Gene
KWMTBOMO04369
Pre Gene Modal
BGIBMGA005251
Annotation
PREDICTED:_centromere_protein_S-like_[Papilio_xuthus]
Full name
Centromere protein S
Alternative Name
Apoptosis-inducing TAF9-like domain-containing protein 1
FANCM-associated histone fold protein 1
FANCM-interacting histone fold protein 1
Fanconi anemia-associated polypeptide of 16 kDa
FANCM-associated histone fold protein 1
FANCM-interacting histone fold protein 1
Fanconi anemia-associated polypeptide of 16 kDa
Location in the cell
Nuclear Reliability : 2.341
Sequence
CDS
ATGTCTGCTTTTGAAGATTTATCTGCTTCGCAAAGGCTACGTGCAGCGTTAAAGCGGGACGTAACAGCCATCTGTTTGGAATCAACTGTCGGATTGGAAATCACCAAACCAGCAATGGACTTAATACTAGAACTGATTTATAAGAAGCTGTCTGTCTACGCCTCTGATTTAGAAGTCTTCGCAAGGCATGCTAGACGCTGCAAAATCCAAGGGGAAGATGTCAAGCTACTGGTGAGACGAAACAAATCTTTACGATCTCAACTTGAATCGAGGTCCCCAACAGCGGCTCTCAAGCGCAAGTCATCGCTCGCCGAAGATATATTCGAAGACGCATCCTCCAACTTTGACGAGCCCGCAATGAAAGACAAAATGCGCAAGGAAGAGCCGCCAATGGAAGACGCAATTGACATGACCGTTGAAAATGTCGTCGATTTGACCGCCGATTAA
Protein
MSAFEDLSASQRLRAALKRDVTAICLESTVGLEITKPAMDLILELIYKKLSVYASDLEVFARHARRCKIQGEDVKLLVRRNKSLRSQLESRSPTAALKRKSSLAEDIFEDASSNFDEPAMKDKMRKEEPPMEDAIDMTVENVVDLTAD
Summary
Description
DNA-binding component of the Fanconi anemia (FA) core complex. Required for the normal activation of the FA pathway, leading to monoubiquitination of the FANCI-FANCD2 complex in response to DNA damage, cellular resistance to DNA cross-linking drugs, and prevention of chromosomal breakage (PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429). In complex with CENPX (MHF heterodimer), crucial cofactor for FANCM in both binding and ATP-dependent remodeling of DNA. Stabilizes FANCM (PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429). In complex with CENPX and FANCM (but not other FANC proteins), rapidly recruited to blocked forks and promotes gene conversion at blocked replication forks (PubMed:20347428). In complex with CENPT, CENPW and CENPX (CENP-T-W-S-X heterotetramer), involved in the formation of a functional kinetochore outer plate, which is essential for kinetochore-microtubule attachment and faithful mitotic progression (PubMed:19620631). As a component of MHF and CENP-T-W-S-X complexes, binds DNA and bends it to form a nucleosome-like structure (PubMed:20347428, PubMed:22304917). DNA-binding function is fulfilled in the presence of CENPX, with the following preference for DNA substates: Holliday junction > double-stranded > splay arm > single-stranded. Does not bind DNA on its own (PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429).
Subunit
Heterodimer with CENPX, sometimes called MHF; this interaction stabilizes both partners (PubMed:19620631, PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429, PubMed:24522885). MHF heterodimers can assemble to form tetrameric structures (PubMed:22304917). MHF also coassemble with CENPT-CENPW heterodimers at centromeres to form the tetrameric CENP-T-W-S-X complex (PubMed:22304917, PubMed:24522885). Forms a discrete complex with FANCM and CENPX, called FANCM-MHF; this interaction, probably mediated by direct binding between CENPS and FANCM, leads to synergistic activation of double-stranded DNA binding and strongly stimulates FANCM-mediated DNA remodeling (PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429). Recruited by FANCM to the Fanconi anemia (FA) core complex, which consists of CENPS, CENPX, FANCA, FANCB, FANCC, FANCE, FANCF, FANCG, FANCL, FANCM, FAAP24 and FAAP100. The FA core complex associates with Bloom syndrome (BLM) complex, which consists of at least BLM, DNA topoisomerase 3-alpha (TOP3A), RMI1/BLAP75, RPA1/RPA70 and RPA2/RPA32. The super complex between FA and BLM is called BRAFT (PubMed:20347428, PubMed:20347429). Component of the CENPA-CAD complex, composed of CENPI, CENPK, CENPL, CENPO, CENPP, CENPQ, CENPR and CENPS. The CENPA-CAD complex is probably recruited on centromeres by the CENPA-NAC complex, composed of at least CENPA, CENPC, CENPH, CENPM, CENPN, CENPT and CENPU (PubMed:16622419).
Similarity
Belongs to the TAF9 family. CENP-S/MHF1 subfamily.
Keywords
3D-structure
Acetylation
Alternative splicing
Cell cycle
Cell division
Centromere
Chromosome
Complete proteome
DNA damage
DNA repair
DNA-binding
Kinetochore
Mitosis
Nucleus
Reference proteome
Feature
chain Centromere protein S
splice variant In isoform 3.
splice variant In isoform 3.
Uniprot
H9J6V9
A0A2A4J4M9
A0A194Q148
A0A1E1WK96
A0A2H1W697
A0A3S2M5X2
+ More
A0A2K6N705 H0X487 H9FU73 G3RAC8 G1RE55 H2N958 Q8N2Z9 A0A2K5MMV6 A0A096N6R5 A0A0D9S8N8 A0A1U7UB85 A0A2K5V9J7 I0FRJ7 G7NU59 G7MGU0 Q8N2Z9-2 A0A2K6GYI2 A0A2Y9F6T6 A0A341BRX7 A0A2Y9Q5W8 A0A340XV37 A0A0P6J9Z2 G1NSQ4 A0A2U3V8J9 A0A383Z4Q1 D2HXB9 G5C529 A0A3Q2GCY8
A0A2K6N705 H0X487 H9FU73 G3RAC8 G1RE55 H2N958 Q8N2Z9 A0A2K5MMV6 A0A096N6R5 A0A0D9S8N8 A0A1U7UB85 A0A2K5V9J7 I0FRJ7 G7NU59 G7MGU0 Q8N2Z9-2 A0A2K6GYI2 A0A2Y9F6T6 A0A341BRX7 A0A2Y9Q5W8 A0A340XV37 A0A0P6J9Z2 G1NSQ4 A0A2U3V8J9 A0A383Z4Q1 D2HXB9 G5C529 A0A3Q2GCY8
Pubmed
EMBL
BABH01028412
AB766232
BAN29073.1
NWSH01003279
PCG66628.1
KQ459580
+ More
KPI99307.1 GDQN01003763 JAT87291.1 ODYU01006620 SOQ48625.1 RSAL01000030 RVE51705.1 AAQR03101467 AAQR03101468 AAQR03101469 AAQR03101470 AAQR03101471 JU334429 AFE78182.1 CABD030000727 CABD030000728 ADFV01080659 ADFV01080660 ADFV01080661 ADFV01080662 ABGA01043965 ABGA01043966 ABGA01043967 ABGA01043968 NDHI03003447 PNJ48190.1 AF516753 AF521016 AL139424 AL354956 BC029430 AHZZ02015242 AHZZ02020767 AQIB01136407 AQIA01005920 JU471812 JV047002 AFH28616.1 AFI37073.1 CM001276 EHH49532.1 CM001253 EHH14312.1 GEBF01004246 JAN99386.1 AAPE02050832 GL193605 EFB21548.1 JH173407 EHB16640.1
KPI99307.1 GDQN01003763 JAT87291.1 ODYU01006620 SOQ48625.1 RSAL01000030 RVE51705.1 AAQR03101467 AAQR03101468 AAQR03101469 AAQR03101470 AAQR03101471 JU334429 AFE78182.1 CABD030000727 CABD030000728 ADFV01080659 ADFV01080660 ADFV01080661 ADFV01080662 ABGA01043965 ABGA01043966 ABGA01043967 ABGA01043968 NDHI03003447 PNJ48190.1 AF516753 AF521016 AL139424 AL354956 BC029430 AHZZ02015242 AHZZ02020767 AQIB01136407 AQIA01005920 JU471812 JV047002 AFH28616.1 AFI37073.1 CM001276 EHH49532.1 CM001253 EHH14312.1 GEBF01004246 JAN99386.1 AAPE02050832 GL193605 EFB21548.1 JH173407 EHB16640.1
Proteomes
UP000005204
UP000218220
UP000053268
UP000283053
UP000233200
UP000005225
+ More
UP000001519 UP000001073 UP000001595 UP000005640 UP000233060 UP000028761 UP000029965 UP000189704 UP000233100 UP000009130 UP000233160 UP000248484 UP000252040 UP000248483 UP000265300 UP000001074 UP000245320 UP000261681 UP000006813 UP000265020
UP000001519 UP000001073 UP000001595 UP000005640 UP000233060 UP000028761 UP000029965 UP000189704 UP000233100 UP000009130 UP000233160 UP000248484 UP000252040 UP000248483 UP000265300 UP000001074 UP000245320 UP000261681 UP000006813 UP000265020
Interpro
SUPFAM
SSF47113
SSF47113
Gene 3D
ProteinModelPortal
H9J6V9
A0A2A4J4M9
A0A194Q148
A0A1E1WK96
A0A2H1W697
A0A3S2M5X2
+ More
A0A2K6N705 H0X487 H9FU73 G3RAC8 G1RE55 H2N958 Q8N2Z9 A0A2K5MMV6 A0A096N6R5 A0A0D9S8N8 A0A1U7UB85 A0A2K5V9J7 I0FRJ7 G7NU59 G7MGU0 Q8N2Z9-2 A0A2K6GYI2 A0A2Y9F6T6 A0A341BRX7 A0A2Y9Q5W8 A0A340XV37 A0A0P6J9Z2 G1NSQ4 A0A2U3V8J9 A0A383Z4Q1 D2HXB9 G5C529 A0A3Q2GCY8
A0A2K6N705 H0X487 H9FU73 G3RAC8 G1RE55 H2N958 Q8N2Z9 A0A2K5MMV6 A0A096N6R5 A0A0D9S8N8 A0A1U7UB85 A0A2K5V9J7 I0FRJ7 G7NU59 G7MGU0 Q8N2Z9-2 A0A2K6GYI2 A0A2Y9F6T6 A0A341BRX7 A0A2Y9Q5W8 A0A340XV37 A0A0P6J9Z2 G1NSQ4 A0A2U3V8J9 A0A383Z4Q1 D2HXB9 G5C529 A0A3Q2GCY8
PDB
4DRA
E-value=7.41256e-09,
Score=138
Ontologies
GO
GO:0046982
GO:0071821
GO:0006281
GO:0051382
GO:0000776
GO:0003682
GO:0003690
GO:0031297
GO:0043240
GO:0000712
GO:0005829
GO:0006974
GO:0036297
GO:0003677
GO:0000777
GO:0005654
GO:0034080
GO:0051301
GO:0031398
GO:0005576
GO:0005179
GO:0006508
GO:0015074
GO:0016311
GO:0016791
GO:0006470
GO:0004674
GO:0009058
GO:0016742
GO:0003824
PANTHER
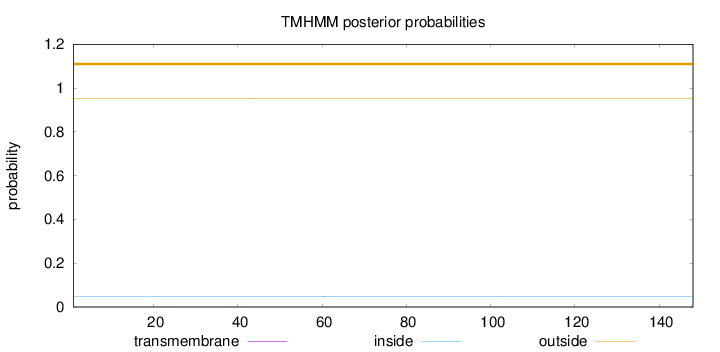
Topology
Subcellular location
Nucleus
Assembly of CENPS and CENPX and its partner subunits CENPT and CENPW at centromeres occurs through a dynamic exchange mechanism. Although exchange is continuous in the cell cycle, de novo assembly starts principally during mid-late S phase and is complete by G2. CENPS is more stably bound at the kinetochore than CENPX (PubMed:19620631, PubMed:24522885). During S phase, rapidly recruited to DNA interstrand cross-links that block replication (PubMed:20347428). Recruited to DNA damage sites about 20 minutes following UV irradiation, reaching a plateau after approximately 40 minutes (PubMed:24522885). With evidence from 7 publications.
Chromosome Assembly of CENPS and CENPX and its partner subunits CENPT and CENPW at centromeres occurs through a dynamic exchange mechanism. Although exchange is continuous in the cell cycle, de novo assembly starts principally during mid-late S phase and is complete by G2. CENPS is more stably bound at the kinetochore than CENPX (PubMed:19620631, PubMed:24522885). During S phase, rapidly recruited to DNA interstrand cross-links that block replication (PubMed:20347428). Recruited to DNA damage sites about 20 minutes following UV irradiation, reaching a plateau after approximately 40 minutes (PubMed:24522885). With evidence from 7 publications.
Centromere Assembly of CENPS and CENPX and its partner subunits CENPT and CENPW at centromeres occurs through a dynamic exchange mechanism. Although exchange is continuous in the cell cycle, de novo assembly starts principally during mid-late S phase and is complete by G2. CENPS is more stably bound at the kinetochore than CENPX (PubMed:19620631, PubMed:24522885). During S phase, rapidly recruited to DNA interstrand cross-links that block replication (PubMed:20347428). Recruited to DNA damage sites about 20 minutes following UV irradiation, reaching a plateau after approximately 40 minutes (PubMed:24522885). With evidence from 7 publications.
Kinetochore Assembly of CENPS and CENPX and its partner subunits CENPT and CENPW at centromeres occurs through a dynamic exchange mechanism. Although exchange is continuous in the cell cycle, de novo assembly starts principally during mid-late S phase and is complete by G2. CENPS is more stably bound at the kinetochore than CENPX (PubMed:19620631, PubMed:24522885). During S phase, rapidly recruited to DNA interstrand cross-links that block replication (PubMed:20347428). Recruited to DNA damage sites about 20 minutes following UV irradiation, reaching a plateau after approximately 40 minutes (PubMed:24522885). With evidence from 7 publications.
Chromosome Assembly of CENPS and CENPX and its partner subunits CENPT and CENPW at centromeres occurs through a dynamic exchange mechanism. Although exchange is continuous in the cell cycle, de novo assembly starts principally during mid-late S phase and is complete by G2. CENPS is more stably bound at the kinetochore than CENPX (PubMed:19620631, PubMed:24522885). During S phase, rapidly recruited to DNA interstrand cross-links that block replication (PubMed:20347428). Recruited to DNA damage sites about 20 minutes following UV irradiation, reaching a plateau after approximately 40 minutes (PubMed:24522885). With evidence from 7 publications.
Centromere Assembly of CENPS and CENPX and its partner subunits CENPT and CENPW at centromeres occurs through a dynamic exchange mechanism. Although exchange is continuous in the cell cycle, de novo assembly starts principally during mid-late S phase and is complete by G2. CENPS is more stably bound at the kinetochore than CENPX (PubMed:19620631, PubMed:24522885). During S phase, rapidly recruited to DNA interstrand cross-links that block replication (PubMed:20347428). Recruited to DNA damage sites about 20 minutes following UV irradiation, reaching a plateau after approximately 40 minutes (PubMed:24522885). With evidence from 7 publications.
Kinetochore Assembly of CENPS and CENPX and its partner subunits CENPT and CENPW at centromeres occurs through a dynamic exchange mechanism. Although exchange is continuous in the cell cycle, de novo assembly starts principally during mid-late S phase and is complete by G2. CENPS is more stably bound at the kinetochore than CENPX (PubMed:19620631, PubMed:24522885). During S phase, rapidly recruited to DNA interstrand cross-links that block replication (PubMed:20347428). Recruited to DNA damage sites about 20 minutes following UV irradiation, reaching a plateau after approximately 40 minutes (PubMed:24522885). With evidence from 7 publications.
Length:
148
Number of predicted TMHs:
0
Exp number of AAs in TMHs:
0.02082
Exp number, first 60 AAs:
0.02077
Total prob of N-in:
0.04817
outside
1 - 148
Population Genetic Test Statistics
Pi
26.456861
Theta
21.777184
Tajima's D
0.906317
CLR
0.688066
CSRT
0.636318184090795
Interpretation
Uncertain
