Pre Gene Modal
BGIBMGA003044
Annotation
PREDICTED:_myosin-VIIa_[Papilio_polytes]
Full name
Myosin-VIIa
Alternative Name
Protein crinkled
Location in the cell
Mitochondrial Reliability : 2.071
Sequence
CDS
ATGAAAAAGCTATGGACCAACACAGTTCCGGGTAAAGACAGGGCAGCAGACGTCATCTTCCACTTCCACCAGGAGCTCCCGAAGTTGCTGCGCGGCTACCACCGCTGCGGCCGCGAGGAGGCTGCCCGGCTCGCCGCCCTCGCCTACAGAGCGAGGTTCGGGGACAACAAGCAGGAGTTGCAAGCTATTCCACAAATGCTCCGCGAGTTAGCGCCGGCCGACCTCATCAAGCTTCAGAGTTCAGCGGATTGGAAGCGCGCCATCGTGGCTTCGTATAACCAGGACGCCGGAATGACACCCGAAGACGCCAAGATAACGTTCCTGAAGGTCATATACAGATGGCCAACGTTTGGATCCGCGTTCTTCGAGGTCAAACAAACTACGGAACCAAATTACCCTGAACTTTTACTTATAGCGATCAATAAACATGGAGTCAGTTTGATTCATCCTCAAACTAAGGACATTTTGGTGACGCACCCATTTACAAGAATATCTAACTGGTCGTCCGGGAACACATATTTCCACATGACCATCGGGAATTTGGTCCGTGGCTCTAAGCTTCTCTGCGAGACTTCGCTAGGGTACAAAATGGACGATCTTCTGACCTCTTATATATCGCTAATGCTGACTAACATGAACAAACAACGTTCCGTTAGAGTTAAATAG
Protein
MKKLWTNTVPGKDRAADVIFHFHQELPKLLRGYHRCGREEAARLAALAYRARFGDNKQELQAIPQMLRELAPADLIKLQSSADWKRAIVASYNQDAGMTPEDAKITFLKVIYRWPTFGSAFFEVKQTTEPNYPELLLIAINKHGVSLIHPQTKDILVTHPFTRISNWSSGNTYFHMTIGNLVRGSKLLCETSLGYKMDDLLTSYISLMLTNMNKQRSVRVK
Summary
Description
Myosins are actin-based motor molecules with ATPase activity. Unconventional myosins serve in intracellular movements: can function in cells as a single-molecule cargo transporter. A very slow and high-duty-ratio motor, may be suitable for tension maintenance of actin filaments. Their highly divergent tails are presumed to bind to membranous compartments, which would be moved relative to actin filaments. Plays a key role in the formation of cellular projections and other actin-based functions required for embryonic and larval viability. Necessary for auditory transduction: plays a role in Johnston organ (JO) organization by functioning in scolopidial apical attachment and therefore to acoustic stimulus propagation from the antenna a2/a3 joint to transducing elements (By similarity).
Myosins are actin-based motor molecules with ATPase activity (PubMed:16585515). Unconventional myosins serve in intracellular movements: can function in cells as a single-molecule cargo transporter (PubMed:16585515). A very slow and high-duty-ratio motor, may be suitable for tension maintenance of actin filaments (PubMed:16585515). Their highly divergent tails are presumed to bind to membranous compartments, which would be moved relative to actin filaments (PubMed:15579689). Plays a key role in the formation of cellular projections and other actin-based functions required for embryonic and larval viability (PubMed:15579689, PubMed:16585515). Necessary for auditory transduction: plays a role in Johnston's organ organization by functioning in scolopidial apical attachment and therefore to acoustic stimulus propagation from the antenna a2/a3 joint to transducing elements (PubMed:15886106, PubMed:27331610). Interaction with the myosin zip may be important for its function in scolopidial apical attachment (PubMed:27331610). During oogenesis it has Cad99c-dependent and Cad99c-independent roles in regulating the shape and spacing of the follicle cell microvilli which secrete eggshell material such as the vitelline membrane (PubMed:25236597). May be required for the normal expression of Cad99c in the follicle cell microvilli (PubMed:25236597).
Myosins are actin-based motor molecules with ATPase activity (PubMed:16585515). Unconventional myosins serve in intracellular movements: can function in cells as a single-molecule cargo transporter (PubMed:16585515). A very slow and high-duty-ratio motor, may be suitable for tension maintenance of actin filaments (PubMed:16585515). Their highly divergent tails are presumed to bind to membranous compartments, which would be moved relative to actin filaments (PubMed:15579689). Plays a key role in the formation of cellular projections and other actin-based functions required for embryonic and larval viability (PubMed:15579689, PubMed:16585515). Necessary for auditory transduction: plays a role in Johnston's organ organization by functioning in scolopidial apical attachment and therefore to acoustic stimulus propagation from the antenna a2/a3 joint to transducing elements (PubMed:15886106, PubMed:27331610). Interaction with the myosin zip may be important for its function in scolopidial apical attachment (PubMed:27331610). During oogenesis it has Cad99c-dependent and Cad99c-independent roles in regulating the shape and spacing of the follicle cell microvilli which secrete eggshell material such as the vitelline membrane (PubMed:25236597). May be required for the normal expression of Cad99c in the follicle cell microvilli (PubMed:25236597).
Subunit
Homodimerizes in a two headed molecule through the formation of a coiled-coil rod.
Homodimerizes in a two headed molecule through the formation of a coiled-coil rod (PubMed:16585515). Homodimers motility is approximately 8-10 times slower than that of myosin V, and its step size is 30 nm, which is consistent with the presence of five IQ motifs in its neck region (PubMed:16585515). Interacts with Cad99C (via the cytoplasmic domain) (PubMed:25236597, PubMed:27331610). Interacts with zip and Sans (PubMed:27331610).
Homodimerizes in a two headed molecule through the formation of a coiled-coil rod (PubMed:16585515). Homodimers motility is approximately 8-10 times slower than that of myosin V, and its step size is 30 nm, which is consistent with the presence of five IQ motifs in its neck region (PubMed:16585515). Interacts with Cad99C (via the cytoplasmic domain) (PubMed:25236597, PubMed:27331610). Interacts with zip and Sans (PubMed:27331610).
Similarity
Belongs to the TRAFAC class myosin-kinesin ATPase superfamily. Myosin family.
Keywords
Actin-binding
ATP-binding
Coiled coil
Complete proteome
Cytoplasm
Motor protein
Myosin
Nucleotide-binding
Reference proteome
Repeat
SH3 domain
Cell projection
Phosphoprotein
Feature
chain Myosin-VIIa
Uniprot
S4PY43
A0A2H1VD92
A0A1B6JFQ5
A0A1B6JY50
A0A1W4VJ54
A0A1B6MEB8
+ More
A0A194PMR5 A0A2A4JZM2 A0A0N1PEV6 A0A1B0C9Y5 T1PJ75 A0A1B6H5W4 W8AZS4 A0A182SXR4 A0A2J7QBQ5 A0A088A376 A0A2P6KC23 A0A154P506 A0A1B6ETW6 A0A0L7QXL8 E2BI60 A0A348G641 A0A151HY88 A0A195DUL7 A0A158NSP1 A0A195CAT1 F4W8A1 A0A151XDL4 E2AKY2 A0A0J7KBG7 A0A026WSA2 A0A0C9RPF2 A0A1L8E5A4 A0A0K2TL06 A0A195EXJ5 A0A2M4A239 A0A182H556 B0WB21 Q17LW0 A0A2M4CMY6 A0A2M4B870 A0A2M4A185 A0A2M3YZS8 A0A2M4B856 A0A2M4A1G1 A0A2M4CMB7 A0A2M4CM41 W5JPK4 A0A1S4HE37 A0A182FN67 D6WM41 A0A1Y1LTF3 A0A182WG81 A0A182Y0E2 A0A182RM10 A0A182IPQ8 A0A182LVW6 A0A182PDV3 A0A182MZ42 U4UK26 A0A182TFZ3 A0A182VP23 A0A182R007 A0A182XNT2 A0A182LMR3 A0A182I7D7 A0A034V4Y4 A0A084VL31 A0A182JZ48 A0A0K2TKN1 A0A2J7QBS1 A0A1B6CKI8 A0A067QNC8 A0A293L7I5 A0A226DMI0 T1ICE8 A0A2A3E8T4 A0A1I8N9D6 K7J8Z2 A0A232EMR2 B4JAX3 J9K7H6 A0A1B0G9B5 B4LRY0 A0A2H8TFY4 B4HXL9 B4Q5Z3 G7H829 Q9V3Z6 B3N5N5 A0A1I8NXV5 B4NYT1 B4KLB7 A0A1W4WBQ5 B3MLC3 B4MZD8 A0A034V390 A0A0K8WG24 A0A293M542 E0VVF2
A0A194PMR5 A0A2A4JZM2 A0A0N1PEV6 A0A1B0C9Y5 T1PJ75 A0A1B6H5W4 W8AZS4 A0A182SXR4 A0A2J7QBQ5 A0A088A376 A0A2P6KC23 A0A154P506 A0A1B6ETW6 A0A0L7QXL8 E2BI60 A0A348G641 A0A151HY88 A0A195DUL7 A0A158NSP1 A0A195CAT1 F4W8A1 A0A151XDL4 E2AKY2 A0A0J7KBG7 A0A026WSA2 A0A0C9RPF2 A0A1L8E5A4 A0A0K2TL06 A0A195EXJ5 A0A2M4A239 A0A182H556 B0WB21 Q17LW0 A0A2M4CMY6 A0A2M4B870 A0A2M4A185 A0A2M3YZS8 A0A2M4B856 A0A2M4A1G1 A0A2M4CMB7 A0A2M4CM41 W5JPK4 A0A1S4HE37 A0A182FN67 D6WM41 A0A1Y1LTF3 A0A182WG81 A0A182Y0E2 A0A182RM10 A0A182IPQ8 A0A182LVW6 A0A182PDV3 A0A182MZ42 U4UK26 A0A182TFZ3 A0A182VP23 A0A182R007 A0A182XNT2 A0A182LMR3 A0A182I7D7 A0A034V4Y4 A0A084VL31 A0A182JZ48 A0A0K2TKN1 A0A2J7QBS1 A0A1B6CKI8 A0A067QNC8 A0A293L7I5 A0A226DMI0 T1ICE8 A0A2A3E8T4 A0A1I8N9D6 K7J8Z2 A0A232EMR2 B4JAX3 J9K7H6 A0A1B0G9B5 B4LRY0 A0A2H8TFY4 B4HXL9 B4Q5Z3 G7H829 Q9V3Z6 B3N5N5 A0A1I8NXV5 B4NYT1 B4KLB7 A0A1W4WBQ5 B3MLC3 B4MZD8 A0A034V390 A0A0K8WG24 A0A293M542 E0VVF2
Pubmed
23622113
26354079
24495485
20798317
21347285
21719571
+ More
24508170 30249741 26483478 17510324 20920257 23761445 18362917 19820115 28004739 25244985 23537049 20966253 25348373 24438588 24845553 25315136 20075255 28648823 17994087 22936249 10731132 12537568 12537572 12537573 12537574 16110336 17569856 17569867 26109357 26109356 15579689 15886106 16585515 18327897 25236597 27331610 17550304 18057021 20566863
24508170 30249741 26483478 17510324 20920257 23761445 18362917 19820115 28004739 25244985 23537049 20966253 25348373 24438588 24845553 25315136 20075255 28648823 17994087 22936249 10731132 12537568 12537572 12537573 12537574 16110336 17569856 17569867 26109357 26109356 15579689 15886106 16585515 18327897 25236597 27331610 17550304 18057021 20566863
EMBL
GAIX01003938
JAA88622.1
ODYU01001903
SOQ38761.1
GECU01009626
JAS98080.1
+ More
GECU01003555 JAT04152.1 GEBQ01005748 JAT34229.1 KQ459598 KPI94607.1 NWSH01000324 PCG77465.1 KQ461183 KPJ07555.1 AJWK01003033 KA648816 AFP63445.1 GECU01037649 JAS70057.1 GAMC01020164 JAB86391.1 NEVH01016296 PNF26020.1 MWRG01016409 PRD23880.1 KQ434809 KZC06404.1 GECZ01028367 JAS41402.1 KQ414704 KOC63304.1 GL448450 EFN84631.1 FX985580 BBF97914.1 KQ976723 KYM76657.1 KQ980322 KYN16600.1 ADTU01025086 ADTU01025087 ADTU01025088 ADTU01025089 KQ978023 KYM97974.1 GL887898 EGI69596.1 KQ982275 KYQ58443.1 GL440425 EFN65899.1 LBMM01010038 KMQ87708.1 KK107111 QOIP01000011 EZA58907.1 RLU16549.1 GBYB01009046 JAG78813.1 GFDF01000260 JAV13824.1 HACA01009243 CDW26604.1 KQ981948 KYN32622.1 GGFK01001508 MBW34829.1 JXUM01110817 KQ565447 KXJ70961.1 DS231876 EDS41979.1 CH477210 EAT47711.1 GGFL01002524 MBW66702.1 GGFJ01000103 MBW49244.1 GGFK01001253 MBW34574.1 GGFM01000990 MBW21741.1 GGFJ01000094 MBW49235.1 GGFK01001239 MBW34560.1 GGFL01002304 MBW66482.1 GGFL01002232 MBW66410.1 ADMH02000481 ETN66322.1 KQ971343 EFA03361.1 GEZM01051100 JAV75175.1 AXCM01005165 KB632357 ERL93472.1 AXCN02000794 APCN01003381 GAKP01022339 JAC36613.1 ATLV01014402 KE524970 KFB38675.1 HACA01009242 CDW26603.1 PNF26019.1 GEDC01025701 GEDC01023358 JAS11597.1 JAS13940.1 KK853129 KDR10964.1 GFWV01003887 MAA28617.1 LNIX01000015 OXA46423.1 ACPB03003006 ACPB03003007 ACPB03003008 KZ288322 PBC28193.1 NNAY01003312 OXU19644.1 CH916368 EDW02843.1 ABLF02026551 ABLF02026555 CCAG010021883 CH940649 EDW63656.2 GFXV01001199 MBW13004.1 CH480818 EDW51799.1 CM000361 CM002910 EDX05096.1 KMY90323.1 BT132752 AE014134 AET07635.1 AHN54463.1 AHN54464.1 AY069438 BT011332 AAF53435.1 AAR96124.1 CH954177 EDV57994.1 CM000157 EDW89782.1 CH933807 EDW11778.1 KRG02912.1 KRG02913.1 CH902620 EDV30712.1 CH963913 EDW77477.1 GAKP01022340 JAC36612.1 GDHF01032785 GDHF01002196 JAI19529.1 JAI50118.1 GFWV01010707 MAA35436.1 DS235811 EEB17358.1
GECU01003555 JAT04152.1 GEBQ01005748 JAT34229.1 KQ459598 KPI94607.1 NWSH01000324 PCG77465.1 KQ461183 KPJ07555.1 AJWK01003033 KA648816 AFP63445.1 GECU01037649 JAS70057.1 GAMC01020164 JAB86391.1 NEVH01016296 PNF26020.1 MWRG01016409 PRD23880.1 KQ434809 KZC06404.1 GECZ01028367 JAS41402.1 KQ414704 KOC63304.1 GL448450 EFN84631.1 FX985580 BBF97914.1 KQ976723 KYM76657.1 KQ980322 KYN16600.1 ADTU01025086 ADTU01025087 ADTU01025088 ADTU01025089 KQ978023 KYM97974.1 GL887898 EGI69596.1 KQ982275 KYQ58443.1 GL440425 EFN65899.1 LBMM01010038 KMQ87708.1 KK107111 QOIP01000011 EZA58907.1 RLU16549.1 GBYB01009046 JAG78813.1 GFDF01000260 JAV13824.1 HACA01009243 CDW26604.1 KQ981948 KYN32622.1 GGFK01001508 MBW34829.1 JXUM01110817 KQ565447 KXJ70961.1 DS231876 EDS41979.1 CH477210 EAT47711.1 GGFL01002524 MBW66702.1 GGFJ01000103 MBW49244.1 GGFK01001253 MBW34574.1 GGFM01000990 MBW21741.1 GGFJ01000094 MBW49235.1 GGFK01001239 MBW34560.1 GGFL01002304 MBW66482.1 GGFL01002232 MBW66410.1 ADMH02000481 ETN66322.1 KQ971343 EFA03361.1 GEZM01051100 JAV75175.1 AXCM01005165 KB632357 ERL93472.1 AXCN02000794 APCN01003381 GAKP01022339 JAC36613.1 ATLV01014402 KE524970 KFB38675.1 HACA01009242 CDW26603.1 PNF26019.1 GEDC01025701 GEDC01023358 JAS11597.1 JAS13940.1 KK853129 KDR10964.1 GFWV01003887 MAA28617.1 LNIX01000015 OXA46423.1 ACPB03003006 ACPB03003007 ACPB03003008 KZ288322 PBC28193.1 NNAY01003312 OXU19644.1 CH916368 EDW02843.1 ABLF02026551 ABLF02026555 CCAG010021883 CH940649 EDW63656.2 GFXV01001199 MBW13004.1 CH480818 EDW51799.1 CM000361 CM002910 EDX05096.1 KMY90323.1 BT132752 AE014134 AET07635.1 AHN54463.1 AHN54464.1 AY069438 BT011332 AAF53435.1 AAR96124.1 CH954177 EDV57994.1 CM000157 EDW89782.1 CH933807 EDW11778.1 KRG02912.1 KRG02913.1 CH902620 EDV30712.1 CH963913 EDW77477.1 GAKP01022340 JAC36612.1 GDHF01032785 GDHF01002196 JAI19529.1 JAI50118.1 GFWV01010707 MAA35436.1 DS235811 EEB17358.1
Proteomes
UP000192221
UP000053268
UP000218220
UP000053240
UP000092461
UP000075901
+ More
UP000235965 UP000005203 UP000076502 UP000053825 UP000008237 UP000078540 UP000078492 UP000005205 UP000078542 UP000007755 UP000075809 UP000000311 UP000036403 UP000053097 UP000279307 UP000078541 UP000069940 UP000249989 UP000002320 UP000008820 UP000000673 UP000069272 UP000007266 UP000075920 UP000076408 UP000075900 UP000075880 UP000075883 UP000075885 UP000075884 UP000030742 UP000075902 UP000075903 UP000075886 UP000076407 UP000075882 UP000075840 UP000030765 UP000075881 UP000027135 UP000198287 UP000015103 UP000242457 UP000095301 UP000002358 UP000215335 UP000001070 UP000007819 UP000092444 UP000008792 UP000001292 UP000000304 UP000000803 UP000008711 UP000095300 UP000002282 UP000009192 UP000007801 UP000007798 UP000009046
UP000235965 UP000005203 UP000076502 UP000053825 UP000008237 UP000078540 UP000078492 UP000005205 UP000078542 UP000007755 UP000075809 UP000000311 UP000036403 UP000053097 UP000279307 UP000078541 UP000069940 UP000249989 UP000002320 UP000008820 UP000000673 UP000069272 UP000007266 UP000075920 UP000076408 UP000075900 UP000075880 UP000075883 UP000075885 UP000075884 UP000030742 UP000075902 UP000075903 UP000075886 UP000076407 UP000075882 UP000075840 UP000030765 UP000075881 UP000027135 UP000198287 UP000015103 UP000242457 UP000095301 UP000002358 UP000215335 UP000001070 UP000007819 UP000092444 UP000008792 UP000001292 UP000000304 UP000000803 UP000008711 UP000095300 UP000002282 UP000009192 UP000007801 UP000007798 UP000009046
Pfam
Interpro
IPR036028
SH3-like_dom_sf
+ More
IPR029071 Ubiquitin-like_domsf
IPR000299 FERM_domain
IPR041794 MyoVII_FERM_C2
IPR018979 FERM_N
IPR011993 PH-like_dom_sf
IPR019748 FERM_central
IPR041793 MyoVII_FERM_C1
IPR038185 MyTH4_dom_sf
IPR035963 FERM_2
IPR014352 FERM/acyl-CoA-bd_prot_sf
IPR000857 MyTH4_dom
IPR019749 Band_41_domain
IPR001452 SH3_domain
IPR000048 IQ_motif_EF-hand-BS
IPR036106 MYSc_Myo7
IPR008989 Myosin_S1_N
IPR001609 Myosin_head_motor_dom
IPR036961 Kinesin_motor_dom_sf
IPR027417 P-loop_NTPase
IPR032135 DUF4817
IPR031732 DUF4729
IPR029071 Ubiquitin-like_domsf
IPR000299 FERM_domain
IPR041794 MyoVII_FERM_C2
IPR018979 FERM_N
IPR011993 PH-like_dom_sf
IPR019748 FERM_central
IPR041793 MyoVII_FERM_C1
IPR038185 MyTH4_dom_sf
IPR035963 FERM_2
IPR014352 FERM/acyl-CoA-bd_prot_sf
IPR000857 MyTH4_dom
IPR019749 Band_41_domain
IPR001452 SH3_domain
IPR000048 IQ_motif_EF-hand-BS
IPR036106 MYSc_Myo7
IPR008989 Myosin_S1_N
IPR001609 Myosin_head_motor_dom
IPR036961 Kinesin_motor_dom_sf
IPR027417 P-loop_NTPase
IPR032135 DUF4817
IPR031732 DUF4729
ProteinModelPortal
S4PY43
A0A2H1VD92
A0A1B6JFQ5
A0A1B6JY50
A0A1W4VJ54
A0A1B6MEB8
+ More
A0A194PMR5 A0A2A4JZM2 A0A0N1PEV6 A0A1B0C9Y5 T1PJ75 A0A1B6H5W4 W8AZS4 A0A182SXR4 A0A2J7QBQ5 A0A088A376 A0A2P6KC23 A0A154P506 A0A1B6ETW6 A0A0L7QXL8 E2BI60 A0A348G641 A0A151HY88 A0A195DUL7 A0A158NSP1 A0A195CAT1 F4W8A1 A0A151XDL4 E2AKY2 A0A0J7KBG7 A0A026WSA2 A0A0C9RPF2 A0A1L8E5A4 A0A0K2TL06 A0A195EXJ5 A0A2M4A239 A0A182H556 B0WB21 Q17LW0 A0A2M4CMY6 A0A2M4B870 A0A2M4A185 A0A2M3YZS8 A0A2M4B856 A0A2M4A1G1 A0A2M4CMB7 A0A2M4CM41 W5JPK4 A0A1S4HE37 A0A182FN67 D6WM41 A0A1Y1LTF3 A0A182WG81 A0A182Y0E2 A0A182RM10 A0A182IPQ8 A0A182LVW6 A0A182PDV3 A0A182MZ42 U4UK26 A0A182TFZ3 A0A182VP23 A0A182R007 A0A182XNT2 A0A182LMR3 A0A182I7D7 A0A034V4Y4 A0A084VL31 A0A182JZ48 A0A0K2TKN1 A0A2J7QBS1 A0A1B6CKI8 A0A067QNC8 A0A293L7I5 A0A226DMI0 T1ICE8 A0A2A3E8T4 A0A1I8N9D6 K7J8Z2 A0A232EMR2 B4JAX3 J9K7H6 A0A1B0G9B5 B4LRY0 A0A2H8TFY4 B4HXL9 B4Q5Z3 G7H829 Q9V3Z6 B3N5N5 A0A1I8NXV5 B4NYT1 B4KLB7 A0A1W4WBQ5 B3MLC3 B4MZD8 A0A034V390 A0A0K8WG24 A0A293M542 E0VVF2
A0A194PMR5 A0A2A4JZM2 A0A0N1PEV6 A0A1B0C9Y5 T1PJ75 A0A1B6H5W4 W8AZS4 A0A182SXR4 A0A2J7QBQ5 A0A088A376 A0A2P6KC23 A0A154P506 A0A1B6ETW6 A0A0L7QXL8 E2BI60 A0A348G641 A0A151HY88 A0A195DUL7 A0A158NSP1 A0A195CAT1 F4W8A1 A0A151XDL4 E2AKY2 A0A0J7KBG7 A0A026WSA2 A0A0C9RPF2 A0A1L8E5A4 A0A0K2TL06 A0A195EXJ5 A0A2M4A239 A0A182H556 B0WB21 Q17LW0 A0A2M4CMY6 A0A2M4B870 A0A2M4A185 A0A2M3YZS8 A0A2M4B856 A0A2M4A1G1 A0A2M4CMB7 A0A2M4CM41 W5JPK4 A0A1S4HE37 A0A182FN67 D6WM41 A0A1Y1LTF3 A0A182WG81 A0A182Y0E2 A0A182RM10 A0A182IPQ8 A0A182LVW6 A0A182PDV3 A0A182MZ42 U4UK26 A0A182TFZ3 A0A182VP23 A0A182R007 A0A182XNT2 A0A182LMR3 A0A182I7D7 A0A034V4Y4 A0A084VL31 A0A182JZ48 A0A0K2TKN1 A0A2J7QBS1 A0A1B6CKI8 A0A067QNC8 A0A293L7I5 A0A226DMI0 T1ICE8 A0A2A3E8T4 A0A1I8N9D6 K7J8Z2 A0A232EMR2 B4JAX3 J9K7H6 A0A1B0G9B5 B4LRY0 A0A2H8TFY4 B4HXL9 B4Q5Z3 G7H829 Q9V3Z6 B3N5N5 A0A1I8NXV5 B4NYT1 B4KLB7 A0A1W4WBQ5 B3MLC3 B4MZD8 A0A034V390 A0A0K8WG24 A0A293M542 E0VVF2
PDB
5MV9
E-value=2.51372e-87,
Score=818
Ontologies
GO
GO:0005856
GO:0016459
GO:0005524
GO:0051015
GO:0003774
GO:0003779
GO:0005737
GO:0048800
GO:0030898
GO:0008407
GO:0032027
GO:0007605
GO:0030048
GO:0035317
GO:0016021
GO:0032529
GO:0035182
GO:0070825
GO:0045180
GO:0031477
GO:0045179
GO:0035293
GO:0008586
GO:0007015
GO:0005902
GO:0045296
GO:0016887
GO:0007469
GO:0042623
GO:0007423
GO:0016461
GO:0005938
GO:0051603
GO:0008483
GO:0006418
GO:0016507
GO:0048384
Topology
Subcellular location
Cytoplasm
Cell cortex In scolopale cells (radially organized units in the Johnston's organ), protein is concentrated along actin-rich scolopale rods and more apically near scolopale cell-cap cell junctions (PubMed:15886106). In neurons, protein is concentrated near the basal body where neurons are tethered to the scolopale cell (PubMed:15886106). In germline and associated somatic cells of the ovary, it has a punctate distribution and associates with specific F-actin cell structures (PubMed:25236597). In germline cells, expressed in the F-actin-rich cytocortex of the oocyte (from stage 3, peaking at stages 9 to 10a) and in the cortex of nurse cells (from stage 6) (PubMed:25236597). Expressed in the microvilli and terminal web of follicle cells (PubMed:25236597). High expression at the base of the follicle cell microvilli in the brush border (PubMed:25236597). With evidence from 10 publications.
Cell projection In scolopale cells (radially organized units in the Johnston's organ), protein is concentrated along actin-rich scolopale rods and more apically near scolopale cell-cap cell junctions (PubMed:15886106). In neurons, protein is concentrated near the basal body where neurons are tethered to the scolopale cell (PubMed:15886106). In germline and associated somatic cells of the ovary, it has a punctate distribution and associates with specific F-actin cell structures (PubMed:25236597). In germline cells, expressed in the F-actin-rich cytocortex of the oocyte (from stage 3, peaking at stages 9 to 10a) and in the cortex of nurse cells (from stage 6) (PubMed:25236597). Expressed in the microvilli and terminal web of follicle cells (PubMed:25236597). High expression at the base of the follicle cell microvilli in the brush border (PubMed:25236597). With evidence from 10 publications.
Microvillus In scolopale cells (radially organized units in the Johnston's organ), protein is concentrated along actin-rich scolopale rods and more apically near scolopale cell-cap cell junctions (PubMed:15886106). In neurons, protein is concentrated near the basal body where neurons are tethered to the scolopale cell (PubMed:15886106). In germline and associated somatic cells of the ovary, it has a punctate distribution and associates with specific F-actin cell structures (PubMed:25236597). In germline cells, expressed in the F-actin-rich cytocortex of the oocyte (from stage 3, peaking at stages 9 to 10a) and in the cortex of nurse cells (from stage 6) (PubMed:25236597). Expressed in the microvilli and terminal web of follicle cells (PubMed:25236597). High expression at the base of the follicle cell microvilli in the brush border (PubMed:25236597). With evidence from 10 publications.
Cell cortex In scolopale cells (radially organized units in the Johnston's organ), protein is concentrated along actin-rich scolopale rods and more apically near scolopale cell-cap cell junctions (PubMed:15886106). In neurons, protein is concentrated near the basal body where neurons are tethered to the scolopale cell (PubMed:15886106). In germline and associated somatic cells of the ovary, it has a punctate distribution and associates with specific F-actin cell structures (PubMed:25236597). In germline cells, expressed in the F-actin-rich cytocortex of the oocyte (from stage 3, peaking at stages 9 to 10a) and in the cortex of nurse cells (from stage 6) (PubMed:25236597). Expressed in the microvilli and terminal web of follicle cells (PubMed:25236597). High expression at the base of the follicle cell microvilli in the brush border (PubMed:25236597). With evidence from 10 publications.
Cell projection In scolopale cells (radially organized units in the Johnston's organ), protein is concentrated along actin-rich scolopale rods and more apically near scolopale cell-cap cell junctions (PubMed:15886106). In neurons, protein is concentrated near the basal body where neurons are tethered to the scolopale cell (PubMed:15886106). In germline and associated somatic cells of the ovary, it has a punctate distribution and associates with specific F-actin cell structures (PubMed:25236597). In germline cells, expressed in the F-actin-rich cytocortex of the oocyte (from stage 3, peaking at stages 9 to 10a) and in the cortex of nurse cells (from stage 6) (PubMed:25236597). Expressed in the microvilli and terminal web of follicle cells (PubMed:25236597). High expression at the base of the follicle cell microvilli in the brush border (PubMed:25236597). With evidence from 10 publications.
Microvillus In scolopale cells (radially organized units in the Johnston's organ), protein is concentrated along actin-rich scolopale rods and more apically near scolopale cell-cap cell junctions (PubMed:15886106). In neurons, protein is concentrated near the basal body where neurons are tethered to the scolopale cell (PubMed:15886106). In germline and associated somatic cells of the ovary, it has a punctate distribution and associates with specific F-actin cell structures (PubMed:25236597). In germline cells, expressed in the F-actin-rich cytocortex of the oocyte (from stage 3, peaking at stages 9 to 10a) and in the cortex of nurse cells (from stage 6) (PubMed:25236597). Expressed in the microvilli and terminal web of follicle cells (PubMed:25236597). High expression at the base of the follicle cell microvilli in the brush border (PubMed:25236597). With evidence from 10 publications.
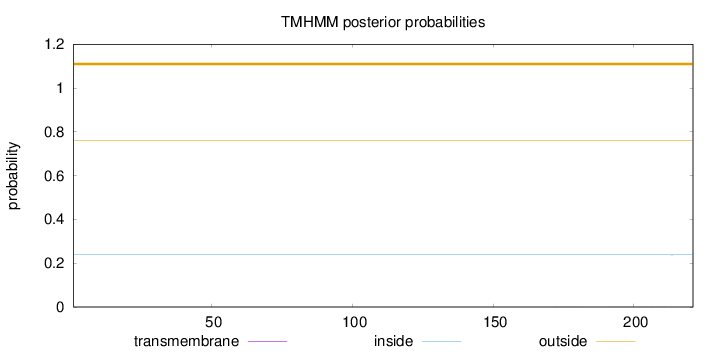
Length:
221
Number of predicted TMHs:
0
Exp number of AAs in TMHs:
0.00939
Exp number, first 60 AAs:
0
Total prob of N-in:
0.23820
outside
1 - 221
Population Genetic Test Statistics
Pi
175.853527
Theta
196.800413
Tajima's D
1.416838
CLR
0.027469
CSRT
0.766661666916654
Interpretation
Uncertain
