Gene
KWMTBOMO01223
Pre Gene Modal
BGIBMGA009037
Annotation
argonaute_3_[Bombyx_mori]
Full name
Piwi-like protein Ago3
+ More
Piwi-like protein 1
Piwi-like protein 1
Location in the cell
Extracellular Reliability : 3.534
Sequence
CDS
ATGTCTGTGCTATCTTACAAGGCTGGCAGTTTTGTAGCATCCTATAATCAAAGCATGACGCTTTGGTATTCGAAAGTGATCTTCCAAGAGAAGGGTCAAGAAATAGTTGATGGCTTGAAATGTTGTCTCGTTGATGCGTTAACTCATTATTTGAGATCAAACGGACAGCTTCCGGACAGGATCATCATATACAGAGACGGTGTAGGCGACGGGCAGCTGAAGTTATTGCAGCAATACGAGATACCTCAAATGAAGATTTGCTTCACGATATTGGGATCGAATTACCAGCCTACCCTGACCTATGTTGTCGTACAAAAACGTATCAACACTAGGATCTTCCTGAAGTCGAGAGACGGCTACGACAATCCGAACCCCGGGACCGTGGTCGATCACTGTATAACGAGACGGGACTGGTACGATTTCCTGATCGTCTCGCAGAAAGTGACCCAGGGCACTGTCACCCCGACCCATTACGTGGTGGTCTACGACGACAGCGGGATCACCCCGGACCAGTGTCAGCGTTTGACGTACAAGATGTGTCACTTGTACTACAACTGGCCGGGGACCGTGCGCGTTCCGGCGCCCTGTCAGTATGCGCACAAACTCTCGTATCTAGTGGGACAGTGCGTGCACGCGCAGCCGTCTGACGTTTTAGTCGATAAGCTGTTCTTTTTGTAG
Protein
MSVLSYKAGSFVASYNQSMTLWYSKVIFQEKGQEIVDGLKCCLVDALTHYLRSNGQLPDRIIIYRDGVGDGQLKLLQQYEIPQMKICFTILGSNYQPTLTYVVVQKRINTRIFLKSRDGYDNPNPGTVVDHCITRRDWYDFLIVSQKVTQGTVTPTHYVVVYDDSGITPDQCQRLTYKMCHLYYNWPGTVRVPAPCQYAHKLSYLVGQCVHAQPSDVLVDKLFFL
Summary
Description
Endoribonuclease that plays a central role during spermatogenesis by repressing transposable elements and preventing their mobilization, which is essential for the germline integrity (PubMed:19460866). Plays an essential role in meiotic differentiation of spermatocytes, germ cell differentiation and in self-renewal of spermatogonial stem cells (PubMed:19460866, PubMed:25558067). Its presence in oocytes suggests that it may participate in similar functions during oogenesis in females (PubMed:18191035). Acts via the piRNA metabolic process, which mediates the repression of transposable elements during meiosis by forming complexes composed of piRNAs and Piwi proteins and govern the methylation and subsequent repression of transposons (PubMed:19460866, PubMed:25558067). Directly binds piRNAs, a class of 24 to 30 nucleotide RNAs that are generated by a Dicer-independent mechanism and are primarily derived from transposons and other repeated sequence elements (PubMed:19460866, PubMed:25558067). Strongly prefers a have adenine at position 10 of their guide (g10A preference) (PubMed:24757166, PubMed:25558067). Plays a key role in the piRNA amplification loop, also named ping-pong amplification cycle: antisense piRNA-bound Siwi and sense piRNA-bound Ago3 reciprocally cleave complementary transcripts, to couple the amplification of piRNAs with the repression of transposable elements (PubMed:25558067).
Endoribonuclease that plays a central role in postnatal germ cells by repressing transposable elements and preventing their mobilization, which is essential for the germline integrity. Acts via the piRNA metabolic process, which mediates the repression of transposable elements during meiosis by forming complexes composed of piRNAs and Piwi proteins and governs the methylation and subsequent repression of transposons. Directly binds methylated piRNAs, a class of 24 to 30 nucleotide RNAs that are generated by a Dicer-independent mechanism and are primarily derived from transposons and other repeated sequence elements. Strongly prefers a uridine in the first position of their guide (g1U preference, also named 1U-bias). Not involved in the piRNA amplification loop, also named ping-pong amplification cycle. Acts as an endoribonuclease that cleaves transposon messenger RNAs. Besides their function in transposable elements repression, piRNAs are probably involved in other processes during meiosis such as translation regulation. Probable component of some RISC complex, which mediates RNA cleavage and translational silencing. Also plays a role in the formation of chromatoid bodies and is required for some miRNAs stability. Required to sequester RNF8 in the cytoplasm until late spermatogenesis; RNF8 being released upon ubiquitination and degradation of PIWIL1.
Isoform 3: May be a negative developmental regulator (PubMed:12037681, PubMed:16287078).
Endoribonuclease that plays a central role in postnatal germ cells by repressing transposable elements and preventing their mobilization, which is essential for the germline integrity. Acts via the piRNA metabolic process, which mediates the repression of transposable elements during meiosis by forming complexes composed of piRNAs and Piwi proteins and governs the methylation and subsequent repression of transposons. Directly binds methylated piRNAs, a class of 24 to 30 nucleotide RNAs that are generated by a Dicer-independent mechanism and are primarily derived from transposons and other repeated sequence elements. Strongly prefers a uridine in the first position of their guide (g1U preference, also named 1U-bias). Not involved in the piRNA amplification loop, also named ping-pong amplification cycle. Acts as an endoribonuclease that cleaves transposon messenger RNAs. Besides their function in transposable elements repression, piRNAs are probably involved in other processes during meiosis such as translation regulation. Probable component of some RISC complex, which mediates RNA cleavage and translational silencing. Also plays a role in the formation of chromatoid bodies and is required for some miRNAs stability. Required to sequester RNF8 in the cytoplasm until late spermatogenesis; RNF8 being released upon ubiquitination and degradation of PIWIL1.
Isoform 3: May be a negative developmental regulator (PubMed:12037681, PubMed:16287078).
Cofactor
Mg(2+)
Subunit
Interacts (when symmetrically methylated) with Papi/TDRKH (PubMed:23970546). Interacts with Vasa.
Interacts (via Piwi domain) with DICER1, suggesting that it forms ribonucleoprotein RISC complexes; this interaction is regulated by HSP90AB1 activity. Interacts with MAEL, KIF17, PABPC1, PRMT5 and WDR77. Interacts (when methylated on arginine residues) with TDRD1, TDRKH/TDRD2, RNF17/TDRD4, TDRD6, TDRD7 and TDRD9. Interacts with CLOCK. Interacts with MOV10L1. Interacts with ANAPC10; interaction oly takes place following piRNA-binding. Interacts with RNF8; leading to sequester RNF8 in the cytoplasm. Interacts with TEX19 (By similarity).
Interacts (via Piwi domain) with DICER1, suggesting that it forms ribonucleoprotein RISC complexes; this interaction is regulated by HSP90AB1 activity. Interacts with MAEL, KIF17, PABPC1, PRMT5 and WDR77. Interacts (when methylated on arginine residues) with TDRD1, TDRKH/TDRD2, RNF17/TDRD4, TDRD6, TDRD7 and TDRD9. Interacts with CLOCK. Interacts with MOV10L1. Interacts with ANAPC10; interaction oly takes place following piRNA-binding. Interacts with RNF8; leading to sequester RNF8 in the cytoplasm. Interacts with TEX19 (By similarity).
Miscellaneous
The sequence shown here is derived from an EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ third party annotation (TPA) entry.
Similarity
Belongs to the argonaute family. Piwi subfamily.
Belongs to the argonaute family.
Belongs to the argonaute family.
Keywords
Complete proteome
Cytoplasm
Developmental protein
Differentiation
Endonuclease
Hydrolase
Magnesium
Meiosis
Metal-binding
Methylation
Nuclease
Reference proteome
RNA-binding
RNA-mediated gene silencing
Spermatogenesis
3D-structure
Alternative splicing
Disease mutation
Polymorphism
Translation regulation
Ubl conjugation
Feature
chain Piwi-like protein Ago3
splice variant In isoform 3.
sequence variant Probable disease-associated mutation found in a patient with azoospermia; requires 2 nucleotide substitutions.
splice variant In isoform 3.
sequence variant Probable disease-associated mutation found in a patient with azoospermia; requires 2 nucleotide substitutions.
Uniprot
A9ZSZ2
A0A194QIA0
A0A0N1IAN2
A0A212EYG1
A0A2R3SZW5
A7LNN5
+ More
A0A2A4IUY8 A0A2H1WWK2 A0A2J7QHM1 A0A0L8HBN2 D1LXB5 V3ZNA5 A0A067R2W4 M9SWK5 W4Y9C2 A0A140H127 A0A210Q0Y2 A0A2J7QHJ0 Q3ZUK2 A0A1B2INM3 T2M9F7 U5XHW4 T2HRQ9 M9T4E3 A0A1S3HC55 M7C721 F9W2Z9 A0A1A6FVQ9 A0A1W5RXT9 F7BJH1 F7BJH8 A0A1S3JM11 A0A2B4RHN2 A0A2W1BMN2 A0A2S1PRU3 A0A293MTE2 A0A1X7VQA2 A0A0A7E975 A0A1W1ELL3 A0A3M6TDL1 S4W5D9 A0A3B4F4M4 A7SQI3 R7T852 Q96J94-3 A0A3B4F4S5 A0A212D8Q6 A0A1L7NZM5 A0A2S1PRU2 A0A024RBS5 Q96J94 A0A226N1F3 G3RI55 A0A2R8ZHG2 H2Q773 A0A2R5L8D7 A0A1W1ELM4 M3XKI6 A0A2K5CU01 B0FLQ9 A0A2K5JMW7 F7G629 F6WCQ1 A0A226PZU4 A0A2K6JPH8 F6Y409 A0A2K6P951 A0A093HBQ4 H2NJ51 A0A2K6E924 A0A2K5Z5K0 A0A096N174 A0A2K5M4Z5 G8F4S6 E1AWN5 A0A1U7UQH2 H0V419 A0A091K3D4 G1RA00 A0A151NS62 A0A2B4SRI4 T2M7W7 A0A195DHR5 V8NXN3 A0A1B6LP60 H9GH46 A0A091MFV6 T2HRA5 A0A0D9S5H9 G5AWP4 H9GML7 R0L9M7 G3ICR8 M4IU22 A0A286RTI8 A0A2K6UPL2 A0A384ARC3 A0A091CXM4 A0A2K5S8N6 F6YFN1
A0A2A4IUY8 A0A2H1WWK2 A0A2J7QHM1 A0A0L8HBN2 D1LXB5 V3ZNA5 A0A067R2W4 M9SWK5 W4Y9C2 A0A140H127 A0A210Q0Y2 A0A2J7QHJ0 Q3ZUK2 A0A1B2INM3 T2M9F7 U5XHW4 T2HRQ9 M9T4E3 A0A1S3HC55 M7C721 F9W2Z9 A0A1A6FVQ9 A0A1W5RXT9 F7BJH1 F7BJH8 A0A1S3JM11 A0A2B4RHN2 A0A2W1BMN2 A0A2S1PRU3 A0A293MTE2 A0A1X7VQA2 A0A0A7E975 A0A1W1ELL3 A0A3M6TDL1 S4W5D9 A0A3B4F4M4 A7SQI3 R7T852 Q96J94-3 A0A3B4F4S5 A0A212D8Q6 A0A1L7NZM5 A0A2S1PRU2 A0A024RBS5 Q96J94 A0A226N1F3 G3RI55 A0A2R8ZHG2 H2Q773 A0A2R5L8D7 A0A1W1ELM4 M3XKI6 A0A2K5CU01 B0FLQ9 A0A2K5JMW7 F7G629 F6WCQ1 A0A226PZU4 A0A2K6JPH8 F6Y409 A0A2K6P951 A0A093HBQ4 H2NJ51 A0A2K6E924 A0A2K5Z5K0 A0A096N174 A0A2K5M4Z5 G8F4S6 E1AWN5 A0A1U7UQH2 H0V419 A0A091K3D4 G1RA00 A0A151NS62 A0A2B4SRI4 T2M7W7 A0A195DHR5 V8NXN3 A0A1B6LP60 H9GH46 A0A091MFV6 T2HRA5 A0A0D9S5H9 G5AWP4 H9GML7 R0L9M7 G3ICR8 M4IU22 A0A286RTI8 A0A2K6UPL2 A0A384ARC3 A0A091CXM4 A0A2K5S8N6 F6YFN1
EC Number
3.1.26.-
Pubmed
18191035
19121390
19460866
24757166
23970546
25558067
+ More
26354079 22118469 17698031 23254933 24845553 23777831 28812685 24065732 24367095 23624526 21545709 18464734 28756777 30382153 23792802 17615350 11154219 12037681 14702039 15489334 17544373 12906857 14749716 16287078 23436708 21193640 21465557 28552346 28034629 11181995 22398555 22722832 16136131 9215903 17431167 24621616 19892987 25362486 22002653 21993624 22293439 24297900 21881562 21993625 21804562 28783426 17495919
26354079 22118469 17698031 23254933 24845553 23777831 28812685 24065732 24367095 23624526 21545709 18464734 28756777 30382153 23792802 17615350 11154219 12037681 14702039 15489334 17544373 12906857 14749716 16287078 23436708 21193640 21465557 28552346 28034629 11181995 22398555 22722832 16136131 9215903 17431167 24621616 19892987 25362486 22002653 21993624 22293439 24297900 21881562 21993625 21804562 28783426 17495919
EMBL
AB332312
AB372007
BABH01012993
KQ458756
KPJ05288.1
KQ460317
+ More
KPJ16015.1 AGBW02011540 OWR46501.1 MG778697 AVP80830.1 EU045577 ABS53349.1 NWSH01006379 PCG63479.1 ODYU01011556 SOQ57367.1 NEVH01013973 PNF28066.1 KQ418598 KOF86592.1 GU076092 ACY92621.1 KB203566 ESO83925.1 KK853043 KDR12118.1 KC516709 AGI95996.1 AAGJ04172579 KT447256 AMN88362.1 NEDP02005287 OWF42401.1 PNF28067.1 AM076487 CAJ28986.1 KT598029 ANZ54961.1 HAAD01002308 CDG68540.1 KF411462 AGZ62175.1 AB840993 BAN82534.1 KC516710 AGI95997.1 KB514175 EMP40308.1 BK007975 DAA34898.1 LZPO01116974 OBS58036.1 KX216828 AQX83033.1 AAPN01152697 AAPN01152698 LSMT01000612 PFX15775.1 KZ150022 PZC74874.1 MF288050 AWH61367.1 GFWV01019048 MAA43776.1 KJ820744 AIY62327.1 LT674429 SIP62985.1 RCHS01003812 RMX39472.1 KF032644 AGO85969.1 DS469746 EDO34027.1 AMQN01016043 KB312483 ELT87139.1 AF264004 AF104260 AF387507 AK093133 BC028581 AB274731 MKHE01000005 OWK14572.1 LC194147 BAW35369.1 MF288049 AWH61366.1 CH471054 EAW98511.1 MCFN01000275 OXB61416.1 CABD030087598 AJFE02060708 AACZ04070178 AACZ04070179 AACZ04070180 AACZ04070181 NBAG03000260 PNI57209.1 GGLE01001645 MBY05771.1 LT674441 SIP62997.1 AFYH01006730 AFYH01006731 AFYH01006732 EU334659 ABY58155.1 JSUE03008236 AWGT02000001 OXB84992.1 KL205919 KFV76830.1 ABGA01210979 NDHI03003599 PNJ17167.1 AHZZ02003328 AQIA01013399 JH331040 EHH62290.1 HQ012500 CM001263 ADM25309.1 EHH21328.1 AAKN02057840 KK543301 KFP31525.1 ADFV01092537 AKHW03002185 KYO39583.1 LSMT01000032 PFX31729.1 KF411461 HAAD01001793 AGZ62174.1 CDG68025.1 KQ980824 KYN12440.1 AZIM01001592 ETE66337.1 GEBQ01014580 JAT25397.1 AAWZ02029889 KK824226 KFP71848.1 AB840994 BAN82535.1 AQIB01028922 AQIB01028923 AQIB01028924 AQIB01028925 AQIB01028926 AQIB01028927 AQIB01028928 JH167272 GEBF01002981 EHB01502.1 JAO00652.1 AAWZ02033214 KB742969 EOB02334.1 JH001951 EGV97144.1 JQ745644 AGA54129.1 MF683123 ASW22511.1 KN123762 KFO23477.1
KPJ16015.1 AGBW02011540 OWR46501.1 MG778697 AVP80830.1 EU045577 ABS53349.1 NWSH01006379 PCG63479.1 ODYU01011556 SOQ57367.1 NEVH01013973 PNF28066.1 KQ418598 KOF86592.1 GU076092 ACY92621.1 KB203566 ESO83925.1 KK853043 KDR12118.1 KC516709 AGI95996.1 AAGJ04172579 KT447256 AMN88362.1 NEDP02005287 OWF42401.1 PNF28067.1 AM076487 CAJ28986.1 KT598029 ANZ54961.1 HAAD01002308 CDG68540.1 KF411462 AGZ62175.1 AB840993 BAN82534.1 KC516710 AGI95997.1 KB514175 EMP40308.1 BK007975 DAA34898.1 LZPO01116974 OBS58036.1 KX216828 AQX83033.1 AAPN01152697 AAPN01152698 LSMT01000612 PFX15775.1 KZ150022 PZC74874.1 MF288050 AWH61367.1 GFWV01019048 MAA43776.1 KJ820744 AIY62327.1 LT674429 SIP62985.1 RCHS01003812 RMX39472.1 KF032644 AGO85969.1 DS469746 EDO34027.1 AMQN01016043 KB312483 ELT87139.1 AF264004 AF104260 AF387507 AK093133 BC028581 AB274731 MKHE01000005 OWK14572.1 LC194147 BAW35369.1 MF288049 AWH61366.1 CH471054 EAW98511.1 MCFN01000275 OXB61416.1 CABD030087598 AJFE02060708 AACZ04070178 AACZ04070179 AACZ04070180 AACZ04070181 NBAG03000260 PNI57209.1 GGLE01001645 MBY05771.1 LT674441 SIP62997.1 AFYH01006730 AFYH01006731 AFYH01006732 EU334659 ABY58155.1 JSUE03008236 AWGT02000001 OXB84992.1 KL205919 KFV76830.1 ABGA01210979 NDHI03003599 PNJ17167.1 AHZZ02003328 AQIA01013399 JH331040 EHH62290.1 HQ012500 CM001263 ADM25309.1 EHH21328.1 AAKN02057840 KK543301 KFP31525.1 ADFV01092537 AKHW03002185 KYO39583.1 LSMT01000032 PFX31729.1 KF411461 HAAD01001793 AGZ62174.1 CDG68025.1 KQ980824 KYN12440.1 AZIM01001592 ETE66337.1 GEBQ01014580 JAT25397.1 AAWZ02029889 KK824226 KFP71848.1 AB840994 BAN82535.1 AQIB01028922 AQIB01028923 AQIB01028924 AQIB01028925 AQIB01028926 AQIB01028927 AQIB01028928 JH167272 GEBF01002981 EHB01502.1 JAO00652.1 AAWZ02033214 KB742969 EOB02334.1 JH001951 EGV97144.1 JQ745644 AGA54129.1 MF683123 ASW22511.1 KN123762 KFO23477.1
Proteomes
UP000005204
UP000053268
UP000053240
UP000007151
UP000218220
UP000235965
+ More
UP000053454 UP000030746 UP000027135 UP000007110 UP000242188 UP000085678 UP000031443 UP000092124 UP000002279 UP000225706 UP000007879 UP000275408 UP000261460 UP000001593 UP000014760 UP000005640 UP000198323 UP000001519 UP000240080 UP000002277 UP000008672 UP000233020 UP000233080 UP000006718 UP000198419 UP000233180 UP000002281 UP000233200 UP000053584 UP000001595 UP000233120 UP000233140 UP000028761 UP000233060 UP000009130 UP000233100 UP000189704 UP000005447 UP000001073 UP000050525 UP000078492 UP000001646 UP000029965 UP000006813 UP000001075 UP000233220 UP000261681 UP000028990 UP000233040 UP000002280
UP000053454 UP000030746 UP000027135 UP000007110 UP000242188 UP000085678 UP000031443 UP000092124 UP000002279 UP000225706 UP000007879 UP000275408 UP000261460 UP000001593 UP000014760 UP000005640 UP000198323 UP000001519 UP000240080 UP000002277 UP000008672 UP000233020 UP000233080 UP000006718 UP000198419 UP000233180 UP000002281 UP000233200 UP000053584 UP000001595 UP000233120 UP000233140 UP000028761 UP000233060 UP000009130 UP000233100 UP000189704 UP000005447 UP000001073 UP000050525 UP000078492 UP000001646 UP000029965 UP000006813 UP000001075 UP000233220 UP000261681 UP000028990 UP000233040 UP000002280
Pfam
Interpro
IPR012337
RNaseH-like_sf
+ More
IPR003165 Piwi
IPR003100 PAZ_dom
IPR036397 RNaseH_sf
IPR036085 PAZ_dom_sf
IPR001075 NIF_FeS_clus_asmbl_NifU_C
IPR014824 Nfu/NifU_N
IPR034904 FSCA_dom_sf
IPR036498 Nfu/NifU_N_sf
IPR031326 PIWIL1
IPR014811 ArgoL1
IPR032474 Argonaute_N
IPR031320 GAGE
IPR038765 Papain-like_cys_pep_sf
IPR001607 Znf_UBP
IPR001394 Peptidase_C19_UCH
IPR033809 USP39
IPR013083 Znf_RING/FYVE/PHD
IPR028889 USP_dom
IPR003165 Piwi
IPR003100 PAZ_dom
IPR036397 RNaseH_sf
IPR036085 PAZ_dom_sf
IPR001075 NIF_FeS_clus_asmbl_NifU_C
IPR014824 Nfu/NifU_N
IPR034904 FSCA_dom_sf
IPR036498 Nfu/NifU_N_sf
IPR031326 PIWIL1
IPR014811 ArgoL1
IPR032474 Argonaute_N
IPR031320 GAGE
IPR038765 Papain-like_cys_pep_sf
IPR001607 Znf_UBP
IPR001394 Peptidase_C19_UCH
IPR033809 USP39
IPR013083 Znf_RING/FYVE/PHD
IPR028889 USP_dom
SUPFAM
ProteinModelPortal
A9ZSZ2
A0A194QIA0
A0A0N1IAN2
A0A212EYG1
A0A2R3SZW5
A7LNN5
+ More
A0A2A4IUY8 A0A2H1WWK2 A0A2J7QHM1 A0A0L8HBN2 D1LXB5 V3ZNA5 A0A067R2W4 M9SWK5 W4Y9C2 A0A140H127 A0A210Q0Y2 A0A2J7QHJ0 Q3ZUK2 A0A1B2INM3 T2M9F7 U5XHW4 T2HRQ9 M9T4E3 A0A1S3HC55 M7C721 F9W2Z9 A0A1A6FVQ9 A0A1W5RXT9 F7BJH1 F7BJH8 A0A1S3JM11 A0A2B4RHN2 A0A2W1BMN2 A0A2S1PRU3 A0A293MTE2 A0A1X7VQA2 A0A0A7E975 A0A1W1ELL3 A0A3M6TDL1 S4W5D9 A0A3B4F4M4 A7SQI3 R7T852 Q96J94-3 A0A3B4F4S5 A0A212D8Q6 A0A1L7NZM5 A0A2S1PRU2 A0A024RBS5 Q96J94 A0A226N1F3 G3RI55 A0A2R8ZHG2 H2Q773 A0A2R5L8D7 A0A1W1ELM4 M3XKI6 A0A2K5CU01 B0FLQ9 A0A2K5JMW7 F7G629 F6WCQ1 A0A226PZU4 A0A2K6JPH8 F6Y409 A0A2K6P951 A0A093HBQ4 H2NJ51 A0A2K6E924 A0A2K5Z5K0 A0A096N174 A0A2K5M4Z5 G8F4S6 E1AWN5 A0A1U7UQH2 H0V419 A0A091K3D4 G1RA00 A0A151NS62 A0A2B4SRI4 T2M7W7 A0A195DHR5 V8NXN3 A0A1B6LP60 H9GH46 A0A091MFV6 T2HRA5 A0A0D9S5H9 G5AWP4 H9GML7 R0L9M7 G3ICR8 M4IU22 A0A286RTI8 A0A2K6UPL2 A0A384ARC3 A0A091CXM4 A0A2K5S8N6 F6YFN1
A0A2A4IUY8 A0A2H1WWK2 A0A2J7QHM1 A0A0L8HBN2 D1LXB5 V3ZNA5 A0A067R2W4 M9SWK5 W4Y9C2 A0A140H127 A0A210Q0Y2 A0A2J7QHJ0 Q3ZUK2 A0A1B2INM3 T2M9F7 U5XHW4 T2HRQ9 M9T4E3 A0A1S3HC55 M7C721 F9W2Z9 A0A1A6FVQ9 A0A1W5RXT9 F7BJH1 F7BJH8 A0A1S3JM11 A0A2B4RHN2 A0A2W1BMN2 A0A2S1PRU3 A0A293MTE2 A0A1X7VQA2 A0A0A7E975 A0A1W1ELL3 A0A3M6TDL1 S4W5D9 A0A3B4F4M4 A7SQI3 R7T852 Q96J94-3 A0A3B4F4S5 A0A212D8Q6 A0A1L7NZM5 A0A2S1PRU2 A0A024RBS5 Q96J94 A0A226N1F3 G3RI55 A0A2R8ZHG2 H2Q773 A0A2R5L8D7 A0A1W1ELM4 M3XKI6 A0A2K5CU01 B0FLQ9 A0A2K5JMW7 F7G629 F6WCQ1 A0A226PZU4 A0A2K6JPH8 F6Y409 A0A2K6P951 A0A093HBQ4 H2NJ51 A0A2K6E924 A0A2K5Z5K0 A0A096N174 A0A2K5M4Z5 G8F4S6 E1AWN5 A0A1U7UQH2 H0V419 A0A091K3D4 G1RA00 A0A151NS62 A0A2B4SRI4 T2M7W7 A0A195DHR5 V8NXN3 A0A1B6LP60 H9GH46 A0A091MFV6 T2HRA5 A0A0D9S5H9 G5AWP4 H9GML7 R0L9M7 G3ICR8 M4IU22 A0A286RTI8 A0A2K6UPL2 A0A384ARC3 A0A091CXM4 A0A2K5S8N6 F6YFN1
PDB
5GUH
E-value=8.4614e-51,
Score=503
Ontologies
GO
GO:0051321
GO:0007275
GO:0005737
GO:0004519
GO:0046872
GO:0003723
GO:0030154
GO:0007283
GO:0031047
GO:0003676
GO:0016226
GO:0051536
GO:0005506
GO:0034584
GO:0007286
GO:0003729
GO:0033391
GO:0035093
GO:0006417
GO:1905538
GO:0140262
GO:0005634
GO:0004521
GO:0010529
GO:0043186
GO:0097433
GO:0019901
GO:0003727
GO:0034587
GO:0003743
GO:0016021
GO:0004497
GO:0005507
GO:0006000
GO:0004553
GO:0006334
GO:0003779
PANTHER
Topology
Subcellular location
Cytoplasm
Component of the meiotic nuage, also named P granule, a germ-cell-specific organelle required to repress transposon activity during meiosis. With evidence from 8 publications.
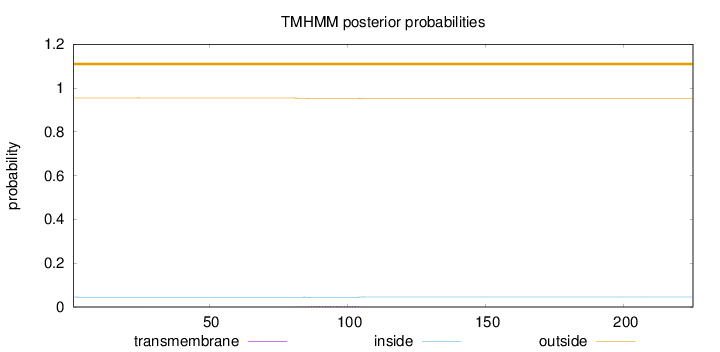
Length:
225
Number of predicted TMHs:
0
Exp number of AAs in TMHs:
0.09243
Exp number, first 60 AAs:
0.00703
Total prob of N-in:
0.04520
outside
1 - 225
Population Genetic Test Statistics
Pi
257.528665
Theta
175.944899
Tajima's D
1.386452
CLR
0.014857
CSRT
0.759662016899155
Interpretation
Uncertain
