Gene
KWMTBOMO02732 Validated by peptides from experiments
Pre Gene Modal
BGIBMGA003474
Annotation
PREDICTED:_casein_kinase_2_alpha_subunit_isoform_X1_[Bombyx_mori]
Full name
Casein kinase II subunit alpha
Location in the cell
Cytoplasmic Reliability : 2.94
Sequence
CDS
ATGGCAGTACCTAGTAGAGCGAGGGTCTACGCTGATGTGAACTCACAACGTCCAAGGGAATATTGGGATTACGAAAGTTATGTAGTTGACTGGGGCAACCAAGAAGACTATCAGTTGGTTCGCAAGCTGGGTCGCGGGAAATACAGTGAAGTATTTGAAGCAATAAATATTACGAATAATGAAAAATGTGTAGTTAAAATATTAAAGCCTGTAAAAAAGAAGAAAATTAAAAGAGAAATAAAAATTTTAGAAAACTTAAGAGGAGGCACTAATATAATATCTTTACAAGCTGTAGTCAAAGACCCTGTCTCGCGTACACCTGCACTTATATTTGAACATGTGAACAATACTGACTTTAAACAGCTATATTCGACATTGTCAGATTATGATATAAGATACTACTTATATGAGCTTTTAAAGGCATTAGATTATTGCCATAGTATGGGGATAATGCATAGGGATGTGAAACCTCATAATGTGATGATTGACCATGAACATAGAATGTTACGCCTTATTGACTGGGGGTTAGCTGAGTTCTACCATCCGGGGCAAGATTATAATGTTCGTGTTGCTTCTAGATACTTTAAGGGCCCTGAACTTTTGGTAGATTATCAAATGTATGATTATTCATTGGATATGTGGTCACTAGGATGTATGTTGGCATCCATGATTTTCCGTAAAGAGCCATTCTTTCATGGCCATGATAATTATGACCAGCTTGTACGTATTGCGAAAGTACTGGGTACAGAAGAATTGTTTGAGTACTTGGATAAATATCATATAGAACTGGATCCTCGGTTTAATGACATACTTGGCAGACACTCACGTAAGAGATGGGAGCGATTTATACATTCAGAAAATCAACATCTTGTATCACCAGAGGCACTGGACTTTCTTGACCGTTTACTGCGTTATGATCATTATGAACGCTACACTGCTCGTGAAGCTATGGACCATCCATATTTTTGTAAGTTTTTTTTTTTTGTTGTTGTTTAG
Protein
MAVPSRARVYADVNSQRPREYWDYESYVVDWGNQEDYQLVRKLGRGKYSEVFEAINITNNEKCVVKILKPVKKKKIKREIKILENLRGGTNIISLQAVVKDPVSRTPALIFEHVNNTDFKQLYSTLSDYDIRYYLYELLKALDYCHSMGIMHRDVKPHNVMIDHEHRMLRLIDWGLAEFYHPGQDYNVRVASRYFKGPELLVDYQMYDYSLDMWSLGCMLASMIFRKEPFFHGHDNYDQLVRIAKVLGTEELFEYLDKYHIELDPRFNDILGRHSRKRWERFIHSENQHLVSPEALDFLDRLLRYDHYERYTAREAMDHPYFCKFFFFVVV
Summary
Description
Catalytic subunit of a constitutively active serine/threonine-protein kinase complex that phosphorylates a large number of substrates containing acidic residues C-terminal to the phosphorylated serine or threonine. Regulates numerous cellular processes, such as cell cycle progression, apoptosis and transcription, as well as viral infection. May act as a regulatory node which integrates and coordinates numerous signals leading to an appropriate cellular response. During mitosis, functions as a component of the p53/TP53-dependent spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) that maintains cyclin-B-CDK1 activity and G2 arrest in response to spindle damage. Also required for p53/TP53-mediated apoptosis, phosphorylating 'Ser-392' of p53/TP53 following UV irradiation. Can also negatively regulate apoptosis. Phosphorylates the caspases CASP9 and CASP2 and the apoptotic regulator NOL3. Phosphorylation protects CASP9 from cleavage and activation by CASP8, and inhibits the dimerization of CASP2 and activation of CASP8. Regulates transcription by direct phosphorylation of RNA polymerases I, II, III and IV. Also phosphorylates and regulates numerous transcription factors including NF-kappa-B, STAT1, CREB1, IRF1, IRF2, ATF1, SRF, MAX, JUN, FOS, MYC and MYB. Phosphorylates Hsp90 and its co-chaperones FKBP4 and CDC37, which is essential for chaperone function. Regulates Wnt signaling by phosphorylating CTNNB1 and the transcription factor LEF1. Acts as an ectokinase that phosphorylates several extracellular proteins. Phosphorylates PML at 'Ser-565' and primes it for ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Plays an important role in the circadian clock function by phosphorylating ARNTL/BMAL1 at 'Ser-90' which is pivotal for its interaction with CLOCK and which controls CLOCK nuclear entry. Phosphorylates CCAR2 at 'Thr-454' (By similarity).
Catalytic subunit of a constitutively active serine/threonine-protein kinase complex that phosphorylates a large number of substrates containing acidic residues C-terminal to the phosphorylated serine or threonine. Regulates numerous cellular processes, such as cell cycle progression, apoptosis and transcription, as well as viral infection. May act as a regulatory node which integrates and coordinates numerous signals leading to an appropriate cellular response. During mitosis, functions as a component of the p53/TP53-dependent spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) that maintains cyclin-B-CDK1 activity and G2 arrest in response to spindle damage. Also required for p53/TP53-mediated apoptosis, phosphorylating 'Ser-392' of p53/TP53 following UV irradiation. Can also negatively regulate apoptosis. Phosphorylates the caspases CASP9 and CASP2 and the apoptotic regulator NOL3. Phosphorylation protects CASP9 from cleavage and activation by CASP8, and inhibits the dimerization of CASP2 and activation of CASP8. Regulates transcription by direct phosphorylation of RNA polymerases I, II, III and IV. Also phosphorylates and regulates numerous transcription factors including NF-kappa-B, STAT1, CREB1, IRF1, IRF2, ATF1, SRF, MAX, JUN, FOS, MYC and MYB. Phosphorylates Hsp90 and its co-chaperones FKBP4 and CDC37, which is essential for chaperone function. Regulates Wnt signaling by phosphorylating CTNNB1 and the transcription factor LEF1. Acts as an ectokinase that phosphorylates several extracellular proteins. Phosphorylates PML at 'Ser-565' and primes it for ubiquitin-mediated degradation (By similarity). Plays an important role in the circadian clock function by phosphorylating ARNTL/BMAL1 at 'Ser-90' which is pivotal for its interaction with CLOCK and which controls CLOCK nuclear entry. Phosphorylates CCAR2 at 'Thr-454' (By similarity).
Catalytic subunit of a constitutively active serine/threonine-protein kinase complex that phosphorylates a large number of substrates containing acidic residues C-terminal to the phosphorylated serine or threonine. Regulates numerous cellular processes, such as cell cycle progression, apoptosis and transcription, as well as viral infection. May act as a regulatory node which integrates and coordinates numerous signals leading to an appropriate cellular response. During mitosis, functions as a component of the p53/TP53-dependent spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) that maintains cyclin-B-CDK1 activity and G2 arrest in response to spindle damage. Also required for p53/TP53-mediated apoptosis, phosphorylating 'Ser-392' of p53/TP53 following UV irradiation. Can also negatively regulate apoptosis. Phosphorylates the caspases CASP9 and CASP2 and the apoptotic regulator NOL3. Phosphorylation protects CASP9 from cleavage and activation by CASP8, and inhibits the dimerization of CASP2 and activation of CASP8. Regulates transcription by direct phosphorylation of RNA polymerases I, II, III and IV. Also phosphorylates and regulates numerous transcription factors including NF-kappa-B, STAT1, CREB1, IRF1, IRF2, ATF1, SRF, MAX, JUN, FOS, MYC and MYB. Phosphorylates Hsp90 and its co-chaperones FKBP4 and CDC37, which is essential for chaperone function. Regulates Wnt signaling by phosphorylating CTNNB1 and the transcription factor LEF1. Acts as an ectokinase that phosphorylates several extracellular proteins. Phosphorylates PML at 'Ser-565' and primes it for ubiquitin-mediated degradation (By similarity). Plays an important role in the circadian clock function by phosphorylating ARNTL/BMAL1 at 'Ser-90' which is pivotal for its interaction with CLOCK and which controls CLOCK nuclear entry. Phosphorylates CCAR2 at 'Thr-454' (By similarity).
Catalytic Activity
ATP + L-seryl-[protein] = ADP + H(+) + O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein]
ATP + L-threonyl-[protein] = ADP + H(+) + O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein]
ATP + L-threonyl-[protein] = ADP + H(+) + O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein]
Subunit
Tetramer of two alpha and two beta chains.
Tetramer composed of an alpha chain, an alpha' and two beta chains.
Heterotetramer composed of two catalytic subunits (alpha chain and/or alpha' chain) and two regulatory subunits (beta chains). The tetramer can exist as a combination of 2 alpha/2 beta, 2 alpha'/2 beta or 1 alpha/1 alpha'/2 beta subunits. Also part of a CK2-SPT16-SSRP1 complex composed of SSRP1, SUPT16H, CSNK2A1, CSNK2A2 and CSNK2B, which forms following UV irradiation (By similarity). Interacts with RNPS1 (By similarity). Interacts with SNAI1 (PubMed:19923321). Interacts with PML and CCAR2 (By similarity).
Heterotetramer composed of two catalytic subunits (alpha chain and/or alpha' chain) and two regulatory subunits (beta chains). The tetramer can exist as a combination of 2 alpha/2 beta, 2 alpha'/2 beta or 1 alpha/1 alpha'/2 beta subunits. Also part of a CK2-SPT16-SSRP1 complex composed of SSRP1, SUPT16H, CSNK2A1, CSNK2A2 and CSNK2B, which forms following UV irradiation. Interacts with RNPS1, SNAI1, PML and CCAR2 (By similarity).
Tetramer composed of an alpha chain, an alpha' and two beta chains.
Heterotetramer composed of two catalytic subunits (alpha chain and/or alpha' chain) and two regulatory subunits (beta chains). The tetramer can exist as a combination of 2 alpha/2 beta, 2 alpha'/2 beta or 1 alpha/1 alpha'/2 beta subunits. Also part of a CK2-SPT16-SSRP1 complex composed of SSRP1, SUPT16H, CSNK2A1, CSNK2A2 and CSNK2B, which forms following UV irradiation (By similarity). Interacts with RNPS1 (By similarity). Interacts with SNAI1 (PubMed:19923321). Interacts with PML and CCAR2 (By similarity).
Heterotetramer composed of two catalytic subunits (alpha chain and/or alpha' chain) and two regulatory subunits (beta chains). The tetramer can exist as a combination of 2 alpha/2 beta, 2 alpha'/2 beta or 1 alpha/1 alpha'/2 beta subunits. Also part of a CK2-SPT16-SSRP1 complex composed of SSRP1, SUPT16H, CSNK2A1, CSNK2A2 and CSNK2B, which forms following UV irradiation. Interacts with RNPS1, SNAI1, PML and CCAR2 (By similarity).
Miscellaneous
Can use both ATP and GTP as phosphoryl donors. Phosphorylation by casein kinase 2 has been estimated to represent up to one quarter of the eukaryotic phosphoproteome.
Similarity
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Ser/Thr protein kinase family. CK2 subfamily.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Ser/Thr protein kinase family. CK2 subfamily.
Keywords
ATP-binding
Kinase
Nucleotide-binding
Transferase
Wnt signaling pathway
Nucleus
Apoptosis
Biological rhythms
Cell cycle
Complete proteome
Phosphoprotein
Reference proteome
Transcription
Transcription regulation
3D-structure
Direct protein sequencing
Feature
chain Casein kinase II subunit alpha
Uniprot
H9J1T7
Q59HV9
A0A2H1WWX2
O76484
A0A2A4JZD8
A0A0L7KL16
+ More
S4P9Z6 A0A194RGM1 A0A194PUN6 B0LBZ3 A0A212FIX3 A0A151I5B1 A0A0C9R8G5 E2BH98 E2AW17 A0A0J7KIF9 A0A151J3G8 A0A026VYW4 A0A195C1G2 E0VRT5 A0A2J7RHG1 F4WU82 A0A151JW70 A0A151X092 A0A1B6JP93 A0A067RQK2 A0A2Z5TZA5 A0A1B6DFA8 A0A1B6HBX2 A0A1B6EQA3 A0A2P8XVP2 A0A1B6C1T2 A0A1Y1LNF4 A0A1Y1LQ48 A0A1Y1LHJ1 V5GSL7 D6W7M8 J9JP30 A0A0N0BJQ2 A0A1Y1LJX6 A0A2H8TFK4 A0A087ZW71 A0A2S2QNP6 V9I7J1 A0A2S2PLG9 A0A0L7QV90 A0A2A3EL85 A0A2S2QTX1 A0A0P6IJG4 A0A0N8A556 A0A1W4WNT1 A0A139WPC3 A0A0P5CF09 A0A0N8BMQ4 Q16N28 H9AZT4 A0A154PRR3 A0A1Q3F4A5 A0A0P6DFT2 A0A0P5JST8 A0A0P5GIQ8 H9AZT3 B0WWU1 Q6INV5 A0A2K5Q3H4 A0A023EP31 A0A1L8ETF4 A0A1L8EM01 J3JU18 T1D4A2 A0A2D4HA14 M7B5N8 A0A0P5CHH3 A0A336MN57 P28020 A0A3L8S9E7 W5MKN8 A0A218US37 A0A1V4KKK6 A0A093BP39 H0Z8S4 A0A1S2ZQS3 S7N7R0 A0A076FER8 Q60737 G1KCJ4 Q61177 A0A3L7HE43 H0WLB6 A0A1W7RAV4 P19139 G1N6J4 A0A093LJS6 A0A099Z576 A0A093FU89 A0A093PMS6 A0A091G8J4 A0A091I711 A0A091V228 A0A091MCM8
S4P9Z6 A0A194RGM1 A0A194PUN6 B0LBZ3 A0A212FIX3 A0A151I5B1 A0A0C9R8G5 E2BH98 E2AW17 A0A0J7KIF9 A0A151J3G8 A0A026VYW4 A0A195C1G2 E0VRT5 A0A2J7RHG1 F4WU82 A0A151JW70 A0A151X092 A0A1B6JP93 A0A067RQK2 A0A2Z5TZA5 A0A1B6DFA8 A0A1B6HBX2 A0A1B6EQA3 A0A2P8XVP2 A0A1B6C1T2 A0A1Y1LNF4 A0A1Y1LQ48 A0A1Y1LHJ1 V5GSL7 D6W7M8 J9JP30 A0A0N0BJQ2 A0A1Y1LJX6 A0A2H8TFK4 A0A087ZW71 A0A2S2QNP6 V9I7J1 A0A2S2PLG9 A0A0L7QV90 A0A2A3EL85 A0A2S2QTX1 A0A0P6IJG4 A0A0N8A556 A0A1W4WNT1 A0A139WPC3 A0A0P5CF09 A0A0N8BMQ4 Q16N28 H9AZT4 A0A154PRR3 A0A1Q3F4A5 A0A0P6DFT2 A0A0P5JST8 A0A0P5GIQ8 H9AZT3 B0WWU1 Q6INV5 A0A2K5Q3H4 A0A023EP31 A0A1L8ETF4 A0A1L8EM01 J3JU18 T1D4A2 A0A2D4HA14 M7B5N8 A0A0P5CHH3 A0A336MN57 P28020 A0A3L8S9E7 W5MKN8 A0A218US37 A0A1V4KKK6 A0A093BP39 H0Z8S4 A0A1S2ZQS3 S7N7R0 A0A076FER8 Q60737 G1KCJ4 Q61177 A0A3L7HE43 H0WLB6 A0A1W7RAV4 P19139 G1N6J4 A0A093LJS6 A0A099Z576 A0A093FU89 A0A093PMS6 A0A091G8J4 A0A091I711 A0A091V228 A0A091MCM8
EC Number
2.7.11.1
Pubmed
19121390
26227816
23622113
26354079
18184036
18183285
+ More
22118469 20798317 24508170 30249741 20566863 21719571 24845553 26760975 29403074 28004739 18362917 19820115 17510324 26483478 24945155 27762356 22516182 24330624 23624526 1544409 30282656 20360741 7846532 16141072 19468303 15489334 10806215 18467326 17954558 21183079 19923321 29704459 8173590 2752008 19330005 12191471 20838655
22118469 20798317 24508170 30249741 20566863 21719571 24845553 26760975 29403074 28004739 18362917 19820115 17510324 26483478 24945155 27762356 22516182 24330624 23624526 1544409 30282656 20360741 7846532 16141072 19468303 15489334 10806215 18467326 17954558 21183079 19923321 29704459 8173590 2752008 19330005 12191471 20838655
EMBL
BABH01007991
AB206394
BAD91393.1
ODYU01011613
SOQ57466.1
AF071210
+ More
NWSH01000357 PCG77048.1 JTDY01009137 KOB64058.1 GAIX01003484 JAA89076.1 KQ460207 KPJ16737.1 KQ459597 KPI94850.1 EF554579 ABU49714.1 AGBW02008321 OWR53693.1 KQ976437 KYM86937.1 GBYB01009162 JAG78929.1 GL448287 EFN84867.1 GL443213 EFN62439.1 LBMM01007090 KMQ90052.1 KQ980313 KYN16718.1 KK107591 QOIP01000013 EZA48626.1 RLU15526.1 KQ978350 KYM94682.1 DS235562 EEB16091.1 NEVH01003743 PNF40271.1 GL888353 EGI62250.1 KQ981664 KYN38485.1 KQ982617 KYQ53785.1 GECU01006642 JAT01065.1 KK852527 KDR22024.1 FX985745 BBA93632.1 GEDC01012962 JAS24336.1 GECU01035519 JAS72187.1 GECZ01032459 GECZ01031828 GECZ01029689 GECZ01023360 GECZ01017867 GECZ01010528 GECZ01008514 GECZ01008214 JAS37310.1 JAS37941.1 JAS40080.1 JAS46409.1 JAS51902.1 JAS59241.1 JAS61255.1 JAS61555.1 PYGN01001278 PSN36080.1 GEDC01029815 JAS07483.1 GEZM01055133 GEZM01055130 JAV73116.1 GEZM01055132 GEZM01055128 GEZM01055126 JAV73117.1 GEZM01055127 JAV73122.1 GALX01001302 JAB67164.1 KQ971307 EFA11314.2 ABLF02039862 KQ435713 KOX79291.1 GEZM01055131 GEZM01055129 JAV73118.1 GFXV01001050 MBW12855.1 GGMS01010186 MBY79389.1 JR036295 JR036297 JR036299 JR036301 AEY57056.1 AEY57058.1 AEY57060.1 AEY57062.1 GGMR01017509 MBY30128.1 KQ414727 KOC62558.1 KZ288215 PBC32470.1 GGMS01012013 MBY81216.1 GDIQ01040756 GDIQ01003471 JAN91266.1 GDIP01181489 JAJ41913.1 KYB29773.1 GDIP01171494 JAJ51908.1 GDIQ01162627 JAK89098.1 CH477841 EAT35758.1 EAT35759.1 JXUM01049605 JN967628 KQ561613 AFC78721.1 KXJ77998.1 KQ435078 KZC14427.1 GFDL01012651 JAV22394.1 GDIQ01081251 JAN13486.1 GDIQ01220012 JAK31713.1 GDIQ01247353 JAK04372.1 JN967627 AFC78720.1 DS232152 EDS36202.1 BC072167 AAH72167.1 GAPW01002391 JAC11207.1 CM004482 OCT62569.1 CM004483 OCT60351.1 BT126729 AEE61691.1 GALA01001033 JAA93819.1 IACK01019095 LAA68825.1 KB536575 EMP33256.1 GDIP01171495 JAJ51907.1 UFQS01000459 UFQS01000826 UFQT01000459 UFQT01000826 SSX04203.1 SSX27418.1 X62375 QUSF01000037 RLV98797.1 AHAT01018140 MUZQ01000152 OWK56617.1 LSYS01002950 OPJ84980.1 KN126853 KFU93120.1 ABQF01028338 KE163659 EPQ13026.1 KF516619 AII16523.1 U17112 AK146032 AK158077 AL831735 CH466551 BC026149 BC060742 BC089343 U51866 AAA96795.1 RAZU01000234 RLQ64175.1 AAQR03180014 AAQR03180015 AAQR03180016 AAQR03180017 AAQR03180018 AAQR03180019 AAQR03180020 GFAH01000133 JAV48256.1 L15618 BC091130 J02853 KK606023 KFW09181.1 KL889446 KGL76866.1 KK635004 KFV57919.1 KL670017 KFW77726.1 KL447823 KFO77504.1 KL218292 KFP03997.1 KL410370 KFQ96325.1 KK526524 KFP68324.1
NWSH01000357 PCG77048.1 JTDY01009137 KOB64058.1 GAIX01003484 JAA89076.1 KQ460207 KPJ16737.1 KQ459597 KPI94850.1 EF554579 ABU49714.1 AGBW02008321 OWR53693.1 KQ976437 KYM86937.1 GBYB01009162 JAG78929.1 GL448287 EFN84867.1 GL443213 EFN62439.1 LBMM01007090 KMQ90052.1 KQ980313 KYN16718.1 KK107591 QOIP01000013 EZA48626.1 RLU15526.1 KQ978350 KYM94682.1 DS235562 EEB16091.1 NEVH01003743 PNF40271.1 GL888353 EGI62250.1 KQ981664 KYN38485.1 KQ982617 KYQ53785.1 GECU01006642 JAT01065.1 KK852527 KDR22024.1 FX985745 BBA93632.1 GEDC01012962 JAS24336.1 GECU01035519 JAS72187.1 GECZ01032459 GECZ01031828 GECZ01029689 GECZ01023360 GECZ01017867 GECZ01010528 GECZ01008514 GECZ01008214 JAS37310.1 JAS37941.1 JAS40080.1 JAS46409.1 JAS51902.1 JAS59241.1 JAS61255.1 JAS61555.1 PYGN01001278 PSN36080.1 GEDC01029815 JAS07483.1 GEZM01055133 GEZM01055130 JAV73116.1 GEZM01055132 GEZM01055128 GEZM01055126 JAV73117.1 GEZM01055127 JAV73122.1 GALX01001302 JAB67164.1 KQ971307 EFA11314.2 ABLF02039862 KQ435713 KOX79291.1 GEZM01055131 GEZM01055129 JAV73118.1 GFXV01001050 MBW12855.1 GGMS01010186 MBY79389.1 JR036295 JR036297 JR036299 JR036301 AEY57056.1 AEY57058.1 AEY57060.1 AEY57062.1 GGMR01017509 MBY30128.1 KQ414727 KOC62558.1 KZ288215 PBC32470.1 GGMS01012013 MBY81216.1 GDIQ01040756 GDIQ01003471 JAN91266.1 GDIP01181489 JAJ41913.1 KYB29773.1 GDIP01171494 JAJ51908.1 GDIQ01162627 JAK89098.1 CH477841 EAT35758.1 EAT35759.1 JXUM01049605 JN967628 KQ561613 AFC78721.1 KXJ77998.1 KQ435078 KZC14427.1 GFDL01012651 JAV22394.1 GDIQ01081251 JAN13486.1 GDIQ01220012 JAK31713.1 GDIQ01247353 JAK04372.1 JN967627 AFC78720.1 DS232152 EDS36202.1 BC072167 AAH72167.1 GAPW01002391 JAC11207.1 CM004482 OCT62569.1 CM004483 OCT60351.1 BT126729 AEE61691.1 GALA01001033 JAA93819.1 IACK01019095 LAA68825.1 KB536575 EMP33256.1 GDIP01171495 JAJ51907.1 UFQS01000459 UFQS01000826 UFQT01000459 UFQT01000826 SSX04203.1 SSX27418.1 X62375 QUSF01000037 RLV98797.1 AHAT01018140 MUZQ01000152 OWK56617.1 LSYS01002950 OPJ84980.1 KN126853 KFU93120.1 ABQF01028338 KE163659 EPQ13026.1 KF516619 AII16523.1 U17112 AK146032 AK158077 AL831735 CH466551 BC026149 BC060742 BC089343 U51866 AAA96795.1 RAZU01000234 RLQ64175.1 AAQR03180014 AAQR03180015 AAQR03180016 AAQR03180017 AAQR03180018 AAQR03180019 AAQR03180020 GFAH01000133 JAV48256.1 L15618 BC091130 J02853 KK606023 KFW09181.1 KL889446 KGL76866.1 KK635004 KFV57919.1 KL670017 KFW77726.1 KL447823 KFO77504.1 KL218292 KFP03997.1 KL410370 KFQ96325.1 KK526524 KFP68324.1
Proteomes
UP000005204
UP000218220
UP000037510
UP000053240
UP000053268
UP000007151
+ More
UP000078540 UP000008237 UP000000311 UP000036403 UP000078492 UP000053097 UP000279307 UP000078542 UP000009046 UP000235965 UP000007755 UP000078541 UP000075809 UP000027135 UP000245037 UP000007266 UP000007819 UP000053105 UP000005203 UP000053825 UP000242457 UP000192223 UP000008820 UP000069940 UP000249989 UP000076502 UP000002320 UP000233040 UP000186698 UP000031443 UP000276834 UP000018468 UP000197619 UP000190648 UP000007754 UP000079721 UP000000589 UP000001646 UP000273346 UP000005225 UP000002494 UP000001645 UP000053641 UP000053258 UP000053760 UP000054308 UP000053283
UP000078540 UP000008237 UP000000311 UP000036403 UP000078492 UP000053097 UP000279307 UP000078542 UP000009046 UP000235965 UP000007755 UP000078541 UP000075809 UP000027135 UP000245037 UP000007266 UP000007819 UP000053105 UP000005203 UP000053825 UP000242457 UP000192223 UP000008820 UP000069940 UP000249989 UP000076502 UP000002320 UP000233040 UP000186698 UP000031443 UP000276834 UP000018468 UP000197619 UP000190648 UP000007754 UP000079721 UP000000589 UP000001646 UP000273346 UP000005225 UP000002494 UP000001645 UP000053641 UP000053258 UP000053760 UP000054308 UP000053283
Interpro
ProteinModelPortal
H9J1T7
Q59HV9
A0A2H1WWX2
O76484
A0A2A4JZD8
A0A0L7KL16
+ More
S4P9Z6 A0A194RGM1 A0A194PUN6 B0LBZ3 A0A212FIX3 A0A151I5B1 A0A0C9R8G5 E2BH98 E2AW17 A0A0J7KIF9 A0A151J3G8 A0A026VYW4 A0A195C1G2 E0VRT5 A0A2J7RHG1 F4WU82 A0A151JW70 A0A151X092 A0A1B6JP93 A0A067RQK2 A0A2Z5TZA5 A0A1B6DFA8 A0A1B6HBX2 A0A1B6EQA3 A0A2P8XVP2 A0A1B6C1T2 A0A1Y1LNF4 A0A1Y1LQ48 A0A1Y1LHJ1 V5GSL7 D6W7M8 J9JP30 A0A0N0BJQ2 A0A1Y1LJX6 A0A2H8TFK4 A0A087ZW71 A0A2S2QNP6 V9I7J1 A0A2S2PLG9 A0A0L7QV90 A0A2A3EL85 A0A2S2QTX1 A0A0P6IJG4 A0A0N8A556 A0A1W4WNT1 A0A139WPC3 A0A0P5CF09 A0A0N8BMQ4 Q16N28 H9AZT4 A0A154PRR3 A0A1Q3F4A5 A0A0P6DFT2 A0A0P5JST8 A0A0P5GIQ8 H9AZT3 B0WWU1 Q6INV5 A0A2K5Q3H4 A0A023EP31 A0A1L8ETF4 A0A1L8EM01 J3JU18 T1D4A2 A0A2D4HA14 M7B5N8 A0A0P5CHH3 A0A336MN57 P28020 A0A3L8S9E7 W5MKN8 A0A218US37 A0A1V4KKK6 A0A093BP39 H0Z8S4 A0A1S2ZQS3 S7N7R0 A0A076FER8 Q60737 G1KCJ4 Q61177 A0A3L7HE43 H0WLB6 A0A1W7RAV4 P19139 G1N6J4 A0A093LJS6 A0A099Z576 A0A093FU89 A0A093PMS6 A0A091G8J4 A0A091I711 A0A091V228 A0A091MCM8
S4P9Z6 A0A194RGM1 A0A194PUN6 B0LBZ3 A0A212FIX3 A0A151I5B1 A0A0C9R8G5 E2BH98 E2AW17 A0A0J7KIF9 A0A151J3G8 A0A026VYW4 A0A195C1G2 E0VRT5 A0A2J7RHG1 F4WU82 A0A151JW70 A0A151X092 A0A1B6JP93 A0A067RQK2 A0A2Z5TZA5 A0A1B6DFA8 A0A1B6HBX2 A0A1B6EQA3 A0A2P8XVP2 A0A1B6C1T2 A0A1Y1LNF4 A0A1Y1LQ48 A0A1Y1LHJ1 V5GSL7 D6W7M8 J9JP30 A0A0N0BJQ2 A0A1Y1LJX6 A0A2H8TFK4 A0A087ZW71 A0A2S2QNP6 V9I7J1 A0A2S2PLG9 A0A0L7QV90 A0A2A3EL85 A0A2S2QTX1 A0A0P6IJG4 A0A0N8A556 A0A1W4WNT1 A0A139WPC3 A0A0P5CF09 A0A0N8BMQ4 Q16N28 H9AZT4 A0A154PRR3 A0A1Q3F4A5 A0A0P6DFT2 A0A0P5JST8 A0A0P5GIQ8 H9AZT3 B0WWU1 Q6INV5 A0A2K5Q3H4 A0A023EP31 A0A1L8ETF4 A0A1L8EM01 J3JU18 T1D4A2 A0A2D4HA14 M7B5N8 A0A0P5CHH3 A0A336MN57 P28020 A0A3L8S9E7 W5MKN8 A0A218US37 A0A1V4KKK6 A0A093BP39 H0Z8S4 A0A1S2ZQS3 S7N7R0 A0A076FER8 Q60737 G1KCJ4 Q61177 A0A3L7HE43 H0WLB6 A0A1W7RAV4 P19139 G1N6J4 A0A093LJS6 A0A099Z576 A0A093FU89 A0A093PMS6 A0A091G8J4 A0A091I711 A0A091V228 A0A091MCM8
PDB
5ONI
E-value=3.25715e-161,
Score=1457
Ontologies
PATHWAY
GO
GO:0005524
GO:0004674
GO:0016055
GO:0008353
GO:0016021
GO:0004672
GO:0005634
GO:0018105
GO:0005956
GO:1905818
GO:0000785
GO:0046777
GO:0018107
GO:0016301
GO:0005654
GO:0008284
GO:0005737
GO:0006468
GO:0016581
GO:0008013
GO:0043154
GO:0030307
GO:0045732
GO:0016580
GO:0043021
GO:0042802
GO:0030177
GO:0047485
GO:2000059
GO:1903076
GO:0005886
GO:0006915
GO:0048511
GO:0007049
GO:0019888
GO:0097421
GO:0021987
GO:0033574
GO:0005667
GO:0006631
GO:0006635
GO:0006281
GO:0048384
Topology
Subcellular location
Nucleus
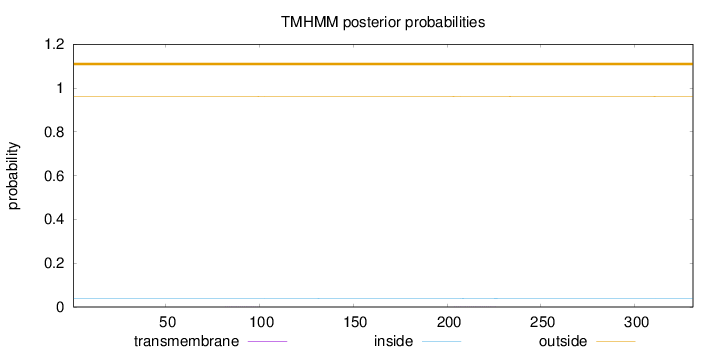
Length:
331
Number of predicted TMHs:
0
Exp number of AAs in TMHs:
0.01699
Exp number, first 60 AAs:
0
Total prob of N-in:
0.03847
outside
1 - 331
Population Genetic Test Statistics
Pi
264.024878
Theta
225.30262
Tajima's D
0.49384
CLR
144.314851
CSRT
0.512874356282186
Interpretation
Uncertain
