Pre Gene Modal
BGIBMGA009969
Annotation
PREDICTED:_putative_riboflavin_kinase_[Plutella_xylostella]
Full name
Putative riboflavin kinase
+ More
Riboflavin kinase
Riboflavin kinase
Alternative Name
ATP:riboflavin 5'-phosphotransferase
Flavokinase
KOI-4
Flavokinase
KOI-4
Location in the cell
Cytoplasmic Reliability : 1.708
Sequence
CDS
ATGAAAATATTTTTTCAATTGAGGAAAATGTCATCAGTTCTGCCTTTTTTCCTTGAAGGAGAGGTAGTCAAGGGTTTTGGAAGAGGTTCTAAGGAACTAGGATGCCCAACAGCTAATTATCCTTTGGAAGTTGTAAAATCTTTACCAAAAGGTTTGGAGCCAGGTGTTTATTATGGATGGGCTCAAGTTGACACAGGACCTGTATATGAGATGGTAGCAAATATAGGATGGTGTCCTTTTTACCAAAATAAAGAGATGTCTGTTGAAACCCATATAATGCACAATTTCCAGGGTGATTTCTATGGTTCTAATTTAAAAATTGCTCTAATTGGGTATCTGAGGGGAGAGAAGAACTTCAATTGTCTGGATGCTCTCATAGAGCAAATTCGAGAAGATATAAAAAATTCTGAACAAAATTTAAAGCAACCCTCAGCACAAAGTCTTCGTAATCATAGCTTTTTCAATAAAAGCATGTAA
Protein
MKIFFQLRKMSSVLPFFLEGEVVKGFGRGSKELGCPTANYPLEVVKSLPKGLEPGVYYGWAQVDTGPVYEMVANIGWCPFYQNKEMSVETHIMHNFQGDFYGSNLKIALIGYLRGEKNFNCLDALIEQIREDIKNSEQNLKQPSAQSLRNHSFFNKSM
Summary
Description
Catalyzes the phosphorylation of riboflavin (vitamin B2) to form flavin-mononucleotide (FMN).
Catalyzes the phosphorylation of riboflavin (vitamin B2) to form flavin-mononucleotide (FMN), hence rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of FAD. Essential for TNF-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Through its interaction with both TNFRSF1A and CYBA, physically and functionally couples TNFRSF1A to NADPH oxidase. TNF-activation of RFK may enhance the incorporation of FAD in NADPH oxidase, a critical step for the assembly and activation of NADPH oxidase.
Catalyzes the phosphorylation of riboflavin (vitamin B2) to form flavin-mononucleotide (FMN), hence rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of FAD. Essential for TNF-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Through its interaction with both TNFRSF1A and CYBA, physically and functionally couples TNFRSF1A to NADPH oxidase. TNF-activation of RFK may enhance the incorporation of FAD in NADPH oxidase, a critical step for the assembly and activation of NADPH oxidase (By similarity).
Catalyzes the phosphorylation of riboflavin (vitamin B2) to form flavin-mononucleotide (FMN), hence rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of FAD. Essential for TNF-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Through its interaction with both TNFRSF1A and CYBA, physically and functionally couples TNFRSF1A to NADPH oxidase. TNF-activation of RFK may enhance the incorporation of FAD in NADPH oxidase, a critical step for the assembly and activation of NADPH oxidase.
Catalyzes the phosphorylation of riboflavin (vitamin B2) to form flavin-mononucleotide (FMN), hence rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of FAD. Essential for TNF-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Through its interaction with both TNFRSF1A and CYBA, physically and functionally couples TNFRSF1A to NADPH oxidase. TNF-activation of RFK may enhance the incorporation of FAD in NADPH oxidase, a critical step for the assembly and activation of NADPH oxidase (By similarity).
Catalytic Activity
ATP + riboflavin = ADP + FMN + H(+)
Subunit
Monomer.
Monomer. Directly interacts with TNFRSF1A death domain. TNFRSF1A-binding may be supported by TRADD. In the absence of TNFRSF1A, interacts with TRADD. Independently of TNFRSF1A, interacts with the NADPH oxidase subunit CYBA.
Monomer (By similarity). Directly interacts with TNFRSF1A death domain; this interaction may be supported by TRADD. In the absence of TNFRSF1A, interacts with TRADD. Independently of TNFRSF1A, interacts with the NADPH oxidase subunit CYBA.
Monomer. Directly interacts with TNFRSF1A death domain. TNFRSF1A-binding may be supported by TRADD. In the absence of TNFRSF1A, interacts with TRADD. Independently of TNFRSF1A, interacts with the NADPH oxidase subunit CYBA.
Monomer (By similarity). Directly interacts with TNFRSF1A death domain; this interaction may be supported by TRADD. In the absence of TNFRSF1A, interacts with TRADD. Independently of TNFRSF1A, interacts with the NADPH oxidase subunit CYBA.
Keywords
ATP-binding
Complete proteome
Cytoplasm
Flavoprotein
FMN
Kinase
Magnesium
Metal-binding
Nucleotide-binding
Reference proteome
Transferase
Zinc
3D-structure
Feature
chain Putative riboflavin kinase
Uniprot
H9JKB8
A0A2W1BQT9
A0A2H1WGC4
A0A194R4I0
I4DQ09
A0A194PMI2
+ More
A0A212EJD8 A0A1I8P4B1 A0A0L7LMY2 A0A1I8N456 A0A1L8EHV7 A0A1L8EI26 A0A1W4VL03 A0A0K8TSR2 B3NYT2 A0A0P5EPB3 A0A0P5X617 A0A0P6EP51 A0A0P6BNK2 Q294L0 A0A1B6MDA5 B4GMY4 A0A0R1E4F6 A0A0P6JGZ0 A0A336M2L4 B4N8D4 A0A336MMS0 A0A0L0CKM9 B4I4Y8 A0A0B4LHX1 O76206 B4PRD2 A0A3B0JPJ2 B4R0B3 B4M0H9 A0A087T3K5 A0A0Q9WP87 G1KE90 A0A1S3HJ39 H2ZGQ1 A0A3M6V2G9 V3ZVW7 A0A224Z7U8 A0A131YJ67 A0A1B6H8G8 A0A0A9YFN1 A0A2G8KWS1 T1IZI2 N6T522 B4K7J1 A0A1B6EZ25 A0A2P6K5B7 A0A0M4F6W4 A0A131X903 J3JTL6 A0A2B4SLA7 L7M0S8 E9H6N6 A0A293LWZ4 A0A226N591 A0A226P767 A0A3B3Q3N0 W4Z3T3 A0A067R7D5 A0A3R7PCW0 A0A1W4XMP8 Q5ZMM2 A0A250YAD5 A0A3B1KFE5 A0A2U4BAJ7 A0A023FYV5 A0A210PJY5 F6R223 B3LXG1 A0A1E1WZS3 U3DWQ1 K1RIW2 A0A151M8C1 A0A1Z5L780 F6W1T1 Q32N80 A7RL68 Q7ZWQ3 F6VD21 A0A2R8M5B9 Q6AX19 L5K992 A0A2Y9DZG6 A0A1U7R5X4 A0A1L8HYD9 H0X8E3 A0A2J8MRF2 Q969G6 A0A1B6DQB9 A0A023FHF9 Q6AYA7 A0A286XNW9 Q8CFV9 A0A3Q4GXR2 A0A3M0L1C3
A0A212EJD8 A0A1I8P4B1 A0A0L7LMY2 A0A1I8N456 A0A1L8EHV7 A0A1L8EI26 A0A1W4VL03 A0A0K8TSR2 B3NYT2 A0A0P5EPB3 A0A0P5X617 A0A0P6EP51 A0A0P6BNK2 Q294L0 A0A1B6MDA5 B4GMY4 A0A0R1E4F6 A0A0P6JGZ0 A0A336M2L4 B4N8D4 A0A336MMS0 A0A0L0CKM9 B4I4Y8 A0A0B4LHX1 O76206 B4PRD2 A0A3B0JPJ2 B4R0B3 B4M0H9 A0A087T3K5 A0A0Q9WP87 G1KE90 A0A1S3HJ39 H2ZGQ1 A0A3M6V2G9 V3ZVW7 A0A224Z7U8 A0A131YJ67 A0A1B6H8G8 A0A0A9YFN1 A0A2G8KWS1 T1IZI2 N6T522 B4K7J1 A0A1B6EZ25 A0A2P6K5B7 A0A0M4F6W4 A0A131X903 J3JTL6 A0A2B4SLA7 L7M0S8 E9H6N6 A0A293LWZ4 A0A226N591 A0A226P767 A0A3B3Q3N0 W4Z3T3 A0A067R7D5 A0A3R7PCW0 A0A1W4XMP8 Q5ZMM2 A0A250YAD5 A0A3B1KFE5 A0A2U4BAJ7 A0A023FYV5 A0A210PJY5 F6R223 B3LXG1 A0A1E1WZS3 U3DWQ1 K1RIW2 A0A151M8C1 A0A1Z5L780 F6W1T1 Q32N80 A7RL68 Q7ZWQ3 F6VD21 A0A2R8M5B9 Q6AX19 L5K992 A0A2Y9DZG6 A0A1U7R5X4 A0A1L8HYD9 H0X8E3 A0A2J8MRF2 Q969G6 A0A1B6DQB9 A0A023FHF9 Q6AYA7 A0A286XNW9 Q8CFV9 A0A3Q4GXR2 A0A3M0L1C3
EC Number
2.7.1.26
Pubmed
19121390
28756777
26354079
22651552
22118469
26227816
+ More
25315136 26369729 17994087 15632085 17550304 26108605 10731132 12537568 12537572 12537573 12537574 16110336 17569856 17569867 26109357 26109356 9601978 12537569 30382153 23254933 28797301 26830274 25401762 26823975 29023486 23537049 28049606 22516182 25576852 21292972 24621616 29240929 24845553 15642098 28087693 25329095 28812685 19393038 28503490 25243066 22992520 22293439 28528879 17495919 17615350 27762356 19892987 23258410 14702039 15164053 15489334 19641494 21269460 12623014 15057822 15632090 21993624 16141072 21183079 25186727
25315136 26369729 17994087 15632085 17550304 26108605 10731132 12537568 12537572 12537573 12537574 16110336 17569856 17569867 26109357 26109356 9601978 12537569 30382153 23254933 28797301 26830274 25401762 26823975 29023486 23537049 28049606 22516182 25576852 21292972 24621616 29240929 24845553 15642098 28087693 25329095 28812685 19393038 28503490 25243066 22992520 22293439 28528879 17495919 17615350 27762356 19892987 23258410 14702039 15164053 15489334 19641494 21269460 12623014 15057822 15632090 21993624 16141072 21183079 25186727
EMBL
BABH01036754
KZ149930
PZC77388.1
ODYU01008384
SOQ51932.1
KQ460930
+ More
KPJ10766.1 AK403878 BAM19999.1 KQ459600 KPI94198.1 AGBW02014474 OWR41613.1 JTDY01000583 KOB76576.1 GFDG01000469 JAV18330.1 GFDG01000468 JAV18331.1 GDAI01000201 JAI17402.1 CH954181 EDV48195.1 GDIP01145162 LRGB01002993 JAJ78240.1 KZS05163.1 GDIP01077218 JAM26497.1 GDIQ01059827 JAN34910.1 GDIP01015446 JAM88269.1 CM000070 EAL28954.3 GEBQ01006065 JAT33912.1 CH479185 EDW38208.1 CM000160 KRK03075.1 GDIQ01007981 JAN86756.1 UFQT01000450 SSX24496.1 CH964232 EDW81385.1 UFQT01001404 SSX30399.1 JRES01000266 KNC32792.1 CH480821 EDW55281.1 AE014297 KX532029 AHN57217.1 ANY27839.1 AF017096 AY071393 AY060898 BT050515 AAL28446.1 EDW96320.1 OUUW01000008 SPP84055.1 CM000364 EDX12038.1 CH940650 EDW68358.2 KK113247 KFM59694.1 KRF83799.1 RCHS01000253 RMX59994.1 KB203331 ESO85091.1 GFPF01011344 MAA22490.1 GEDV01009949 JAP78608.1 GECU01036691 JAS71015.1 GBHO01013158 GBRD01003115 GDHC01002661 JAG30446.1 JAG62706.1 JAQ15968.1 MRZV01000328 PIK52458.1 AFFK01020457 APGK01052196 KB741211 ENN72753.1 CH933806 EDW15335.1 GECZ01026611 JAS43158.1 MWRG01025870 PRD21523.1 CP012526 ALC47862.1 GEFH01005208 JAP63373.1 BT126573 AEE61537.1 LSMT01000059 PFX29899.1 GACK01007562 JAA57472.1 GL732598 EFX72605.1 GFWV01006525 MAA31255.1 MCFN01000202 OXB62687.1 AWGT02000143 OXB75534.1 AAGJ04004981 KK852657 KDR19241.1 QCYY01000856 ROT82227.1 AJ719362 CAG31021.1 GFFW01004201 JAV40587.1 GBBL01000651 JAC26669.1 NEDP02076448 OWF36726.1 CH902617 EDV42805.1 GFAC01006679 JAT92509.1 GAMT01009964 GAMS01005355 GAMR01008867 GAMR01008866 GAMQ01006526 GAMP01002680 GAMP01002679 GAMP01002678 JAB01897.1 JAB17781.1 JAB25065.1 JAB35325.1 JAB50075.1 JH816788 EKC41535.1 AKHW03006358 KYO20762.1 GFJQ02003707 JAW03263.1 BC108783 AAI08784.1 DS469517 EDO47880.1 BC046843 CM004467 AAH46843.1 OCT97901.1 BC079807 AAH79807.1 KB030986 ELK07073.1 CM004466 OCU01123.1 AAQR03015046 NBAG03000246 PNI62103.1 AK002011 AL391868 BC007069 GEDC01009414 JAS27884.1 GBBK01004007 JAC20475.1 AABR07006473 BC079125 CH473953 AAH79125.1 EDM12977.1 AAKN02026222 AK010607 AK002806 AK008352 BC033521 BC051021 AF031380 AF031381 QRBI01000095 RMC19258.1
KPJ10766.1 AK403878 BAM19999.1 KQ459600 KPI94198.1 AGBW02014474 OWR41613.1 JTDY01000583 KOB76576.1 GFDG01000469 JAV18330.1 GFDG01000468 JAV18331.1 GDAI01000201 JAI17402.1 CH954181 EDV48195.1 GDIP01145162 LRGB01002993 JAJ78240.1 KZS05163.1 GDIP01077218 JAM26497.1 GDIQ01059827 JAN34910.1 GDIP01015446 JAM88269.1 CM000070 EAL28954.3 GEBQ01006065 JAT33912.1 CH479185 EDW38208.1 CM000160 KRK03075.1 GDIQ01007981 JAN86756.1 UFQT01000450 SSX24496.1 CH964232 EDW81385.1 UFQT01001404 SSX30399.1 JRES01000266 KNC32792.1 CH480821 EDW55281.1 AE014297 KX532029 AHN57217.1 ANY27839.1 AF017096 AY071393 AY060898 BT050515 AAL28446.1 EDW96320.1 OUUW01000008 SPP84055.1 CM000364 EDX12038.1 CH940650 EDW68358.2 KK113247 KFM59694.1 KRF83799.1 RCHS01000253 RMX59994.1 KB203331 ESO85091.1 GFPF01011344 MAA22490.1 GEDV01009949 JAP78608.1 GECU01036691 JAS71015.1 GBHO01013158 GBRD01003115 GDHC01002661 JAG30446.1 JAG62706.1 JAQ15968.1 MRZV01000328 PIK52458.1 AFFK01020457 APGK01052196 KB741211 ENN72753.1 CH933806 EDW15335.1 GECZ01026611 JAS43158.1 MWRG01025870 PRD21523.1 CP012526 ALC47862.1 GEFH01005208 JAP63373.1 BT126573 AEE61537.1 LSMT01000059 PFX29899.1 GACK01007562 JAA57472.1 GL732598 EFX72605.1 GFWV01006525 MAA31255.1 MCFN01000202 OXB62687.1 AWGT02000143 OXB75534.1 AAGJ04004981 KK852657 KDR19241.1 QCYY01000856 ROT82227.1 AJ719362 CAG31021.1 GFFW01004201 JAV40587.1 GBBL01000651 JAC26669.1 NEDP02076448 OWF36726.1 CH902617 EDV42805.1 GFAC01006679 JAT92509.1 GAMT01009964 GAMS01005355 GAMR01008867 GAMR01008866 GAMQ01006526 GAMP01002680 GAMP01002679 GAMP01002678 JAB01897.1 JAB17781.1 JAB25065.1 JAB35325.1 JAB50075.1 JH816788 EKC41535.1 AKHW03006358 KYO20762.1 GFJQ02003707 JAW03263.1 BC108783 AAI08784.1 DS469517 EDO47880.1 BC046843 CM004467 AAH46843.1 OCT97901.1 BC079807 AAH79807.1 KB030986 ELK07073.1 CM004466 OCU01123.1 AAQR03015046 NBAG03000246 PNI62103.1 AK002011 AL391868 BC007069 GEDC01009414 JAS27884.1 GBBK01004007 JAC20475.1 AABR07006473 BC079125 CH473953 AAH79125.1 EDM12977.1 AAKN02026222 AK010607 AK002806 AK008352 BC033521 BC051021 AF031380 AF031381 QRBI01000095 RMC19258.1
Proteomes
UP000005204
UP000053240
UP000053268
UP000007151
UP000095300
UP000037510
+ More
UP000095301 UP000192221 UP000008711 UP000076858 UP000001819 UP000008744 UP000002282 UP000007798 UP000037069 UP000001292 UP000000803 UP000268350 UP000000304 UP000008792 UP000054359 UP000001646 UP000085678 UP000007875 UP000275408 UP000030746 UP000230750 UP000019118 UP000009192 UP000092553 UP000225706 UP000000305 UP000198323 UP000198419 UP000261540 UP000007110 UP000027135 UP000283509 UP000192223 UP000018467 UP000245320 UP000242188 UP000009136 UP000007801 UP000005408 UP000050525 UP000002280 UP000001593 UP000186698 UP000002281 UP000008225 UP000010552 UP000248480 UP000189706 UP000005225 UP000005640 UP000002494 UP000005447 UP000000589 UP000261580 UP000269221
UP000095301 UP000192221 UP000008711 UP000076858 UP000001819 UP000008744 UP000002282 UP000007798 UP000037069 UP000001292 UP000000803 UP000268350 UP000000304 UP000008792 UP000054359 UP000001646 UP000085678 UP000007875 UP000275408 UP000030746 UP000230750 UP000019118 UP000009192 UP000092553 UP000225706 UP000000305 UP000198323 UP000198419 UP000261540 UP000007110 UP000027135 UP000283509 UP000192223 UP000018467 UP000245320 UP000242188 UP000009136 UP000007801 UP000005408 UP000050525 UP000002280 UP000001593 UP000186698 UP000002281 UP000008225 UP000010552 UP000248480 UP000189706 UP000005225 UP000005640 UP000002494 UP000005447 UP000000589 UP000261580 UP000269221
Pfam
PF01687 Flavokinase
Interpro
SUPFAM
SSF82114
SSF82114
Gene 3D
ProteinModelPortal
H9JKB8
A0A2W1BQT9
A0A2H1WGC4
A0A194R4I0
I4DQ09
A0A194PMI2
+ More
A0A212EJD8 A0A1I8P4B1 A0A0L7LMY2 A0A1I8N456 A0A1L8EHV7 A0A1L8EI26 A0A1W4VL03 A0A0K8TSR2 B3NYT2 A0A0P5EPB3 A0A0P5X617 A0A0P6EP51 A0A0P6BNK2 Q294L0 A0A1B6MDA5 B4GMY4 A0A0R1E4F6 A0A0P6JGZ0 A0A336M2L4 B4N8D4 A0A336MMS0 A0A0L0CKM9 B4I4Y8 A0A0B4LHX1 O76206 B4PRD2 A0A3B0JPJ2 B4R0B3 B4M0H9 A0A087T3K5 A0A0Q9WP87 G1KE90 A0A1S3HJ39 H2ZGQ1 A0A3M6V2G9 V3ZVW7 A0A224Z7U8 A0A131YJ67 A0A1B6H8G8 A0A0A9YFN1 A0A2G8KWS1 T1IZI2 N6T522 B4K7J1 A0A1B6EZ25 A0A2P6K5B7 A0A0M4F6W4 A0A131X903 J3JTL6 A0A2B4SLA7 L7M0S8 E9H6N6 A0A293LWZ4 A0A226N591 A0A226P767 A0A3B3Q3N0 W4Z3T3 A0A067R7D5 A0A3R7PCW0 A0A1W4XMP8 Q5ZMM2 A0A250YAD5 A0A3B1KFE5 A0A2U4BAJ7 A0A023FYV5 A0A210PJY5 F6R223 B3LXG1 A0A1E1WZS3 U3DWQ1 K1RIW2 A0A151M8C1 A0A1Z5L780 F6W1T1 Q32N80 A7RL68 Q7ZWQ3 F6VD21 A0A2R8M5B9 Q6AX19 L5K992 A0A2Y9DZG6 A0A1U7R5X4 A0A1L8HYD9 H0X8E3 A0A2J8MRF2 Q969G6 A0A1B6DQB9 A0A023FHF9 Q6AYA7 A0A286XNW9 Q8CFV9 A0A3Q4GXR2 A0A3M0L1C3
A0A212EJD8 A0A1I8P4B1 A0A0L7LMY2 A0A1I8N456 A0A1L8EHV7 A0A1L8EI26 A0A1W4VL03 A0A0K8TSR2 B3NYT2 A0A0P5EPB3 A0A0P5X617 A0A0P6EP51 A0A0P6BNK2 Q294L0 A0A1B6MDA5 B4GMY4 A0A0R1E4F6 A0A0P6JGZ0 A0A336M2L4 B4N8D4 A0A336MMS0 A0A0L0CKM9 B4I4Y8 A0A0B4LHX1 O76206 B4PRD2 A0A3B0JPJ2 B4R0B3 B4M0H9 A0A087T3K5 A0A0Q9WP87 G1KE90 A0A1S3HJ39 H2ZGQ1 A0A3M6V2G9 V3ZVW7 A0A224Z7U8 A0A131YJ67 A0A1B6H8G8 A0A0A9YFN1 A0A2G8KWS1 T1IZI2 N6T522 B4K7J1 A0A1B6EZ25 A0A2P6K5B7 A0A0M4F6W4 A0A131X903 J3JTL6 A0A2B4SLA7 L7M0S8 E9H6N6 A0A293LWZ4 A0A226N591 A0A226P767 A0A3B3Q3N0 W4Z3T3 A0A067R7D5 A0A3R7PCW0 A0A1W4XMP8 Q5ZMM2 A0A250YAD5 A0A3B1KFE5 A0A2U4BAJ7 A0A023FYV5 A0A210PJY5 F6R223 B3LXG1 A0A1E1WZS3 U3DWQ1 K1RIW2 A0A151M8C1 A0A1Z5L780 F6W1T1 Q32N80 A7RL68 Q7ZWQ3 F6VD21 A0A2R8M5B9 Q6AX19 L5K992 A0A2Y9DZG6 A0A1U7R5X4 A0A1L8HYD9 H0X8E3 A0A2J8MRF2 Q969G6 A0A1B6DQB9 A0A023FHF9 Q6AYA7 A0A286XNW9 Q8CFV9 A0A3Q4GXR2 A0A3M0L1C3
PDB
1Q9S
E-value=4.24059e-42,
Score=425
Ontologies
PATHWAY
GO
PANTHER
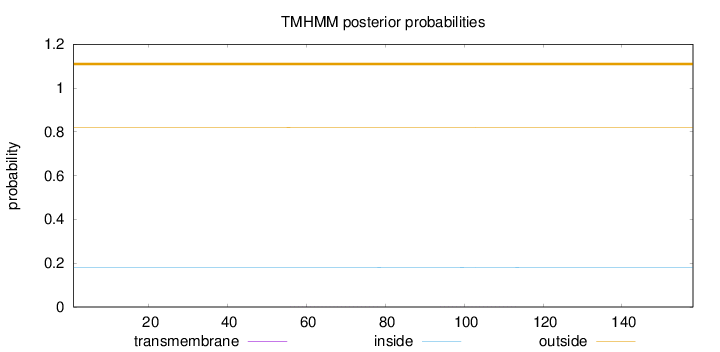
Topology
Subcellular location
Cytoplasm
Length:
158
Number of predicted TMHs:
0
Exp number of AAs in TMHs:
0.01267
Exp number, first 60 AAs:
0.00152
Total prob of N-in:
0.17951
outside
1 - 158
Population Genetic Test Statistics
Pi
166.460888
Theta
159.806896
Tajima's D
0.034624
CLR
135.857068
CSRT
0.377981100944953
Interpretation
Uncertain
