G7P4G1 F7EZ75 U3FQC2 A0A2K6PGP2 A0A341CYS1 A0A2K6SXL1 A0A024R012 Q9NXA8 A0A2Y9P5P3 A0A1B6MII4 A0A2K5IXA9 H2MC35 H2XWF2 A0A340WH59 A0A3Q7QM78 A0A2R9AH39 K7AYD4 A0A1W5BBZ1 A0A2I3G514 A0A3P9K193 A0A1U7QFA6 B0FWP7 G3H0G1 A0A093PXQ6 A0A2R5LA13 D7PD35 H0Z6V4 A0A0N7ZCB6 Q6DHI5 K7CAU0 A0A093FW32 A0A1B6J2U7 F6S899 A7XXV9 R9PXP3 E1BRE2 A0A2C9JNR9 A0A224YUG4 A0A131YYA3 A0A2K5SEN1 W5PVL7 E9GD30
A0A212F1S9 A0A2H1W3C4 A0A3S2TCY5 A0A0L7LGG5 A0A2W1B9B8 A0A2A4J4P9 A0A2P8YXP3 T1JM32 A0A0L8FJ96 A0A1S3I9P2 A0A1S3I3K6 A0A384C9F6 A0A3Q7W2D8 G1L0W8 A0A0A9VU74 R7TYG4 A0A347ZJG9 A0A347ZJH0 A0A2K5Z885 U6CSQ7 M3XNN7 G9KNZ1 L8I353 A0A1S3ARI7 A0A2U3ZJM8 A0A2Y9HU99 A0A2Y9KHV5 A0A2A4J8L1 A0A3Q7S747 A0A232EQW5 E2RDZ6 A0A0D9R5A6 A0A2K6EL10 G1SSN2 A0A3B3DLW2 A0A2K5D7U6 A0A1S3WWN1 L5KVZ6 G7MQR7 A0A1B6F0Z9 A0A2H1V7W5 A0A1U7TB08 I3MLJ1 T1FM78 V3ZQA2 A0A2K6KGU3 A0A2J8WN49 Q5R6G3 A0A2K5U3X0 Q3ZBQ0 A0A2A4IVN0 G7P4G1 F7EZ75 U3FQC2 A0A2K6PGP2 A0A341CYS1 A0A2K6SXL1 A0A024R012 Q9NXA8 A0A2Y9P5P3 A0A1B6MII4 A0A2K5IXA9 H2MC35 H2XWF2 A0A340WH59 A0A3Q7QM78 A0A2R9AH39 K7AYD4 A0A1W5BBZ1 A0A2I3G514 A0A3P9K193 A0A1U7QFA6 B0FWP7 G3H0G1 A0A093PXQ6 A0A2R5LA13 D7PD35 H0Z6V4 A0A0N7ZCB6 Q6DHI5 K7CAU0 A0A093FW32 A0A1B6J2U7 F6S899 A7XXV9 R9PXP3 E1BRE2 A0A2C9JNR9 A0A224YUG4 A0A131YYA3 A0A2K5SEN1 W5PVL7 E9GD30
EC Number
3.5.1.-
Pubmed
19121390
26354079
28756777
22118469
26227816
29403074
+ More
24813606 20010809 25401762 23254933 23236062 22751099 28648823 16341006 21993624 29451363 23258410 22002653 25319552 17431167 25243066 25362486 11181995 10381378 14702039 17974005 14574404 15489334 16079181 18680753 21269460 21143562 21908771 23028781 24140062 23438705 23806337 24703693 24275569 29180469 17355872 22076378 22767592 22849721 23185430 17554307 12481130 15114417 22722832 16136131 26319212 19389481 30723633 21804562 20725513 20360741 23594743 19892987 15592404 15562597 28797301 26830274 20809919 21292972
24813606 20010809 25401762 23254933 23236062 22751099 28648823 16341006 21993624 29451363 23258410 22002653 25319552 17431167 25243066 25362486 11181995 10381378 14702039 17974005 14574404 15489334 16079181 18680753 21269460 21143562 21908771 23028781 24140062 23438705 23806337 24703693 24275569 29180469 17355872 22076378 22767592 22849721 23185430 17554307 12481130 15114417 22722832 16136131 26319212 19389481 30723633 21804562 20725513 20360741 23594743 19892987 15592404 15562597 28797301 26830274 20809919 21292972
EMBL
BABH01023649
NWSH01006780
PCG63241.1
NWSH01002634
PCG67791.1
KQ459606
+ More
KPI91283.1 KZ149974 PZC75979.1 KQ461198 KPJ06017.1 AGBW02010825 OWR47681.1 ODYU01006040 SOQ47533.1 RSAL01000337 RVE42433.1 JTDY01001216 KOB74505.1 KZ150212 PZC72172.1 NWSH01003389 PCG66393.1 PYGN01000298 PSN49016.1 JH431841 KQ430417 KOF64184.1 ACTA01040630 ACTA01048630 GBHO01044838 GBHO01044836 GBHO01044834 GBHO01040378 GBRD01007573 JAF98765.1 JAF98767.1 JAF98769.1 JAG03226.1 JAG58248.1 AMQN01010365 KB307653 ELT98667.1 FX985737 BBA84475.1 FX985738 BBA84476.1 HAAF01001889 CCP73715.1 AEYP01034983 AEYP01034984 JP018022 AES06620.1 JH882311 ELR49979.1 PCG63243.1 PCG67790.1 NNAY01002706 OXU20738.1 AQIB01159368 AAGW02052169 KB030554 ELK14968.1 JU333683 JV046590 CM001256 AFE77438.1 AFI36661.1 EHH17963.1 GECZ01029545 GECZ01025879 GECZ01013838 JAS40224.1 JAS43890.1 JAS55931.1 ODYU01000891 SOQ36334.1 AGTP01056265 AMQM01000782 KB096742 ESO02068.1 KB203049 ESO86512.1 NDHI03003384 PNJ71195.1 CR858318 CR860527 AQIA01052732 GQ166651 BC103176 PCG63242.1 CM001279 EHH52724.1 GAMT01006912 GAMS01004998 GAMR01003110 GAMQ01001890 GAMP01008095 JAB04949.1 JAB18138.1 JAB30822.1 JAB39961.1 JAB44660.1 CH471087 EAW55334.1 AF083110 AK000355 AK294162 AK302467 AM393414 AL441883 BC000126 GEBQ01004275 JAT35702.1 EAAA01001018 AJFE02080843 AJFE02080844 AACZ04065916 GABC01004479 GABD01002959 GABE01004668 NBAG03000244 JAA06859.1 JAA30141.1 JAA40071.1 PNI62788.1 ADFV01015635 ADFV01015636 ADFV01015637 ADFV01015638 ADFV01015639 ADFV01015640 ADFV01015641 EU357901 DQIR01075620 DQIR01075621 DQIR01082689 DQIR01099517 DQIR01103593 DQIR01135437 DQIR01135438 ABY65335.1 HDA31096.1 JH000091 EGV92882.1 KL671098 KFW81166.1 GGLE01002192 MBY06318.1 GU255947 ADI24340.1 ABQF01024072 GDRN01069784 JAI63992.1 BX511260 BC075987 GABF01000825 JAA21320.1 KL214871 KFV62135.1 GECU01014219 JAS93487.1 EU100953 ABU89799.1 AADN04000074 KX400578 APT36903.1 AADN02027504 GFPF01006767 MAA17913.1 GEDV01005025 JAP83532.1 AMGL01059584 AMGL01059585 GL732539
KPI91283.1 KZ149974 PZC75979.1 KQ461198 KPJ06017.1 AGBW02010825 OWR47681.1 ODYU01006040 SOQ47533.1 RSAL01000337 RVE42433.1 JTDY01001216 KOB74505.1 KZ150212 PZC72172.1 NWSH01003389 PCG66393.1 PYGN01000298 PSN49016.1 JH431841 KQ430417 KOF64184.1 ACTA01040630 ACTA01048630 GBHO01044838 GBHO01044836 GBHO01044834 GBHO01040378 GBRD01007573 JAF98765.1 JAF98767.1 JAF98769.1 JAG03226.1 JAG58248.1 AMQN01010365 KB307653 ELT98667.1 FX985737 BBA84475.1 FX985738 BBA84476.1 HAAF01001889 CCP73715.1 AEYP01034983 AEYP01034984 JP018022 AES06620.1 JH882311 ELR49979.1 PCG63243.1 PCG67790.1 NNAY01002706 OXU20738.1 AQIB01159368 AAGW02052169 KB030554 ELK14968.1 JU333683 JV046590 CM001256 AFE77438.1 AFI36661.1 EHH17963.1 GECZ01029545 GECZ01025879 GECZ01013838 JAS40224.1 JAS43890.1 JAS55931.1 ODYU01000891 SOQ36334.1 AGTP01056265 AMQM01000782 KB096742 ESO02068.1 KB203049 ESO86512.1 NDHI03003384 PNJ71195.1 CR858318 CR860527 AQIA01052732 GQ166651 BC103176 PCG63242.1 CM001279 EHH52724.1 GAMT01006912 GAMS01004998 GAMR01003110 GAMQ01001890 GAMP01008095 JAB04949.1 JAB18138.1 JAB30822.1 JAB39961.1 JAB44660.1 CH471087 EAW55334.1 AF083110 AK000355 AK294162 AK302467 AM393414 AL441883 BC000126 GEBQ01004275 JAT35702.1 EAAA01001018 AJFE02080843 AJFE02080844 AACZ04065916 GABC01004479 GABD01002959 GABE01004668 NBAG03000244 JAA06859.1 JAA30141.1 JAA40071.1 PNI62788.1 ADFV01015635 ADFV01015636 ADFV01015637 ADFV01015638 ADFV01015639 ADFV01015640 ADFV01015641 EU357901 DQIR01075620 DQIR01075621 DQIR01082689 DQIR01099517 DQIR01103593 DQIR01135437 DQIR01135438 ABY65335.1 HDA31096.1 JH000091 EGV92882.1 KL671098 KFW81166.1 GGLE01002192 MBY06318.1 GU255947 ADI24340.1 ABQF01024072 GDRN01069784 JAI63992.1 BX511260 BC075987 GABF01000825 JAA21320.1 KL214871 KFV62135.1 GECU01014219 JAS93487.1 EU100953 ABU89799.1 AADN04000074 KX400578 APT36903.1 AADN02027504 GFPF01006767 MAA17913.1 GEDV01005025 JAP83532.1 AMGL01059584 AMGL01059585 GL732539
Proteomes
UP000005204
UP000218220
UP000053268
UP000053240
UP000007151
UP000283053
+ More
UP000037510 UP000245037 UP000053454 UP000085678 UP000261680 UP000291021 UP000286642 UP000008912 UP000014760 UP000233140 UP000000715 UP000079721 UP000245340 UP000248481 UP000248482 UP000286640 UP000215335 UP000002254 UP000029965 UP000233160 UP000001811 UP000261560 UP000233020 UP000010552 UP000189704 UP000005215 UP000015101 UP000030746 UP000233180 UP000001595 UP000233100 UP000009136 UP000009130 UP000006718 UP000008225 UP000233200 UP000252040 UP000233220 UP000005640 UP000248483 UP000233080 UP000001038 UP000008144 UP000265300 UP000286641 UP000240080 UP000002277 UP000001073 UP000265180 UP000189706 UP000001075 UP000053258 UP000007754 UP000000437 UP000053875 UP000002281 UP000000539 UP000076420 UP000233040 UP000002356 UP000000305
UP000037510 UP000245037 UP000053454 UP000085678 UP000261680 UP000291021 UP000286642 UP000008912 UP000014760 UP000233140 UP000000715 UP000079721 UP000245340 UP000248481 UP000248482 UP000286640 UP000215335 UP000002254 UP000029965 UP000233160 UP000001811 UP000261560 UP000233020 UP000010552 UP000189704 UP000005215 UP000015101 UP000030746 UP000233180 UP000001595 UP000233100 UP000009136 UP000009130 UP000006718 UP000008225 UP000233200 UP000252040 UP000233220 UP000005640 UP000248483 UP000233080 UP000001038 UP000008144 UP000265300 UP000286641 UP000240080 UP000002277 UP000001073 UP000265180 UP000189706 UP000001075 UP000053258 UP000007754 UP000000437 UP000053875 UP000002281 UP000000539 UP000076420 UP000233040 UP000002356 UP000000305
Pfam
PF02146 SIR2
Interpro
SUPFAM
SSF52467
SSF52467
Gene 3D
ProteinModelPortal
H9JEN7
A0A2A4IU40
A0A2A4J757
A0A194PE30
A0A2W1BLQ1
A0A194QKF9
+ More
A0A212F1S9 A0A2H1W3C4 A0A3S2TCY5 A0A0L7LGG5 A0A2W1B9B8 A0A2A4J4P9 A0A2P8YXP3 T1JM32 A0A0L8FJ96 A0A1S3I9P2 A0A1S3I3K6 A0A384C9F6 A0A3Q7W2D8 G1L0W8 A0A0A9VU74 R7TYG4 A0A347ZJG9 A0A347ZJH0 A0A2K5Z885 U6CSQ7 M3XNN7 G9KNZ1 L8I353 A0A1S3ARI7 A0A2U3ZJM8 A0A2Y9HU99 A0A2Y9KHV5 A0A2A4J8L1 A0A3Q7S747 A0A232EQW5 E2RDZ6 A0A0D9R5A6 A0A2K6EL10 G1SSN2 A0A3B3DLW2 A0A2K5D7U6 A0A1S3WWN1 L5KVZ6 G7MQR7 A0A1B6F0Z9 A0A2H1V7W5 A0A1U7TB08 I3MLJ1 T1FM78 V3ZQA2 A0A2K6KGU3 A0A2J8WN49 Q5R6G3 A0A2K5U3X0 Q3ZBQ0 A0A2A4IVN0 G7P4G1 F7EZ75 U3FQC2 A0A2K6PGP2 A0A341CYS1 A0A2K6SXL1 A0A024R012 Q9NXA8 A0A2Y9P5P3 A0A1B6MII4 A0A2K5IXA9 H2MC35 H2XWF2 A0A340WH59 A0A3Q7QM78 A0A2R9AH39 K7AYD4 A0A1W5BBZ1 A0A2I3G514 A0A3P9K193 A0A1U7QFA6 B0FWP7 G3H0G1 A0A093PXQ6 A0A2R5LA13 D7PD35 H0Z6V4 A0A0N7ZCB6 Q6DHI5 K7CAU0 A0A093FW32 A0A1B6J2U7 F6S899 A7XXV9 R9PXP3 E1BRE2 A0A2C9JNR9 A0A224YUG4 A0A131YYA3 A0A2K5SEN1 W5PVL7 E9GD30
A0A212F1S9 A0A2H1W3C4 A0A3S2TCY5 A0A0L7LGG5 A0A2W1B9B8 A0A2A4J4P9 A0A2P8YXP3 T1JM32 A0A0L8FJ96 A0A1S3I9P2 A0A1S3I3K6 A0A384C9F6 A0A3Q7W2D8 G1L0W8 A0A0A9VU74 R7TYG4 A0A347ZJG9 A0A347ZJH0 A0A2K5Z885 U6CSQ7 M3XNN7 G9KNZ1 L8I353 A0A1S3ARI7 A0A2U3ZJM8 A0A2Y9HU99 A0A2Y9KHV5 A0A2A4J8L1 A0A3Q7S747 A0A232EQW5 E2RDZ6 A0A0D9R5A6 A0A2K6EL10 G1SSN2 A0A3B3DLW2 A0A2K5D7U6 A0A1S3WWN1 L5KVZ6 G7MQR7 A0A1B6F0Z9 A0A2H1V7W5 A0A1U7TB08 I3MLJ1 T1FM78 V3ZQA2 A0A2K6KGU3 A0A2J8WN49 Q5R6G3 A0A2K5U3X0 Q3ZBQ0 A0A2A4IVN0 G7P4G1 F7EZ75 U3FQC2 A0A2K6PGP2 A0A341CYS1 A0A2K6SXL1 A0A024R012 Q9NXA8 A0A2Y9P5P3 A0A1B6MII4 A0A2K5IXA9 H2MC35 H2XWF2 A0A340WH59 A0A3Q7QM78 A0A2R9AH39 K7AYD4 A0A1W5BBZ1 A0A2I3G514 A0A3P9K193 A0A1U7QFA6 B0FWP7 G3H0G1 A0A093PXQ6 A0A2R5LA13 D7PD35 H0Z6V4 A0A0N7ZCB6 Q6DHI5 K7CAU0 A0A093FW32 A0A1B6J2U7 F6S899 A7XXV9 R9PXP3 E1BRE2 A0A2C9JNR9 A0A224YUG4 A0A131YYA3 A0A2K5SEN1 W5PVL7 E9GD30
PDB
5XHS
E-value=4.66739e-95,
Score=886
Ontologies
GO
GO:0005739
GO:0034979
GO:0036055
GO:0036054
GO:0008270
GO:0070403
GO:0005829
GO:0005634
GO:0010566
GO:0005743
GO:0005758
GO:2000378
GO:0061697
GO:0005759
GO:0036048
GO:0036046
GO:0000035
GO:0006476
GO:0036047
GO:0036049
GO:0031667
GO:0010667
GO:0003950
GO:0061698
GO:0007005
GO:0006342
GO:0006471
GO:1901363
Topology
Subcellular location
Mitochondrion
Cytoplasm Mainly mitochondrial. Also present extramitochondrially, with a fraction present in the cytosol and very small amounts also detected in the nucleus. With evidence from 1 publications.
Cytosol Mainly mitochondrial. Also present extramitochondrially, with a fraction present in the cytosol and very small amounts also detected in the nucleus. With evidence from 1 publications.
Nucleus Mainly mitochondrial. Also present extramitochondrially, with a fraction present in the cytosol and very small amounts also detected in the nucleus. With evidence from 1 publications.
Mitochondrion matrix
Mitochondrion intermembrane space
Cytoplasm Mainly mitochondrial. Also present extramitochondrially, with a fraction present in the cytosol and very small amounts also detected in the nucleus. With evidence from 1 publications.
Cytosol Mainly mitochondrial. Also present extramitochondrially, with a fraction present in the cytosol and very small amounts also detected in the nucleus. With evidence from 1 publications.
Nucleus Mainly mitochondrial. Also present extramitochondrially, with a fraction present in the cytosol and very small amounts also detected in the nucleus. With evidence from 1 publications.
Mitochondrion matrix
Mitochondrion intermembrane space
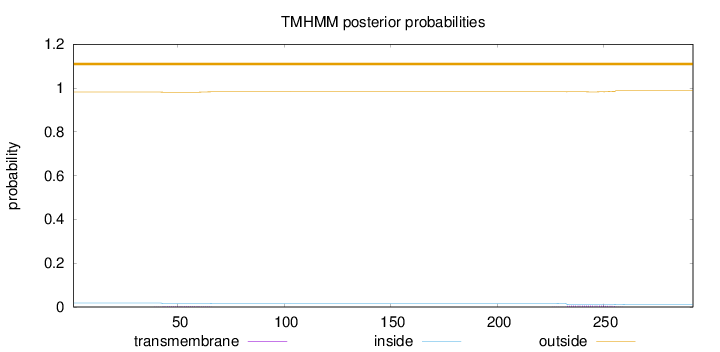
Length:
292
Number of predicted TMHs:
0
Exp number of AAs in TMHs:
0.20787
Exp number, first 60 AAs:
0.05784
Total prob of N-in:
0.01851
outside
1 - 292
Population Genetic Test Statistics
Pi
35.389269
Theta
46.457822
Tajima's D
-1.157083
CLR
0
CSRT
0.115194240287986
Interpretation
Uncertain
